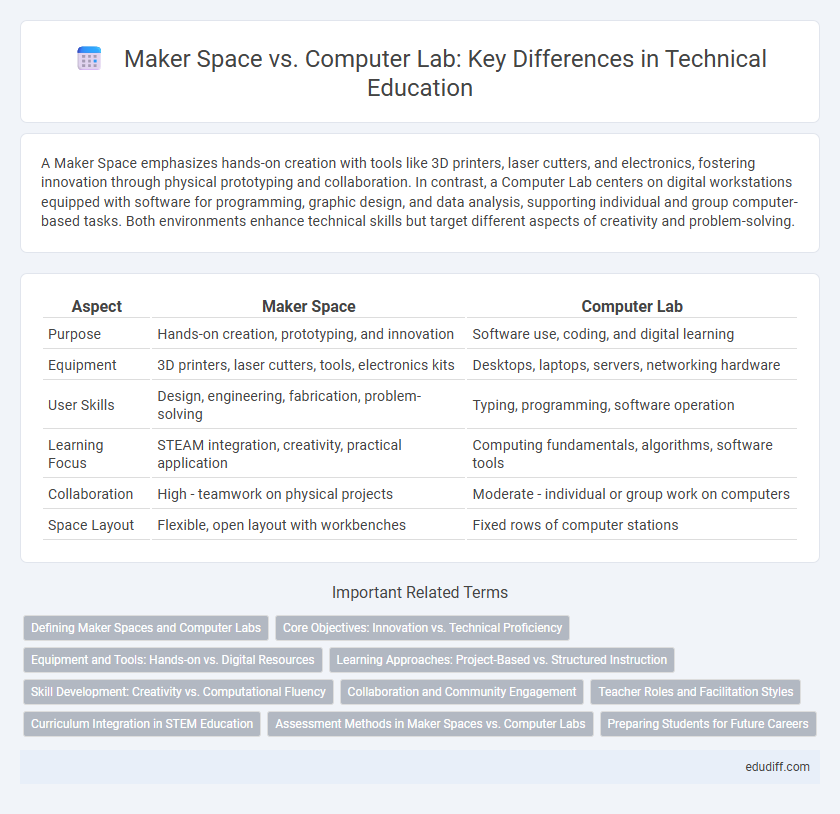
A Maker Space emphasizes hands-on creation with tools like 3D printers, laser cutters, and electronics, fostering innovation through physical prototyping and collaboration. In contrast, a Computer Lab centers on digital workstations equipped with software for programming, graphic design, and data analysis, supporting individual and group computer-based tasks. Both environments enhance technical skills but target different aspects of creativity and problem-solving.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Maker Space | Computer Lab |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hands-on creation, prototyping, and innovation | Software use, coding, and digital learning |
| Equipment | 3D printers, laser cutters, tools, electronics kits | Desktops, laptops, servers, networking hardware |
| User Skills | Design, engineering, fabrication, problem-solving | Typing, programming, software operation |
| Learning Focus | STEAM integration, creativity, practical application | Computing fundamentals, algorithms, software tools |
| Collaboration | High - teamwork on physical projects | Moderate - individual or group work on computers |
| Space Layout | Flexible, open layout with workbenches | Fixed rows of computer stations |
Defining Maker Spaces and Computer Labs
Maker Spaces are collaborative work environments equipped with tools like 3D printers, laser cutters, and electronics designed to foster creativity and hands-on learning in areas such as robotics, prototyping, and digital fabrication. Computer Labs consist primarily of networked computers and peripherals designed for educational activities involving software programming, data analysis, and internet research. While Maker Spaces emphasize physical creation and innovation, Computer Labs focus on digital skills development and software-based learning.
Core Objectives: Innovation vs. Technical Proficiency
Maker Spaces prioritize fostering innovation through hands-on experimentation, encouraging creativity with tools like 3D printers, laser cutters, and robotics kits. Computer Labs focus on developing technical proficiency by providing access to software applications, programming environments, and network resources for skill-building. The core objective of Maker Spaces is to inspire original problem-solving, whereas Computer Labs emphasize mastery of established digital technologies.
Equipment and Tools: Hands-on vs. Digital Resources
Maker spaces provide diverse hands-on equipment such as 3D printers, laser cutters, soldering stations, and woodworking tools that encourage physical creation and prototyping. Computer labs focus primarily on digital resources, offering high-performance computers, coding software, and virtual collaboration platforms for software development and data analysis. The equipment in maker spaces fosters tactile learning and innovation, while computer labs emphasize virtual environments and computational tasks.
Learning Approaches: Project-Based vs. Structured Instruction
Maker Spaces promote project-based learning that encourages creativity, experimentation, and hands-on problem solving through open-ended projects. Computer Labs emphasize structured instruction with a focus on step-by-step guidance, standardized software tools, and predetermined learning objectives. This contrast highlights how Maker Spaces foster innovation and critical thinking, while Computer Labs prioritize skill mastery and curriculum alignment.
Skill Development: Creativity vs. Computational Fluency
Maker Spaces prioritize creativity by providing hands-on activities that enhance problem-solving, design thinking, and prototyping skills. Computer Labs emphasize computational fluency through coding, software use, and digital literacy essential for programming and data analysis. Both environments cultivate critical skill sets, with Maker Spaces fostering innovation and Computer Labs building technical proficiency.
Collaboration and Community Engagement
Maker Spaces foster collaboration through hands-on projects and shared tools, encouraging creative problem-solving and peer learning. Computer Labs primarily support individual work but can facilitate teamwork via networked devices and software applications. Community engagement in Maker Spaces thrives on workshops, events, and open access, promoting inclusivity and innovation beyond traditional computer use.
Teacher Roles and Facilitation Styles
Teachers in Maker Spaces act as facilitators who encourage creativity, problem-solving, and hands-on experimentation, guiding students through open-ended projects. In Computer Labs, educators typically serve as instructors who provide structured lessons and direct software or hardware usage. Facilitation in Maker Spaces emphasizes collaboration and exploration, whereas in Computer Labs it prioritizes skill acquisition and task completion.
Curriculum Integration in STEM Education
Maker spaces enhance STEM education by promoting hands-on, project-based learning that integrates science, technology, engineering, and math through creative problem-solving and design thinking. Computer labs primarily support STEM curriculum by providing access to software, programming environments, and data analysis tools essential for coding, simulations, and computational thinking. Combining maker spaces with computer labs fosters a comprehensive STEM learning environment that bridges theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Assessment Methods in Maker Spaces vs. Computer Labs
Assessment methods in Maker Spaces emphasize project-based evaluations, creativity, and problem-solving skills through iterative design processes and hands-on activities, contrasting with Computer Labs that predominantly rely on standardized tests and software-based quizzes to measure technical proficiency and knowledge retention. Maker Space assessments often include peer reviews, portfolios, and real-world application demonstrations, enabling educators to gauge critical thinking and collaborative abilities. In Computer Labs, automated grading systems and skill-specific benchmarks provide quantifiable results but may overlook holistic understanding and innovation.
Preparing Students for Future Careers
Maker Spaces foster creativity and problem-solving by providing hands-on learning with tools like 3D printers, robotics kits, and coding software, enhancing skills critical for future STEM careers. Computer Labs offer structured environments for developing digital literacy, software proficiency, and technical skills essential for careers in IT, programming, and data analysis. Integrating Maker Spaces with Computer Labs creates a comprehensive learning ecosystem that equips students with both innovative thinking and technical expertise demanded by evolving workplace technologies.
Maker Space vs Computer Lab Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com