Peer review offers nuanced insights by leveraging human expertise to evaluate complex technical work, ensuring context-sensitive feedback and fostering collaborative improvement. Automated assessment provides consistent, scalable, and rapid evaluation using algorithms, ideal for large datasets and standardized criteria. Combining both methods enhances accuracy and efficiency, balancing subjective judgment with objective measurement.
Table of Comparison
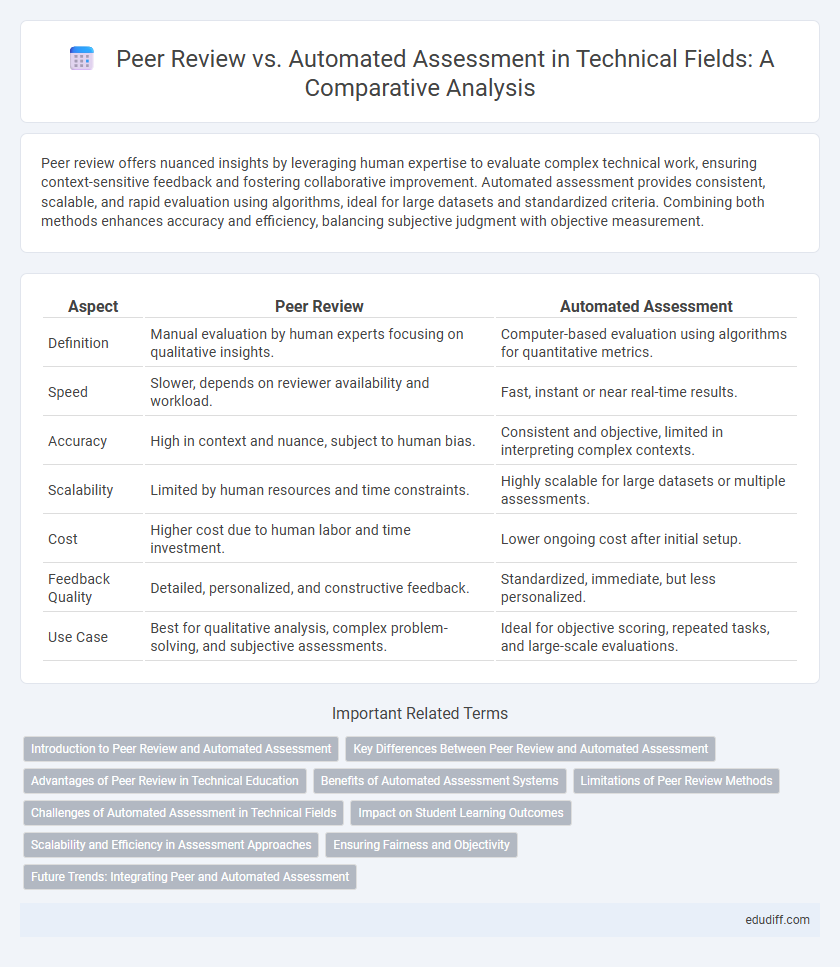
| Aspect | Peer Review | Automated Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual evaluation by human experts focusing on qualitative insights. | Computer-based evaluation using algorithms for quantitative metrics. |
| Speed | Slower, depends on reviewer availability and workload. | Fast, instant or near real-time results. |
| Accuracy | High in context and nuance, subject to human bias. | Consistent and objective, limited in interpreting complex contexts. |
| Scalability | Limited by human resources and time constraints. | Highly scalable for large datasets or multiple assessments. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to human labor and time investment. | Lower ongoing cost after initial setup. |
| Feedback Quality | Detailed, personalized, and constructive feedback. | Standardized, immediate, but less personalized. |
| Use Case | Best for qualitative analysis, complex problem-solving, and subjective assessments. | Ideal for objective scoring, repeated tasks, and large-scale evaluations. |
Introduction to Peer Review and Automated Assessment
Peer review involves experts examining work for accuracy, quality, and relevance, ensuring thorough evaluation through human judgment and contextual understanding. Automated assessment uses algorithms and software to quickly evaluate and score submissions based on predefined criteria, offering scalability and consistency. Combining peer review with automated assessment can optimize quality control and efficiency in technical evaluations.
