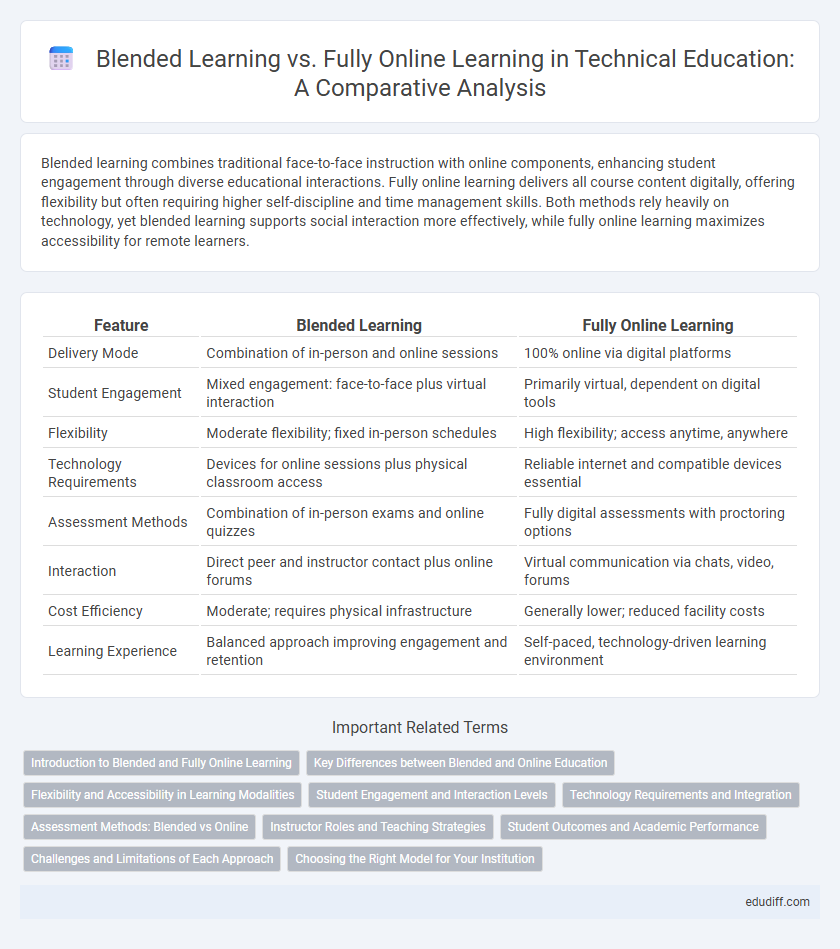
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online components, enhancing student engagement through diverse educational interactions. Fully online learning delivers all course content digitally, offering flexibility but often requiring higher self-discipline and time management skills. Both methods rely heavily on technology, yet blended learning supports social interaction more effectively, while fully online learning maximizes accessibility for remote learners.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blended Learning | Fully Online Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Mode | Combination of in-person and online sessions | 100% online via digital platforms |
| Student Engagement | Mixed engagement: face-to-face plus virtual interaction | Primarily virtual, dependent on digital tools |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility; fixed in-person schedules | High flexibility; access anytime, anywhere |
| Technology Requirements | Devices for online sessions plus physical classroom access | Reliable internet and compatible devices essential |
| Assessment Methods | Combination of in-person exams and online quizzes | Fully digital assessments with proctoring options |
| Interaction | Direct peer and instructor contact plus online forums | Virtual communication via chats, video, forums |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate; requires physical infrastructure | Generally lower; reduced facility costs |
| Learning Experience | Balanced approach improving engagement and retention | Self-paced, technology-driven learning environment |
Introduction to Blended and Fully Online Learning
Blended learning integrates traditional face-to-face classroom methods with online educational materials, enhancing flexibility and engagement through a mix of synchronous and asynchronous activities. Fully online learning delivers all course content via digital platforms, enabling complete remote access without physical location constraints, often supported by interactive tools such as video lectures, discussion forums, and virtual labs. Both approaches leverage Learning Management Systems (LMS) to facilitate content distribution, assessment, and communication, but differ significantly in their dependence on physical presence and real-time interaction.
