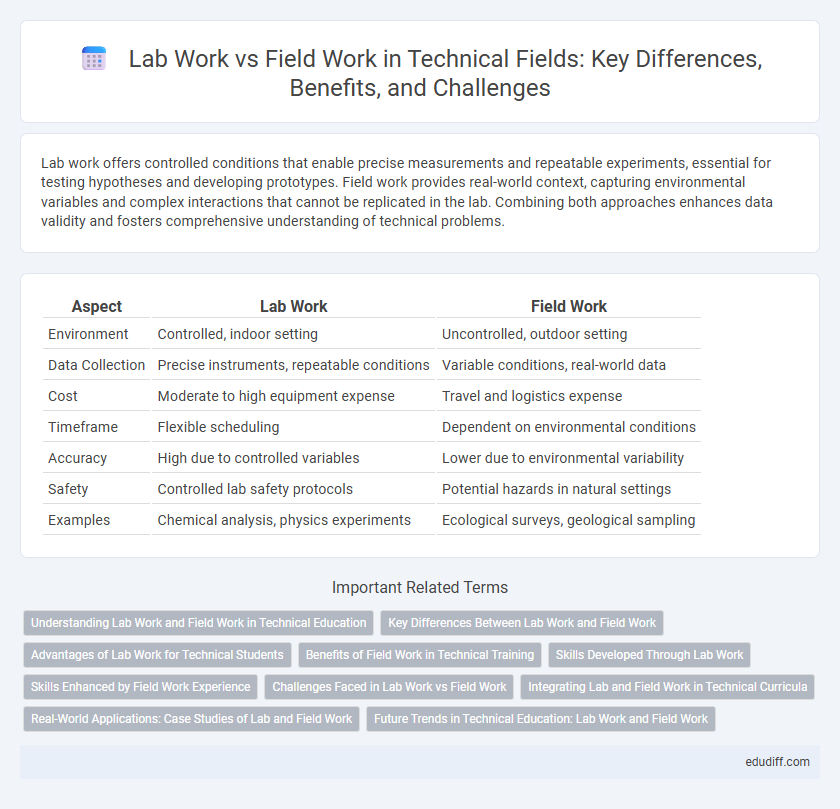
Lab work offers controlled conditions that enable precise measurements and repeatable experiments, essential for testing hypotheses and developing prototypes. Field work provides real-world context, capturing environmental variables and complex interactions that cannot be replicated in the lab. Combining both approaches enhances data validity and fosters comprehensive understanding of technical problems.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lab Work | Field Work |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Controlled, indoor setting | Uncontrolled, outdoor setting |
| Data Collection | Precise instruments, repeatable conditions | Variable conditions, real-world data |
| Cost | Moderate to high equipment expense | Travel and logistics expense |
| Timeframe | Flexible scheduling | Dependent on environmental conditions |
| Accuracy | High due to controlled variables | Lower due to environmental variability |
| Safety | Controlled lab safety protocols | Potential hazards in natural settings |
| Examples | Chemical analysis, physics experiments | Ecological surveys, geological sampling |
Understanding Lab Work and Field Work in Technical Education
Lab work in technical education provides controlled environments for hands-on experimentation, fostering practical skills in equipment handling and data analysis. Field work complements this by offering real-world exposure and situational problem-solving, essential for understanding environmental variables and operational challenges. Integrating both approaches enhances comprehensive technical competence and prepares students for diverse professional scenarios.
Key Differences Between Lab Work and Field Work
Lab work involves controlled environments where variables can be precisely managed, enabling accurate data collection and repeatability. Field work occurs in natural settings, exposing researchers to variable conditions that require adaptive methods and real-time decision making. Data from lab work tends to emphasize internal validity, while field work prioritizes ecological validity and practical applicability.
Advantages of Lab Work for Technical Students
Lab work offers technical students controlled environments allowing precise manipulation of variables, leading to accurate and repeatable experiments. Advanced instruments and tools available in labs facilitate hands-on experience with cutting-edge technology, essential for skill development. This structured setting enhances focused learning, immediate troubleshooting, and thorough data analysis, fostering a deeper understanding of theoretical concepts.
Benefits of Field Work in Technical Training
Field work in technical training offers immersive, real-world experience, enhancing practical skills beyond theoretical knowledge gained in lab settings. It fosters adaptability by exposing trainees to variable environmental conditions and unexpected challenges, essential for problem-solving in actual projects. Direct interaction with equipment and materials in authentic contexts accelerates learning retention and builds confidence critical for professional competence.
Skills Developed Through Lab Work
Lab work enhances technical skills such as precise measurement, controlled experimentation, and data analysis using advanced scientific instruments. It develops critical thinking by allowing systematic hypothesis testing and error analysis in a controlled environment. Laboratory experience fosters proficiency in following protocols and mastering specialized software for data recording and interpretation.
Skills Enhanced by Field Work Experience
Field work enhances critical observational skills, adaptability to unpredictable environments, and real-time problem-solving abilities that are difficult to replicate in controlled lab settings. It develops proficiency in data collection under varying conditions, improving accuracy and reliability in practical applications. Hands-on experience with natural variables fosters a deeper understanding of context-specific challenges, sharpening analytical and decision-making skills essential for applied technical fields.
Challenges Faced in Lab Work vs Field Work
Lab work challenges include maintaining controlled environments, managing expensive and sensitive equipment, and ensuring reproducibility of experiments under strict protocols. Field work difficulties involve dealing with unpredictable environmental conditions, logistical constraints, limited access to resources, and variable data quality due to uncontrollable factors. Both settings demand meticulous planning and adaptability, but field work requires enhanced risk management and real-time problem-solving skills.
Integrating Lab and Field Work in Technical Curricula
Integrating lab and field work in technical curricula enhances practical skills by providing controlled experimentation alongside real-world application, fostering a deeper understanding of theoretical concepts. Combining these approaches enables students to analyze data accurately and adapt techniques to variable conditions, essential for fields such as engineering, environmental science, and geology. Implementing coordinated projects strengthens problem-solving capabilities and prepares graduates for industry demands through experiential learning and critical thinking.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies of Lab and Field Work
Lab work offers controlled environments ideal for hypothesis testing and precise measurements, while field work provides critical insights into environmental variability and real-world challenges. Case studies reveal how laboratory simulations of chemical reactions enable development of new materials, whereas field studies in ecology uncover species interactions crucial for conservation strategies. Integrating lab and field findings enhances the reliability and applicability of research outcomes in practical scenarios.
Future Trends in Technical Education: Lab Work and Field Work
Emerging technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are transforming lab work by enabling immersive simulations that enhance hands-on learning without physical constraints. Field work is increasingly integrated with real-time data analytics and IoT devices, allowing students to collect and analyze environmental or technical data remotely and with higher precision. Future technical education emphasizes hybrid models combining digital lab environments and smart fieldwork to develop practical skills aligned with Industry 4.0 demands.
Lab Work vs Field Work Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com