Applied sciences leverage scientific principles to develop practical technologies and solutions, directly impacting industries such as engineering, medicine, and information technology. Pure sciences prioritize the pursuit of knowledge and understanding of natural phenomena without immediate practical application, often forming the foundational theories upon which applied sciences build. The interplay between both fields drives innovation, with pure science discoveries enabling applied science advancements and applied sciences providing real-world testing grounds for theoretical concepts.
Table of Comparison
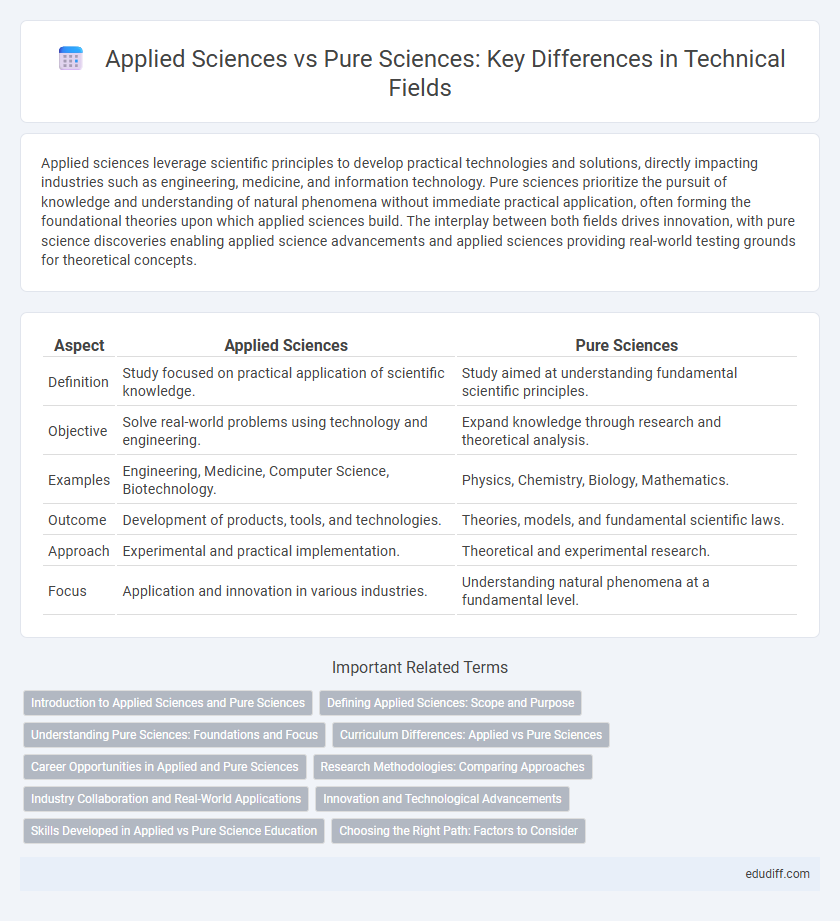
| Aspect | Applied Sciences | Pure Sciences |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study focused on practical application of scientific knowledge. | Study aimed at understanding fundamental scientific principles. |
| Objective | Solve real-world problems using technology and engineering. | Expand knowledge through research and theoretical analysis. |
| Examples | Engineering, Medicine, Computer Science, Biotechnology. | Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics. |
| Outcome | Development of products, tools, and technologies. | Theories, models, and fundamental scientific laws. |
| Approach | Experimental and practical implementation. | Theoretical and experimental research. |
| Focus | Application and innovation in various industries. | Understanding natural phenomena at a fundamental level. |
Introduction to Applied Sciences and Pure Sciences
Applied sciences integrate scientific principles with practical applications to solve real-world problems across engineering, technology, and healthcare fields. Pure sciences concentrate on understanding fundamental phenomena in disciplines like physics, chemistry, and biology through systematic observation and experimentation. The distinction emphasizes applied sciences' goal of innovation and development, while pure sciences focus on expanding theoretical knowledge.
