Synchronous learning requires real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback and collaborative engagement through live sessions. Asynchronous learning offers flexibility, allowing learners to access materials and complete tasks at their own pace without scheduled meetings. Both methods utilize digital platforms but differ in time management, communication dynamics, and learner autonomy.
Table of Comparison
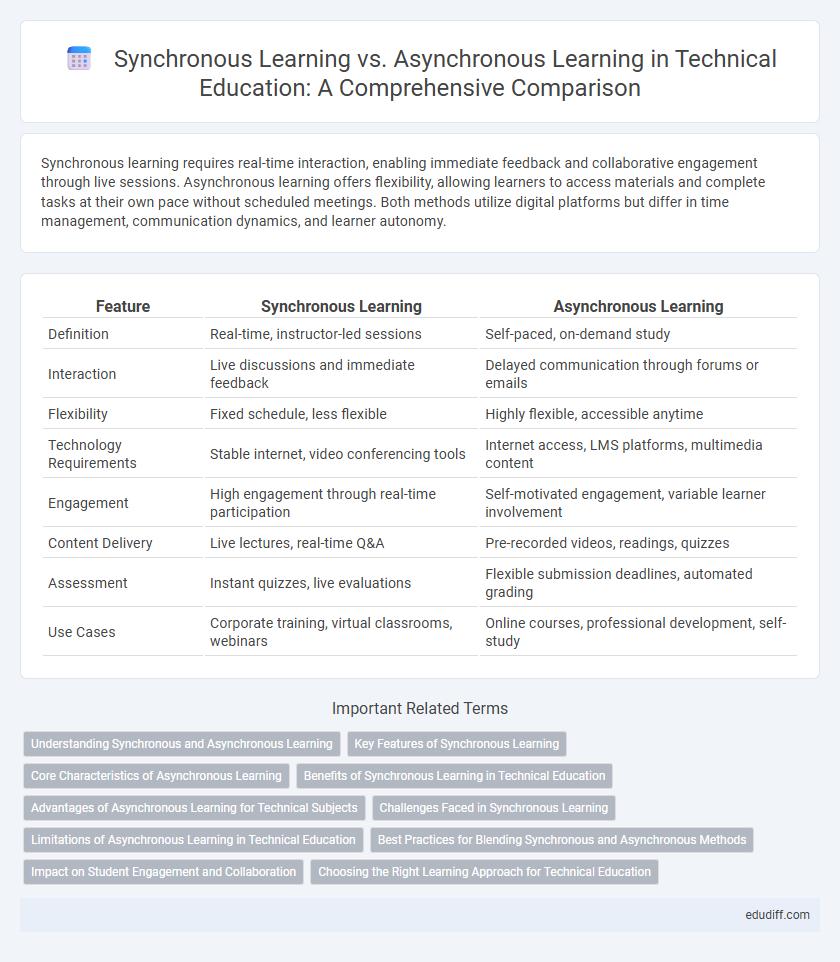
| Feature | Synchronous Learning | Asynchronous Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time, instructor-led sessions | Self-paced, on-demand study |
| Interaction | Live discussions and immediate feedback | Delayed communication through forums or emails |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule, less flexible | Highly flexible, accessible anytime |
| Technology Requirements | Stable internet, video conferencing tools | Internet access, LMS platforms, multimedia content |
| Engagement | High engagement through real-time participation | Self-motivated engagement, variable learner involvement |
| Content Delivery | Live lectures, real-time Q&A | Pre-recorded videos, readings, quizzes |
| Assessment | Instant quizzes, live evaluations | Flexible submission deadlines, automated grading |
| Use Cases | Corporate training, virtual classrooms, webinars | Online courses, professional development, self-study |
Understanding Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction between instructors and students, utilizing platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams for live lectures, discussions, and immediate feedback. Asynchronous learning allows students to access course materials, such as recorded videos and readings, at their own pace without direct interaction during scheduled times. Understanding these modes is crucial for designing effective educational experiences that balance flexibility with engagement.
Key Features of Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction between instructors and students, utilizing video conferencing, live chats, and virtual classrooms to facilitate immediate feedback and collaboration. Key features include scheduled sessions, simultaneous participation, and instant communication, enhancing engagement and dynamic discussions. This method supports structured learning environments and promotes accountability through fixed timetables.
Core Characteristics of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning enables students to access educational materials and complete assignments at their own pace, promoting flexibility and individualized study schedules. Core characteristics include self-paced modules, pre-recorded lectures, and forum-based discussions that foster reflective engagement without real-time interaction. This model supports diverse learning styles by allowing learners to revisit content and manage their time independently, enhancing knowledge retention and accommodation of varied schedules.
Benefits of Synchronous Learning in Technical Education
Synchronous learning in technical education offers real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback and clarification of complex concepts critical for hands-on skills development. This method fosters collaborative problem-solving and teamwork through live discussions and group activities, enhancing practical understanding. The structured schedule of synchronous sessions also promotes consistent engagement and discipline necessary for mastering technical subjects.
Advantages of Asynchronous Learning for Technical Subjects
Asynchronous learning offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing students to engage with complex technical subjects at their own pace, which enhances comprehension and retention of intricate concepts. It supports diverse learning styles by providing access to varied multimedia resources, coding exercises, and simulations anytime, fostering deeper problem-solving skills. This approach also facilitates continuous review and self-assessment, essential for mastering technical material without the constraints of real-time sessions.
Challenges Faced in Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning faces challenges such as rigid scheduling, which limits flexibility for students across different time zones and those with varying personal commitments. Technical issues like unstable internet connections and platform outages disrupt real-time interaction and hinder effective communication between instructors and learners. Furthermore, maintaining student engagement during live sessions is difficult due to distractions and reduced opportunities for personalized attention.
Limitations of Asynchronous Learning in Technical Education
Asynchronous learning in technical education often limits real-time interaction, hindering immediate feedback and collaborative problem-solving essential for mastering complex concepts. The lack of synchronous engagement can delay troubleshooting and clarification of technical issues, thereby impacting the learning curve. Additionally, the absence of scheduled sessions may reduce learner motivation and accountability, affecting course completion rates in hands-on technical training.
Best Practices for Blending Synchronous and Asynchronous Methods
Blending synchronous and asynchronous learning optimizes student engagement and comprehension by leveraging real-time interaction alongside self-paced study. Best practices include structuring live sessions for active discussions and immediate feedback while providing asynchronous materials such as videos and readings for flexible review. Integrating clear communication channels and consistent scheduling enhances the seamless transition between these modalities, fostering an effective and adaptable learning environment.
Impact on Student Engagement and Collaboration
Synchronous learning fosters real-time interaction, enhancing student engagement and collaboration through immediate feedback and dynamic discussions. In contrast, asynchronous learning allows students to engage at their own pace, promoting reflection but potentially reducing spontaneous collaboration and instant peer interaction. The impact on engagement is significant as synchronous formats typically yield higher motivation and active participation, while asynchronous models support flexibility and individualized learning rhythms.
Choosing the Right Learning Approach for Technical Education
Synchronous learning in technical education enables real-time interaction, immediate feedback, and collaborative problem-solving essential for mastering complex concepts such as coding or engineering design. Asynchronous learning offers flexibility, allowing students to access resources, tutorials, and assignments at their own pace, which supports diverse learning schedules and deepens comprehension through repeated review. Choosing the right approach depends on the technical subject complexity, learner preferences, and the need for hands-on practice or live demonstrations.
Synchronous learning vs Asynchronous learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com