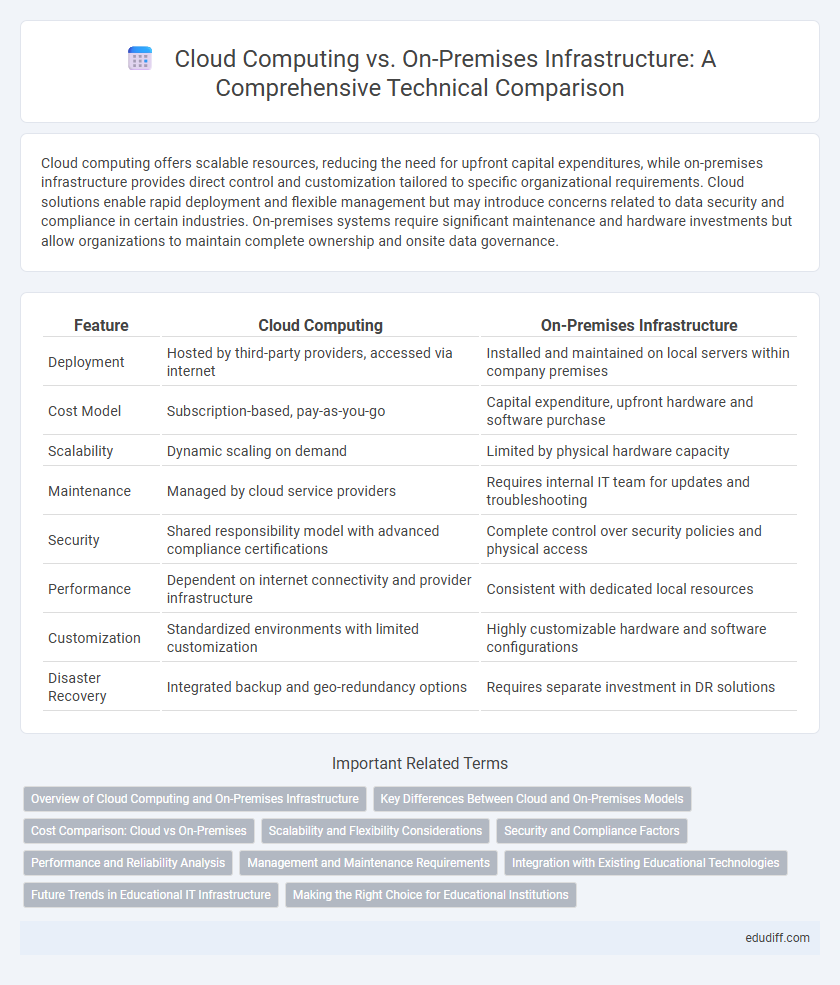
Cloud computing offers scalable resources, reducing the need for upfront capital expenditures, while on-premises infrastructure provides direct control and customization tailored to specific organizational requirements. Cloud solutions enable rapid deployment and flexible management but may introduce concerns related to data security and compliance in certain industries. On-premises systems require significant maintenance and hardware investments but allow organizations to maintain complete ownership and onsite data governance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cloud Computing | On-Premises Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Hosted by third-party providers, accessed via internet | Installed and maintained on local servers within company premises |
| Cost Model | Subscription-based, pay-as-you-go | Capital expenditure, upfront hardware and software purchase |
| Scalability | Dynamic scaling on demand | Limited by physical hardware capacity |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud service providers | Requires internal IT team for updates and troubleshooting |
| Security | Shared responsibility model with advanced compliance certifications | Complete control over security policies and physical access |
| Performance | Dependent on internet connectivity and provider infrastructure | Consistent with dedicated local resources |
| Customization | Standardized environments with limited customization | Highly customizable hardware and software configurations |
| Disaster Recovery | Integrated backup and geo-redundancy options | Requires separate investment in DR solutions |
Overview of Cloud Computing and On-Premises Infrastructure
Cloud computing delivers scalable IT resources over the internet, enabling on-demand access to servers, storage, and applications without physical hardware management. On-premises infrastructure requires organizations to invest in and maintain their own hardware and software within a private facility, offering greater control and data security. Cloud solutions provide flexibility and cost-efficiency, while on-premises setups support customized environments and regulatory compliance.
