Trade schools offer specialized, hands-on training for specific trades, enabling students to enter the workforce quickly with practical skills. Polytechnics provide a broader technical education combining theoretical knowledge and applied science, often leading to more advanced career opportunities. The choice depends on whether immediate job readiness or a comprehensive technical foundation is the priority.
Table of Comparison
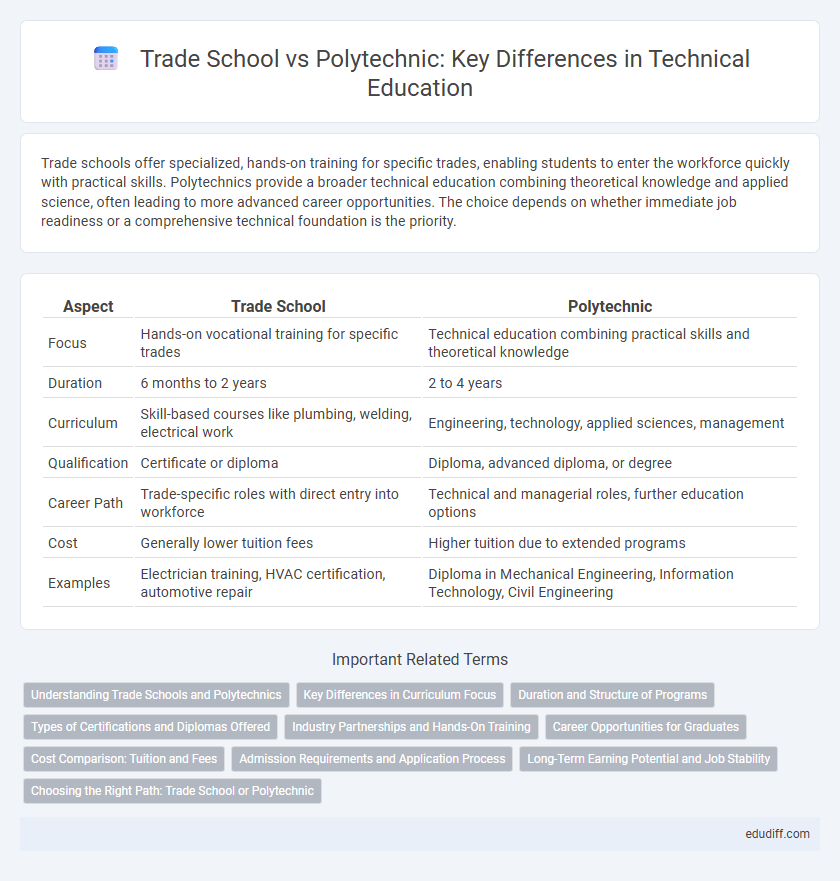
| Aspect | Trade School | Polytechnic |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Hands-on vocational training for specific trades | Technical education combining practical skills and theoretical knowledge |
| Duration | 6 months to 2 years | 2 to 4 years |
| Curriculum | Skill-based courses like plumbing, welding, electrical work | Engineering, technology, applied sciences, management |
| Qualification | Certificate or diploma | Diploma, advanced diploma, or degree |
| Career Path | Trade-specific roles with direct entry into workforce | Technical and managerial roles, further education options |
| Cost | Generally lower tuition fees | Higher tuition due to extended programs |
| Examples | Electrician training, HVAC certification, automotive repair | Diploma in Mechanical Engineering, Information Technology, Civil Engineering |
Understanding Trade Schools and Polytechnics
Trade schools specialize in skill-based training designed to prepare students for specific trades such as electrical work, plumbing, or carpentry, emphasizing hands-on experience and shorter course durations. Polytechnics offer a broader range of technical and applied science programs, often including diploma and degree courses in engineering, information technology, and business, blending theoretical knowledge with practical skills. Both institutions focus on workforce readiness but differ in scope, program length, and academic depth, catering to diverse career goals in the technical education landscape.