Defining Applied Sciences: Scope and Purpose
Applied sciences encompass disciplines that utilize foundational scientific principles to develop practical technologies, tools, and processes aimed at solving real-world problems. This field bridges theoretical knowledge with engineering, medicine, and industry applications, emphasizing innovation and functionality. The scope of applied sciences covers diverse sectors including information technology, healthcare, environmental management, and manufacturing, prioritizing outcomes that enhance societal efficiency and wellbeing.
Understanding Pure Sciences: Foundations and Focus
Pure Sciences establish foundational knowledge through rigorous experimentation and theoretical analysis, focusing on understanding natural phenomena and fundamental principles. Disciplines like physics, chemistry, and biology emphasize developing universal laws and models that explain the behavior of matter and energy without immediate application in mind. This foundational approach in pure sciences drives the advancement of scientific knowledge, enabling future applied research and technological innovation.
Curriculum Differences: Applied vs Pure Sciences
Applied sciences curricula emphasize practical skills and real-world problem-solving through courses in engineering, technology, and laboratory applications, aligning closely with industry requirements. Pure sciences curricula focus on theoretical foundations, research methodologies, and fundamental principles in physics, chemistry, and biology to advance scientific knowledge. The divergence in coursework reflects applied sciences' goal of direct application and innovation, contrasting with pure sciences' pursuit of scientific understanding and discovery.
Career Opportunities in Applied and Pure Sciences
Career opportunities in applied sciences predominantly include engineering, information technology, healthcare, and environmental management, emphasizing practical problem-solving and technology development. Pure sciences offer roles in research, academia, and scientific analysis, focusing on theoretical understanding and fundamental discoveries in physics, chemistry, and biology. Both fields provide diverse career paths, with applied sciences driving innovation and industry solutions while pure sciences contribute to foundational knowledge and long-term scientific breakthroughs.
Research Methodologies: Comparing Approaches
Applied sciences utilize experimental and empirical research methodologies centered on practical problem-solving and real-world applications, integrating interdisciplinary techniques to optimize technological innovation. Pure sciences emphasize theoretical frameworks and hypothesis-driven exploration, often relying on controlled laboratory experiments and quantitative analysis to advance fundamental knowledge. Comparative studies reveal that applied research promotes iterative design and prototyping, whereas pure science prioritizes rigorous validation and reproducibility to establish foundational scientific principles.
Industry Collaboration and Real-World Applications
Applied sciences prioritize direct industry collaboration, driving innovations through practical problem-solving and technology transfer to sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and engineering. Pure sciences focus on fundamental research and theoretical understanding, often laying the groundwork for future technological advancements without immediate commercial objectives. The synergy between applied and pure sciences accelerates real-world applications by integrating foundational discoveries with industry-specific needs and market-driven solutions.
Innovation and Technological Advancements
Applied sciences drive innovation by transforming theoretical concepts from pure sciences into practical technologies that solve real-world problems. The integration of engineering principles and scientific research accelerates technological advancements in industries such as healthcare, energy, and information technology. By leveraging empirical data and experimental methodologies, applied sciences foster the development of cutting-edge devices and systems that enhance productivity and quality of life.
Skills Developed in Applied vs Pure Science Education
Applied science education emphasizes practical skills such as problem-solving, technical proficiency, and real-world application of scientific principles. Pure science education fosters analytical thinking, theoretical understanding, and rigorous research methodologies. Both disciplines develop critical skills, with applied sciences geared towards innovation and implementation, while pure sciences prioritize foundational knowledge and experimental design.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Applied Sciences and Pure Sciences involves evaluating career goals, as Applied Sciences prioritize practical problem-solving and direct industry applications while Pure Sciences emphasize theoretical understanding and foundational research. Consider the demand for technical skills in sectors like engineering or biotechnology for Applied Sciences versus academic or research opportunities that require deep scientific inquiry typical of Pure Sciences. Assess personal strengths in hands-on experimentation versus conceptual analysis to determine the most suitable educational and professional path.
Applied Sciences vs Pure Sciences Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com