Virtual labs offer scalable, cost-effective solutions for remote experimentation and simulation, providing immediate access to diverse scientific environments. Physical labs ensure hands-on experience, critical for developing tactile skills and understanding real-world variables that virtual setups may overlook. Combining virtual and physical labs enhances educational outcomes by blending theoretical simulations with practical application.
Table of Comparison
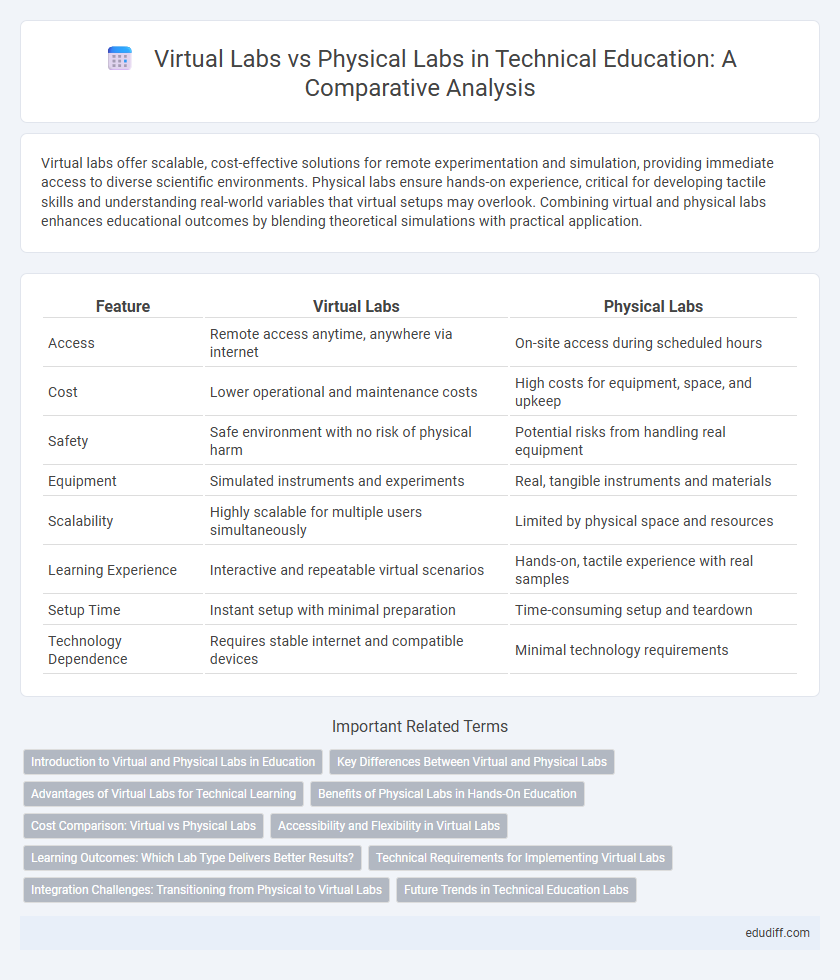
| Feature | Virtual Labs | Physical Labs |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Remote access anytime, anywhere via internet | On-site access during scheduled hours |
| Cost | Lower operational and maintenance costs | High costs for equipment, space, and upkeep |
| Safety | Safe environment with no risk of physical harm | Potential risks from handling real equipment |
| Equipment | Simulated instruments and experiments | Real, tangible instruments and materials |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for multiple users simultaneously | Limited by physical space and resources |
| Learning Experience | Interactive and repeatable virtual scenarios | Hands-on, tactile experience with real samples |
| Setup Time | Instant setup with minimal preparation | Time-consuming setup and teardown |
| Technology Dependence | Requires stable internet and compatible devices | Minimal technology requirements |
Introduction to Virtual and Physical Labs in Education
Virtual labs employ interactive simulations to replicate real-world experiments, offering scalable and cost-effective access to educational resources. Physical labs provide tactile, hands-on experience critical for developing practical skills and understanding material properties through direct manipulation. Combining virtual and physical labs enhances learning by integrating theoretical knowledge with experiential practice in science and engineering education.
