Project-based assessment evaluates students' practical skills and problem-solving abilities through real-world tasks, promoting deeper understanding and creativity. Standardized testing measures knowledge retention and comparison across large populations but often fails to capture individual strengths and critical thinking. Combining both methods can provide a comprehensive evaluation of student learning outcomes.
Table of Comparison
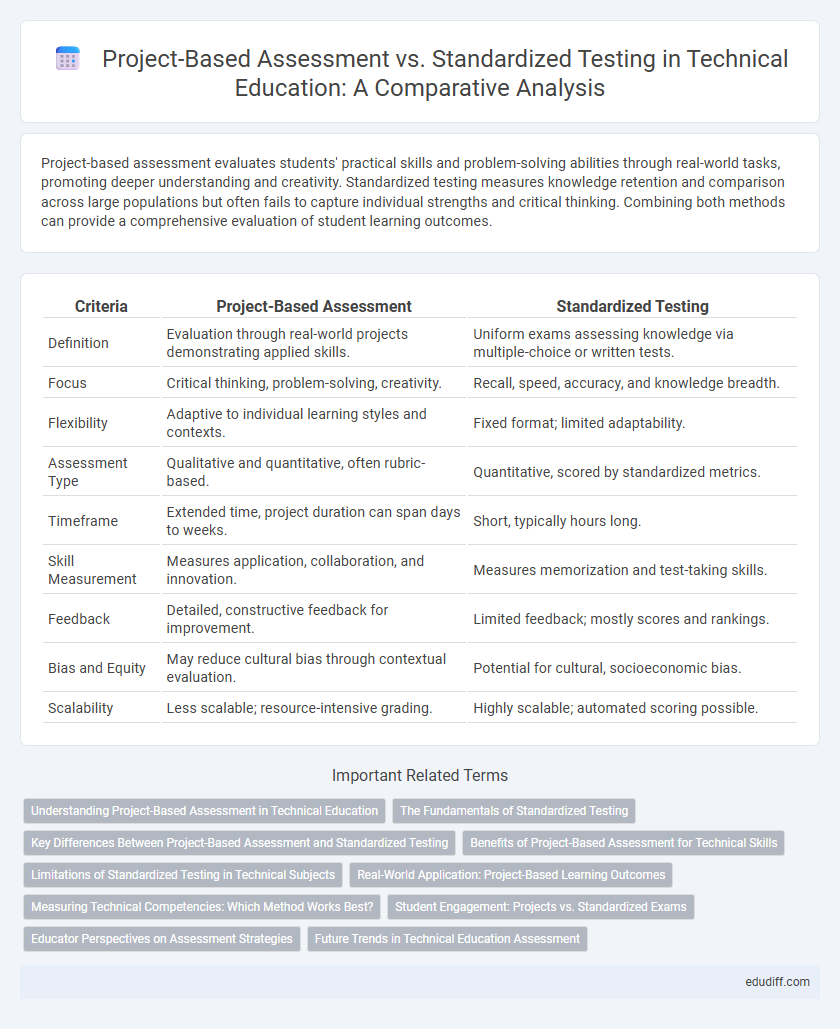
| Criteria | Project-Based Assessment | Standardized Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation through real-world projects demonstrating applied skills. | Uniform exams assessing knowledge via multiple-choice or written tests. |
| Focus | Critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity. | Recall, speed, accuracy, and knowledge breadth. |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to individual learning styles and contexts. | Fixed format; limited adaptability. |
| Assessment Type | Qualitative and quantitative, often rubric-based. | Quantitative, scored by standardized metrics. |
| Timeframe | Extended time, project duration can span days to weeks. | Short, typically hours long. |
| Skill Measurement | Measures application, collaboration, and innovation. | Measures memorization and test-taking skills. |
| Feedback | Detailed, constructive feedback for improvement. | Limited feedback; mostly scores and rankings. |
| Bias and Equity | May reduce cultural bias through contextual evaluation. | Potential for cultural, socioeconomic bias. |
| Scalability | Less scalable; resource-intensive grading. | Highly scalable; automated scoring possible. |
Understanding Project-Based Assessment in Technical Education
Project-based assessment in technical education evaluates students' practical skills and problem-solving abilities through real-world tasks, promoting deeper comprehension of complex concepts. Unlike standardized testing, it measures applied knowledge and technical proficiency by requiring learners to create, design, or troubleshoot projects that mirror industry challenges. This approach aligns assessments with professional standards, fostering critical thinking and hands-on experience essential for technical careers.