Key Differences between Blended and Online Education
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online components, offering a hybrid approach that enhances interaction and flexibility. Fully online learning delivers education exclusively through digital platforms, emphasizing accessibility and self-paced study without physical presence. Key differences include the degree of in-person engagement, instructional methods, and the integration of technology to support diverse learning environments.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Learning Modalities
Blended learning enhances flexibility by combining face-to-face instruction with online resources, allowing learners to access materials anytime while benefiting from direct teacher interaction. Fully online learning offers unparalleled accessibility, enabling students to participate regardless of geographic location or schedule constraints, supported by diverse digital platforms and tools. Both modalities improve learning adaptability, but blended learning balances structured engagement with flexible access, whereas fully online learning maximizes convenience and reach.
Student Engagement and Interaction Levels
Blended learning combines face-to-face classroom methods with online activities, enhancing student engagement by fostering direct interaction and immediate feedback. Fully online learning relies solely on digital platforms, often limiting spontaneous student interaction and requiring more structured strategies to maintain engagement. Research indicates that blended learning environments generally achieve higher levels of collaboration and participation compared to fully online settings.
Technology Requirements and Integration
Blended learning requires seamless integration of both traditional classroom technologies and digital platforms, ensuring compatibility between in-person and online tools such as LMS, video conferencing, and interactive software. Fully online learning depends heavily on robust internet connectivity, cloud-based infrastructure, and scalable software solutions for content delivery, attendance tracking, and real-time collaboration. Institutions must evaluate bandwidth capacity, device compatibility, and system interoperability to optimize the technological ecosystem supporting each learning model.
Assessment Methods: Blended vs Online
Assessment methods in blended learning combine both face-to-face evaluations and digital tools, enabling real-time feedback and interactive assignments that foster deeper understanding. Fully online learning relies heavily on computer-based assessments, such as automated quizzes, video presentations, and AI-driven analytics, to measure student performance asynchronously. The integration of formative and summative assessments in blended environments supports diverse learning styles, while online-only models emphasize scalability and data-driven insights for continuous improvement.
Instructor Roles and Teaching Strategies
Blended learning requires instructors to combine face-to-face facilitation with online content delivery, utilizing strategies like flipped classrooms and interactive discussions to engage students across modalities. Fully online learning demands instructors to leverage digital tools, such as learning management systems and synchronous video sessions, emphasizing clear communication and timely feedback to maintain student motivation. Teaching strategies in blended environments focus on balancing direct interaction and self-paced study, whereas fully online settings prioritize technological proficiency and designing asynchronous activities for autonomous learning.
Student Outcomes and Academic Performance
Blended learning enhances student outcomes by combining face-to-face interaction with online resources, leading to higher academic performance and improved retention rates compared to fully online learning. Research indicates that students in blended environments demonstrate better engagement, critical thinking skills, and practical application of knowledge due to diversified instructional methods. Fully online learning offers flexibility but often faces challenges in maintaining student motivation and interaction, which can impact overall academic achievement negatively.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Blended learning faces challenges in balancing in-person and digital engagement, often requiring complex scheduling and substantial technological infrastructure to support seamless integration. Fully online learning encounters limitations such as reduced student interaction, potential for increased isolation, and reliance on students' self-motivation and access to reliable internet connectivity. Both approaches demand significant investment in instructional design to address diverse learning preferences and maintain academic rigor.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Institution
Blended learning combines face-to-face instruction with online components, offering flexibility and enhanced engagement, making it ideal for institutions seeking a balanced approach to education. Fully online learning delivers complete courses through digital platforms, maximizing accessibility and scalability for institutions with diverse or remote student populations. Evaluating factors such as technological infrastructure, student demographics, faculty readiness, and instructional goals is essential to select the most effective model for your institution's unique needs.
Blended Learning vs Fully Online Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com