Active learning engages learners through hands-on activities and problem-solving, fostering deeper understanding and retention compared to passive learning, which relies on listening or reading without interaction. This interactive approach encourages critical thinking and immediate application of concepts, enhancing long-term comprehension. Technology-enabled tools like simulations and quizzes amplify active learning benefits in technical education.
Table of Comparison
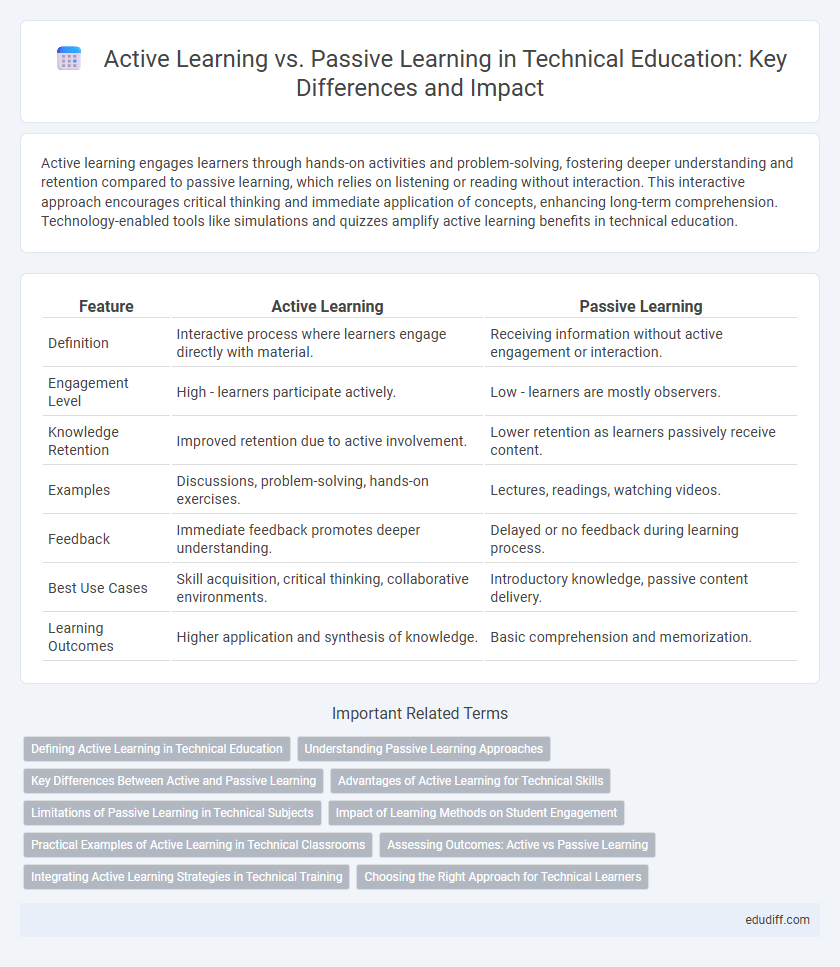
| Feature | Active Learning | Passive Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interactive process where learners engage directly with material. | Receiving information without active engagement or interaction. |
| Engagement Level | High - learners participate actively. | Low - learners are mostly observers. |
| Knowledge Retention | Improved retention due to active involvement. | Lower retention as learners passively receive content. |
| Examples | Discussions, problem-solving, hands-on exercises. | Lectures, readings, watching videos. |
| Feedback | Immediate feedback promotes deeper understanding. | Delayed or no feedback during learning process. |
| Best Use Cases | Skill acquisition, critical thinking, collaborative environments. | Introductory knowledge, passive content delivery. |
| Learning Outcomes | Higher application and synthesis of knowledge. | Basic comprehension and memorization. |
Defining Active Learning in Technical Education
Active learning in technical education emphasizes hands-on, experiential activities that engage students directly in problem-solving and critical thinking tasks, enhancing retention and application of complex concepts. This approach contrasts with passive learning by requiring active participation through simulations, coding exercises, and collaborative projects that mirror real-world technical challenges. Research shows that active learning methods improve skill acquisition and increase student motivation in STEM and engineering disciplines.
Understanding Passive Learning Approaches
Passive learning approaches primarily involve learners receiving information without direct engagement, often through lectures, readings, or watching videos. This method emphasizes information absorption rather than interaction, leading to limited critical thinking and retention. Understanding these approaches highlights the need for more dynamic techniques like active learning that foster deeper comprehension and skill application.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Learning
Active learning engages learners through interactive exercises, problem-solving, and critical thinking activities, promoting deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Passive learning involves the absorption of information primarily through listening or reading without direct interaction, often leading to lower engagement and less effective knowledge consolidation. Key differences include learner participation, feedback mechanisms, and cognitive involvement, where active learning fosters continuous feedback loops and higher cognitive demand compared to the more passive reception in traditional lecture formats.
Advantages of Active Learning for Technical Skills
Active learning enhances technical skills by engaging learners in hands-on problem-solving and real-world applications, which improves retention and understanding. It fosters critical thinking and adaptability, allowing learners to troubleshoot and innovate effectively in dynamic technical environments. This approach also encourages immediate feedback and iterative learning, accelerating skill acquisition compared to passive methods.
Limitations of Passive Learning in Technical Subjects
Passive learning in technical subjects often leads to limited knowledge retention and reduced problem-solving skills, as students primarily receive information without engaging in active application. This approach diminishes critical thinking development, essential for mastering complex concepts in fields like engineering and computer science. Moreover, passive learning frequently results in lower motivation and less adaptability when facing real-world technical challenges.
Impact of Learning Methods on Student Engagement
Active learning methods, such as collaborative projects and problem-solving activities, significantly increase student engagement by promoting critical thinking and participation. In contrast, passive learning approaches, including lectures and rote memorization, often result in lower attention levels and reduced retention rates. Studies indicate that interactive techniques can improve academic performance by up to 30% compared to traditional passive instruction.
Practical Examples of Active Learning in Technical Classrooms
Active learning in technical classrooms involves hands-on coding exercises, real-time problem-solving with software tools, and interactive simulations that engage students deeply with the material. Techniques such as pair programming, coding bootcamps, and lab-based projects enable learners to apply theoretical concepts directly, enhancing retention and skill acquisition. In contrast, passive learning usually relies on lectures and note-taking, which often result in lower engagement and limited practical understanding of complex technical subjects.
Assessing Outcomes: Active vs Passive Learning
Active learning strategies significantly enhance knowledge retention and critical thinking skills by engaging learners in problem-solving and application tasks. Passive learning often results in lower comprehension rates due to minimal interaction and reliance on memorization. Studies show that students involved in active learning exhibit up to 40% higher assessment scores compared to those in passive learning environments.
Integrating Active Learning Strategies in Technical Training
Integrating active learning strategies in technical training enhances skill acquisition by engaging learners in hands-on problem-solving and real-world simulations that reinforce theoretical knowledge. Techniques such as interactive coding exercises, collaborative projects, and immediate feedback mechanisms promote deeper understanding and retention compared to passive learning methods like lectures or reading. This approach accelerates competency development in complex technical domains by fostering critical thinking and adaptive expertise.
Choosing the Right Approach for Technical Learners
Active learning engages technical learners through hands-on experiments, coding challenges, and real-world problem-solving, which enhances comprehension and retention of complex concepts. Passive learning relies on lectures, readings, and demonstrations that provide foundational knowledge but may limit deep understanding and practical application. Selecting the right approach depends on the learner's goals, with active learning preferable for skill acquisition and passive learning suitable for initial exposure to theoretical frameworks.
Active learning vs Passive learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com