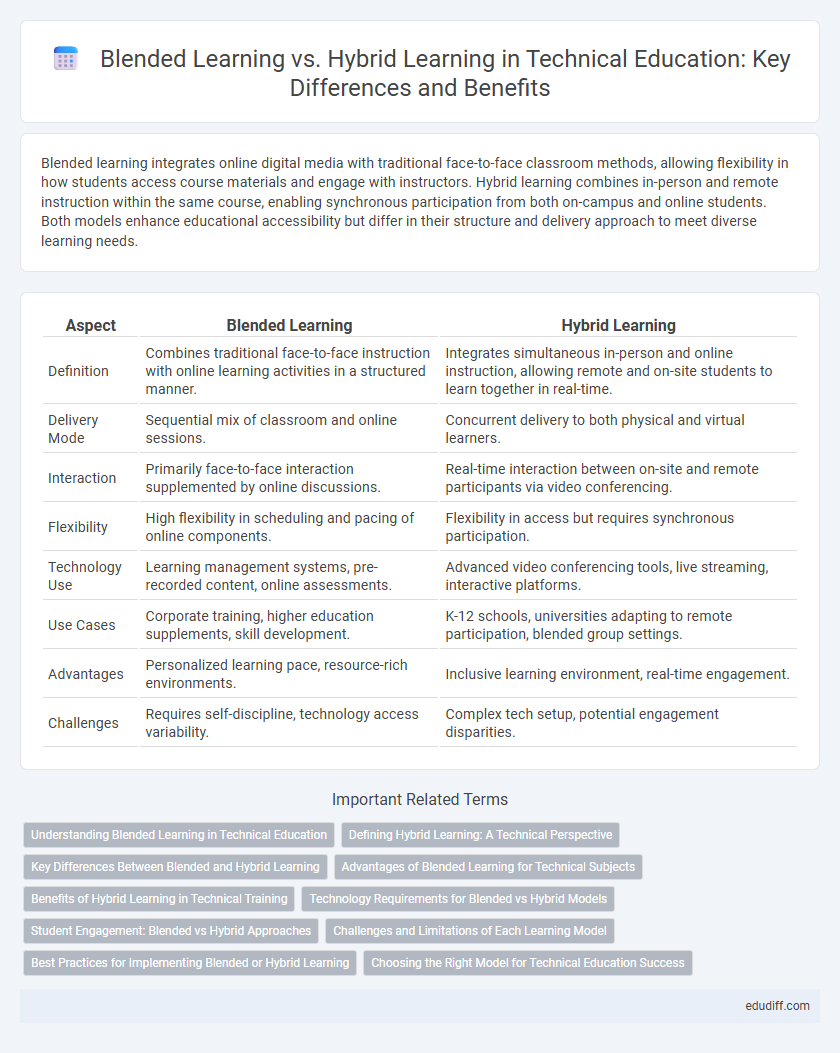
Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional face-to-face classroom methods, allowing flexibility in how students access course materials and engage with instructors. Hybrid learning combines in-person and remote instruction within the same course, enabling synchronous participation from both on-campus and online students. Both models enhance educational accessibility but differ in their structure and delivery approach to meet diverse learning needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Hybrid Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online learning activities in a structured manner. | Integrates simultaneous in-person and online instruction, allowing remote and on-site students to learn together in real-time. |
| Delivery Mode | Sequential mix of classroom and online sessions. | Concurrent delivery to both physical and virtual learners. |
| Interaction | Primarily face-to-face interaction supplemented by online discussions. | Real-time interaction between on-site and remote participants via video conferencing. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in scheduling and pacing of online components. | Flexibility in access but requires synchronous participation. |
| Technology Use | Learning management systems, pre-recorded content, online assessments. | Advanced video conferencing tools, live streaming, interactive platforms. |
| Use Cases | Corporate training, higher education supplements, skill development. | K-12 schools, universities adapting to remote participation, blended group settings. |
| Advantages | Personalized learning pace, resource-rich environments. | Inclusive learning environment, real-time engagement. |
| Challenges | Requires self-discipline, technology access variability. | Complex tech setup, potential engagement disparities. |
Understanding Blended Learning in Technical Education
Blended learning in technical education integrates online digital resources with traditional hands-on instruction, enhancing skill acquisition through flexible, multimodal training. It allows students to access theoretical content asynchronously while engaging in practical labs and collaborative projects on campus, increasing retention and real-world application. This approach supports personalized learning paths and continuous assessment, optimizing the development of technical competencies.