Key Differences Between Cloud and On-Premises Models
Cloud computing offers scalable resources and flexible pay-as-you-go pricing, while on-premises infrastructure requires significant upfront capital investment and fixed capacity. Cloud models provide rapid deployment and remote accessibility, contrasting with the localized control and customization capabilities inherent in on-premises setups. Security management in cloud environments shifts responsibility to the service provider, whereas on-premises demands in-house expertise for maintaining data protection and compliance.
Cost Comparison: Cloud vs On-Premises
Cloud computing reduces upfront capital expenditures by replacing physical hardware with scalable virtual resources, offering pay-as-you-go pricing models that align costs with usage. On-premises infrastructure involves significant initial investment in servers, networking, and maintenance, leading to higher fixed costs but potentially lower long-term expenses for stable workloads. Evaluating total cost of ownership must consider factors like hardware depreciation, energy consumption, staffing, and scalability needs to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Scalability and Flexibility Considerations
Cloud computing offers unmatched scalability by enabling businesses to dynamically adjust resources based on demand through virtualized environments and automated provisioning. On-premises infrastructure requires significant upfront investment and physical hardware expansion for scaling, limiting flexibility and increasing lead times. Flexible resource allocation in cloud environments supports rapid innovation and operational efficiency, while on-premises setups may hinder agility due to fixed capacity and maintenance constraints.
Security and Compliance Factors
Cloud computing offers advanced security features such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular compliance audits aligned with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, ensuring robust data protection. On-premises infrastructure provides direct control over physical security and customization of compliance policies but requires significant investment in specialized personnel and maintenance. Enterprises must assess regulatory requirements, data sensitivity, and internal expertise when choosing between cloud and on-premises solutions for optimal security and compliance management.
Performance and Reliability Analysis
Cloud computing offers scalable performance with dynamic resource allocation, ensuring consistent uptime through distributed data centers and automated failover mechanisms. On-premises infrastructure provides direct control over hardware, enabling customized performance tuning but often requires substantial maintenance to guarantee reliability. Performance in cloud environments benefits from load balancing and redundancy, while on-premises setups depend heavily on local hardware robustness and proactive monitoring.
Management and Maintenance Requirements
Cloud computing significantly reduces management and maintenance requirements by offloading tasks such as hardware updates, security patches, and system monitoring to the cloud provider. On-premises infrastructure demands dedicated IT staff for ongoing maintenance, troubleshooting, and regular upgrades, increasing operational costs and complexity. Efficient management in cloud environments leverages automation tools and centralized monitoring, whereas on-premises systems require manual interventions and physical hardware oversight.
Integration with Existing Educational Technologies
Cloud computing offers seamless integration with existing educational technologies through APIs and scalable middleware, enabling real-time data synchronization and streamlined resource management. On-premises infrastructure requires manual configurations and dedicated IT support to connect legacy systems, often resulting in limited scalability and higher maintenance costs. Educational institutions benefit from cloud-based solutions by enhancing interoperability across learning management systems, student information systems, and digital content platforms.
Future Trends in Educational IT Infrastructure
Educational IT infrastructure is rapidly shifting towards hybrid cloud solutions, combining the scalability of cloud computing with the control of on-premises systems to meet growing demands for remote learning and data security. Edge computing integration enhances real-time data processing for interactive educational tools, reducing latency and improving user experience. AI-driven automation and analytics in cloud platforms enable personalized learning paths and predictive maintenance, optimizing resource allocation and institutional effectiveness.
Making the Right Choice for Educational Institutions
Educational institutions benefit from cloud computing by accessing scalable resources, reduced upfront costs, and enhanced collaboration tools, crucial for dynamic learning environments. On-premises infrastructure provides greater control over data security and compliance, essential for protecting sensitive student information and meeting regulatory requirements. Evaluating workload demands, budget constraints, and long-term IT strategy ensures an optimal infrastructure decision aligned with educational goals.
Cloud Computing vs On-Premises Infrastructure Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com