Key Differences in Curriculum Focus
Trade schools concentrate on specialized, hands-on training tailored to specific trades such as plumbing, welding, or automotive repair, emphasizing practical skills and job readiness. Polytechnics offer a broader curriculum that integrates theoretical knowledge with applied sciences across diverse fields like engineering, information technology, and business management. The distinction lies in the trade school's focus on immediate vocational skills versus the polytechnic's blend of academic and practical education designed for a wider range of technical careers.
Duration and Structure of Programs
Trade school programs typically span 6 months to 2 years, focusing on hands-on training tailored to specific skilled trades such as welding, plumbing, or automotive repair. Polytechnic programs generally extend from 2 to 4 years, offering a more comprehensive curriculum that integrates theoretical coursework with practical applications in fields like engineering technology, information technology, and applied sciences. The structured approach of polytechnic education combines general education, technical theory, and industry-relevant projects, while trade schools emphasize rapid skill acquisition and direct workforce entry.
Types of Certifications and Diplomas Offered
Trade schools primarily offer certifications and diplomas focused on specific skilled trades such as welding, plumbing, and HVAC, emphasizing hands-on training tailored for immediate job readiness. Polytechnics provide a broader range of credentials including diplomas, advanced diplomas, and sometimes degrees in applied sciences, engineering technologies, and business, combining theoretical knowledge with practical application. Certifications from polytechnics often prepare students for both technical roles and further academic pursuits, while trade school qualifications target direct entry into specialized trades.
Industry Partnerships and Hands-On Training
Trade schools and polytechnics excel in industry partnerships, offering apprenticeships and real-world projects that align closely with employer demands. Both institutions emphasize hands-on training through state-of-the-art labs and workshops, equipping students with practical skills and industry certifications. Strong collaborations with local businesses ensure curriculum relevance and enhance job placement rates post-graduation.
Career Opportunities for Graduates
Trade school graduates often enter specialized fields such as plumbing, electrical work, or HVAC with direct pathways to skilled labor positions. Polytechnic institutions provide broader engineering and technology-focused programs, equipping students with versatile skills applicable to industries like manufacturing, software development, and industrial design. Career opportunities from polytechnic diplomas typically offer higher earning potential and advancement into supervisory or technical management roles compared to trade school pathways.
Cost Comparison: Tuition and Fees
Trade schools typically offer lower tuition and fees compared to polytechnic institutes, making them a more affordable option for vocational training. Polytechnic programs often involve higher costs due to comprehensive curricula and advanced facilities, which can include engineering and technology courses. Evaluating the total cost of attendance, including additional fees like lab materials and certification exams, is crucial for an accurate comparison.
Admission Requirements and Application Process
Trade schools typically require a high school diploma or GED for admission, with some programs demanding entrance exams or relevant work experience. Polytechnic institutions often have more rigorous admission standards, including higher GPA thresholds, standardized test scores, and prerequisite coursework in math and science. The application process for trade schools is generally straightforward, involving submission of transcripts and basic forms, while polytechnic admissions require detailed applications, recommendation letters, and occasionally interviews or portfolio reviews.
Long-Term Earning Potential and Job Stability
Trade schools offer specialized training that leads to quicker entry into high-demand fields such as electrical work, plumbing, and HVAC, often resulting in competitive salaries and consistent job stability. Polytechnic institutions provide broader technical education with opportunities for advancement in engineering, computer science, and applied technologies, typically yielding higher long-term earning potential through diversified skill sets. Choosing between the two depends on immediate job market needs versus the pursuit of career growth and income scalability over time.
Choosing the Right Path: Trade School or Polytechnic
Choosing the right educational path depends on career goals and preferred learning styles; trade schools offer specialized, hands-on training in specific trades such as welding or electrical work, leading to faster job placement. Polytechnics provide a broader technical education, combining theoretical knowledge with practical skills across fields like engineering, information technology, and applied sciences, often resulting in diploma or degree qualifications. Assessing factors like program duration, curriculum focus, and industry demand helps determine which option aligns better with individual professional aspirations.
Trade School vs Polytechnic Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com