Defining Hybrid Learning: A Technical Perspective
Hybrid learning integrates face-to-face classroom instruction with synchronous online learning, utilizing advanced digital platforms and learning management systems to facilitate real-time interaction and content delivery. This model enables seamless switching between physical and virtual environments, leveraging multimedia tools and network infrastructure to support diverse learning modalities. Key technical components include robust video conferencing technologies, adaptive learning software, and secure data management systems to ensure consistent engagement and assessment across settings.
Key Differences Between Blended and Hybrid Learning
Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods, allowing students to learn through a combination of face-to-face instruction and online activities within a structured schedule. Hybrid learning combines in-person and remote instruction simultaneously, enabling some students to participate physically while others join virtually in real-time. The key difference lies in blended learning's flexible sequencing of online and offline components versus hybrid learning's concurrent delivery of both formats.
Advantages of Blended Learning for Technical Subjects
Blended learning in technical subjects enhances practical skills by combining online theoretical modules with hands-on lab sessions, fostering deeper comprehension. It allows flexible pacing, enabling students to revisit complex concepts and apply them in simulated environments, which improves retention and skill mastery. Access to diverse multimedia resources and real-time instructor feedback optimizes learning efficiency and prepares students for real-world technical challenges.
Benefits of Hybrid Learning in Technical Training
Hybrid learning in technical training offers enhanced flexibility by combining online theoretical modules with hands-on, in-person labs, which improves skill acquisition and retention. It enables access to diverse resources, such as virtual simulations and real-world equipment, fostering a comprehensive understanding of complex technical concepts. This approach also supports personalized learning paths, allowing trainees to progress at their own pace while maintaining instructor guidance for critical hands-on experience.
Technology Requirements for Blended vs Hybrid Models
Blended learning requires robust Learning Management Systems (LMS) and reliable internet connectivity to integrate synchronous and asynchronous online content with face-to-face instruction. Hybrid learning demands advanced video conferencing tools, interactive digital platforms, and seamless technology integration to accommodate simultaneous in-person and remote participation. Both models necessitate adaptive hardware such as tablets or laptops, but hybrid learning places greater emphasis on real-time collaboration technologies and technical support to ensure equitable learning experiences.
Student Engagement: Blended vs Hybrid Approaches
Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods to enhance student engagement through flexible, interactive content and real-time feedback. Hybrid learning combines in-person and remote instruction, promoting active participation by allowing students to choose their learning mode and engage through synchronous and asynchronous activities. Both approaches leverage technology to increase engagement, but blended learning often offers more seamless integration of instructional materials, boosting motivation and collaboration.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Learning Model
Blended learning faces challenges such as ensuring consistent student engagement and balancing face-to-face with online instruction, which can lead to logistical complexities and potential cognitive overload. Hybrid learning struggles with technological infrastructure demands and equitable access, often causing disparities in student participation and difficulties in synchronizing in-person and remote activities. Both models require robust training for educators to effectively manage diverse learning environments while addressing potential gaps in digital literacy among students.
Best Practices for Implementing Blended or Hybrid Learning
Effective implementation of blended and hybrid learning requires a strategic integration of synchronous and asynchronous instructional methods, leveraging Learning Management Systems (LMS) like Canvas or Moodle to facilitate seamless content delivery. Best practices emphasize ongoing teacher training in digital pedagogies, ensuring educators can design interactive activities that cater to diverse learning styles and promote student engagement. Data-driven assessment tools should be employed to monitor progress and personalize learning experiences, enhancing both academic outcomes and learner satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Model for Technical Education Success
Blended learning integrates traditional face-to-face instruction with online components, offering flexibility and personalized pacing essential for technical education. Hybrid learning combines synchronous in-person sessions with remote participation, enhancing real-time interaction and collaboration critical for hands-on technical skills. Selecting the appropriate model depends on curriculum complexity, student needs, technology infrastructure, and the balance between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Blended learning vs Hybrid learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com