Key Differences Between Peer Review and Automated Assessment
Peer review relies on human evaluators to assess the quality and accuracy of work, enabling nuanced feedback and subjective judgment, while automated assessment uses algorithms to provide rapid, consistent, and objective scoring based on predefined criteria. Peer review excels in evaluating complex, creative, or ambiguous content but can be time-consuming and prone to bias, whereas automated assessment offers scalability and efficiency but may lack the ability to interpret nuances beyond programmed parameters. The key differences lie in human insight versus algorithmic precision, flexibility versus consistency, and interpretative feedback versus quantifiable results.
Advantages of Peer Review in Technical Education
Peer review in technical education fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to analyze diverse solutions, enhancing problem-solving skills beyond automated feedback capabilities. It promotes collaborative learning, communication skills, and knowledge retention through constructive dialogue and varied perspectives, which automated assessments cannot replicate. Peer assessments also help identify nuanced errors and contextual misunderstandings in technical work, offering personalized insights crucial for complex project evaluations.
Benefits of Automated Assessment Systems
Automated assessment systems enhance evaluation accuracy and consistency by eliminating human bias and fatigue, ensuring standardized scoring across large datasets. These systems enable rapid feedback delivery, significantly reducing turnaround times and allowing learners to promptly adjust their understanding. Integration of machine learning algorithms facilitates adaptive testing and personalized learning paths, improving overall educational outcomes and scalability.
Limitations of Peer Review Methods
Peer review methods often face challenges such as subjectivity, inconsistency, and potential bias among reviewers, which can impact the accuracy and fairness of evaluations. Time consumption and scalability issues arise due to the necessity of human involvement for each assessment. Dependence on reviewer expertise and varying interpretation of criteria further limit the reliability of peer-reviewed outcomes compared to automated assessment systems.
Challenges of Automated Assessment in Technical Fields
Automated assessment in technical fields faces significant challenges, including the difficulty of accurately interpreting complex code logic and identifying context-specific errors. Limitations in current AI models often result in misjudgments of innovative or unconventional solutions that deviate from predefined criteria. Ensuring precise evaluation of intricate algorithms and nuanced technical details remains a critical hurdle for automated systems compared to human peer review.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Peer review enhances student learning outcomes by fostering critical thinking, deeper understanding, and active engagement with the material through collaborative feedback. Automated assessment provides immediate, objective evaluation and consistent grading, supporting timely interventions and reinforcing foundational knowledge. Combining both methods optimizes learning by balancing personalized insight with efficient progress tracking.
Scalability and Efficiency in Assessment Approaches
Automated assessment systems leverage algorithms and machine learning to evaluate large volumes of work rapidly, significantly enhancing scalability compared to traditional peer review methods. Peer review offers nuanced feedback and critical thinking insights but struggles with consistency and efficiency in large-scale applications. Balancing automated assessment's speed and scalability with peer review's qualitative depth can optimize overall evaluation effectiveness in educational and professional settings.
Ensuring Fairness and Objectivity
Peer review enhances fairness by incorporating multiple expert perspectives, reducing individual biases in technical assessments. Automated assessment employs consistent algorithms and standardized criteria to ensure objective evaluation, minimizing human error and subjectivity. Combining both methods leverages human judgment and technological precision, fostering balanced and equitable technical evaluations.
Future Trends: Integrating Peer and Automated Assessment
Future trends in educational evaluation emphasize the integration of peer review and automated assessment to leverage the strengths of both methods. Combining human judgment with AI-driven analytics enhances accuracy and provides nuanced feedback, promoting deeper learning engagement. Advanced algorithms can identify patterns missed by peers, while peer assessments contribute contextual insights, creating a comprehensive evaluation framework.
Peer Review vs Automated Assessment Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com