Key Differences Between Virtual and Physical Labs
Virtual labs offer remote access to experiments through computer simulations, enabling safe, cost-effective, and scalable learning environments, whereas physical labs require real equipment and space for hands-on manipulation of materials and instruments. Virtual labs provide instant feedback and the ability to repeat experiments multiple times without material constraints, while physical labs offer tactile experience and realistic sensorimotor engagement critical for certain scientific procedures. The scalability of virtual labs supports large student cohorts simultaneously, contrasting with physical labs' limitations imposed by equipment availability and maintenance needs.
Advantages of Virtual Labs for Technical Learning
Virtual labs offer significant advantages for technical learning by providing scalable, cost-effective access to complex equipment and simulations without the constraints of physical space or resources. They enable real-time experimentation and iterative testing in a risk-free environment, enhancing understanding of intricate technical concepts. Virtual labs support remote collaboration and flexible scheduling, making technical education more accessible and adaptable to diverse learning needs.
Benefits of Physical Labs in Hands-On Education
Physical labs offer tactile learning experiences that enhance students' understanding of complex scientific concepts through direct interaction with equipment and materials. They enable real-time troubleshooting and experimentation, fostering critical problem-solving skills and collaboration among peers. The sensory feedback and authentic environment in physical labs deepen experiential learning, making theoretical knowledge more tangible and retained longer.
Cost Comparison: Virtual vs Physical Labs
Virtual labs significantly reduce costs by eliminating expenses related to physical space, equipment maintenance, and consumables, which are substantial in physical labs. The scalability of virtual labs allows institutions to train large numbers of students simultaneously without proportional increases in budget. Investment in virtual lab software and infrastructure typically results in lower long-term operational costs compared to ongoing expenditures for physical lab resources.
Accessibility and Flexibility in Virtual Labs
Virtual labs offer unparalleled accessibility by enabling users to conduct experiments anytime and anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating geographic and time constraints inherent in physical labs. This flexibility supports diverse learning paces and repeated practice without the limitations of physical resources or lab availability. Advanced virtual lab platforms integrate interactive simulations and real-time feedback, enhancing user engagement and accommodating various educational and research needs seamlessly.
Learning Outcomes: Which Lab Type Delivers Better Results?
Virtual labs enhance learning outcomes by providing interactive simulations that allow repeated practice without resource constraints, leading to improved conceptual understanding and skill acquisition. Physical labs offer hands-on experience with real equipment, fostering critical thinking and troubleshooting abilities essential for practical tasks. Studies indicate a blended approach combining virtual and physical labs yields the most effective learning results by balancing theoretical knowledge with practical application.
Technical Requirements for Implementing Virtual Labs
Implementing virtual labs requires robust IT infrastructure including high-speed internet, powerful servers, and cloud computing resources to support immersive simulations and real-time data processing. Integration of advanced software platforms for virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and interactive 3D modeling ensures accurate representation of physical experiments. Security protocols and compatibility with existing learning management systems (LMS) are critical for seamless access and user management.
Integration Challenges: Transitioning from Physical to Virtual Labs
Transitioning from physical labs to virtual labs presents significant integration challenges, including compatibility issues between legacy equipment and new software platforms. Ensuring accurate real-time data synchronization and maintaining cybersecurity standards are critical to seamless implementation. Technical teams must also address user interface complexity to facilitate effective remote experimentation and collaboration.
Future Trends in Technical Education Labs
Virtual labs leverage advanced simulation technologies and cloud computing to provide scalable, interactive learning environments with real-time data analysis. Physical labs continue evolving with augmented reality (AR) and Internet of Things (IoT) integration to enhance hands-on experience, promoting hybrid learning models. Future trends indicate a convergence of virtual and physical labs, utilizing AI-driven adaptive learning systems to personalize technical education and optimize resource allocation.
Virtual Labs vs Physical Labs Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com