The Fundamentals of Standardized Testing
Standardized testing utilizes uniform procedures and scoring methods to evaluate student performance across diverse populations, emphasizing reliability and validity. These assessments often measure specific academic skills through multiple-choice or short-answer formats, providing comparative data for educational stakeholders. The fundamental goal is to create objective metrics that facilitate large-scale analysis of educational outcomes and identify areas needing improvement.
Key Differences Between Project-Based Assessment and Standardized Testing
Project-Based Assessment evaluates students through hands-on, real-world tasks that demonstrate critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills, whereas Standardized Testing measures knowledge via uniform, multiple-choice or short-answer questions designed for large-scale comparison. Project-Based Assessment offers personalized feedback and deeper understanding of subject matter, contrasting with Standardized Testing's emphasis on quantifiable scores and statistical validity. The flexibility and application-oriented nature of project-based methods foster higher-order learning outcomes, while standardized tests prioritize efficiency and broad scalability in academic evaluation.
Benefits of Project-Based Assessment for Technical Skills
Project-based assessment enhances technical skills by promoting hands-on experience and real-world problem-solving, which leads to deeper understanding and retention. It fosters collaboration, critical thinking, and adaptability, essential competencies in rapidly evolving technical fields. This approach also allows for the evaluation of practical application and innovation, providing a more comprehensive measure of a learner's capabilities than traditional standardized testing.
Limitations of Standardized Testing in Technical Subjects
Standardized testing in technical subjects often fails to accurately measure practical skills and real-world problem-solving abilities, which are crucial for proficiency in fields like engineering or computer science. These tests typically emphasize rote memorization and theoretical knowledge rather than hands-on experience and critical thinking. Consequently, reliance on standardized assessments can lead to an incomplete evaluation of a student's technical competence and innovation potential.
Real-World Application: Project-Based Learning Outcomes
Project-based assessment enhances real-world application by engaging students in practical, hands-on projects aligned with industry standards and authentic problems. This method fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills that standardized tests often fail to measure. Empirical studies show students in project-based learning environments demonstrate higher retention rates and improved ability to transfer knowledge to real-life scenarios.
Measuring Technical Competencies: Which Method Works Best?
Project-based assessment offers a comprehensive evaluation of technical competencies by simulating real-world scenarios that require problem-solving, critical thinking, and practical application of skills. Standardized testing measures theoretical knowledge through uniform questions but often fails to capture hands-on abilities and adaptability crucial in technical fields. Combining project-based assessments with selective standardized tests provides a balanced approach to accurately measure both technical knowledge and applied skills.
Student Engagement: Projects vs. Standardized Exams
Project-based assessments significantly enhance student engagement by encouraging active participation, critical thinking, and real-world problem solving, in contrast to standardized tests that often promote rote memorization and passive learning. Students involved in projects are more likely to retain knowledge and develop collaboration skills, which standardized exams typically do not measure. Research indicates that project-based learning can increase motivation and deepen understanding, leading to improved long-term academic outcomes.
Educator Perspectives on Assessment Strategies
Educators emphasize that project-based assessment fosters critical thinking, creativity, and real-world problem-solving skills, providing a more comprehensive evaluation of student learning compared to standardized testing. Many teachers report that project-based methods allow for personalized feedback and deeper engagement with subject matter, which standardized tests often fail to capture due to their limited scope and format. However, some educators acknowledge challenges in consistency and scalability with project-based assessments, highlighting the need for balanced integration alongside standardized metrics.
Future Trends in Technical Education Assessment
Project-based assessment fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application of technical skills, aligning with industry demands for adaptable professionals. Standardized testing offers quantifiable metrics for benchmarking but often lacks depth in evaluating practical competencies critical in technical fields. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid models integrating adaptive assessments and digital simulations to better measure complex technical proficiencies and prepare students for dynamic engineering and technology careers.
Project-Based Assessment vs Standardized Testing Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com