Technical drawing represents designs through manual sketches or drafting, emphasizing precision and standardized symbols to convey exact dimensions and specifications. CAD modeling utilizes computer software to create detailed, three-dimensional representations, enabling easier modifications, simulations, and enhanced visualization. While technical drawings serve as foundational blueprints, CAD models offer dynamic flexibility and integration with digital manufacturing processes.
Table of Comparison
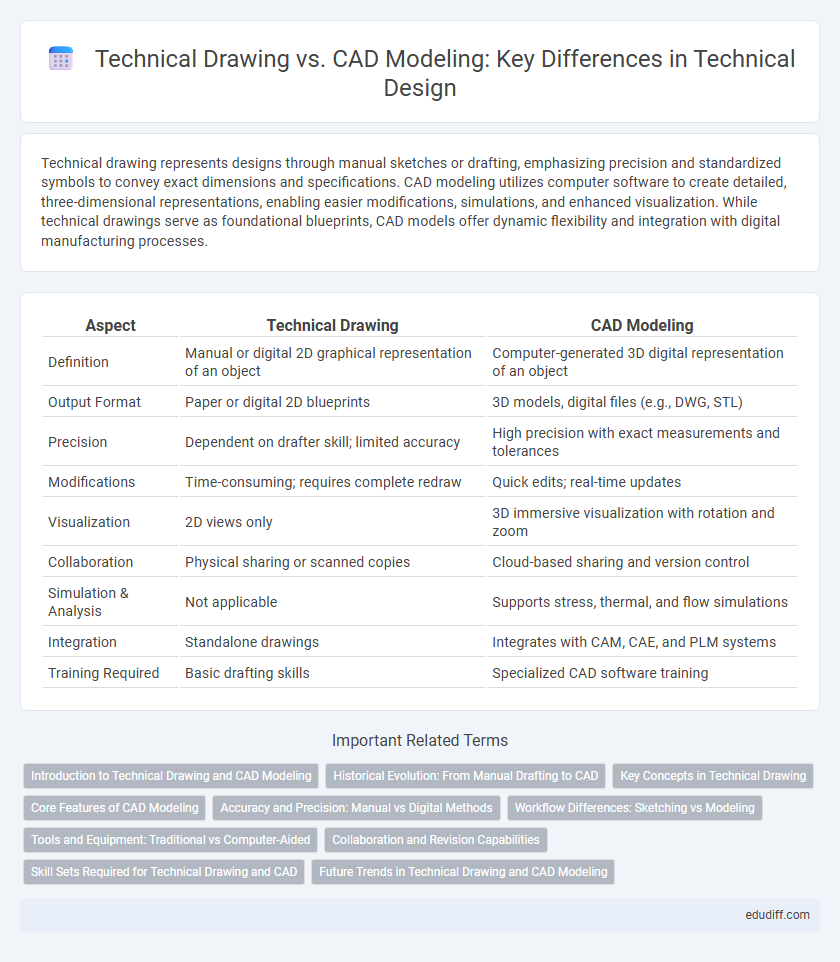
| Aspect | Technical Drawing | CAD Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual or digital 2D graphical representation of an object | Computer-generated 3D digital representation of an object |
| Output Format | Paper or digital 2D blueprints | 3D models, digital files (e.g., DWG, STL) |
| Precision | Dependent on drafter skill; limited accuracy | High precision with exact measurements and tolerances |
| Modifications | Time-consuming; requires complete redraw | Quick edits; real-time updates |
| Visualization | 2D views only | 3D immersive visualization with rotation and zoom |
| Collaboration | Physical sharing or scanned copies | Cloud-based sharing and version control |
| Simulation & Analysis | Not applicable | Supports stress, thermal, and flow simulations |
| Integration | Standalone drawings | Integrates with CAM, CAE, and PLM systems |
| Training Required | Basic drafting skills | Specialized CAD software training |
Introduction to Technical Drawing and CAD Modeling
Technical drawing involves creating precise, scaled, and detailed manual sketches or blueprints for engineering or architectural projects, emphasizing hand-drawn lines and annotations. CAD modeling uses computer-aided software to generate 2D or 3D digital representations, enabling enhanced accuracy, easier modifications, and simulations. Both techniques play crucial roles in design communication, but CAD modeling streamlines the workflow and supports visualization more effectively.
Historical Evolution: From Manual Drafting to CAD
Technical drawing evolved from manual drafting techniques involving paper, pencils, and drafting tools to computer-aided design (CAD) systems that revolutionized precision and efficiency. Early 20th-century draftsmen relied on hand-drawn blueprints, which were time-consuming and prone to human error, whereas modern CAD software enables rapid modifications, 3D modeling, and digital storage. This historical shift dramatically enhanced engineering workflows, allowing for complex designs, better collaboration, and integration with manufacturing processes.
Key Concepts in Technical Drawing
Technical drawing emphasizes precise manual drafting techniques, universal symbols, and standardized conventions such as line types, scales, and projection methods to accurately convey engineering designs. It relies on orthographic projections and sectional views to represent three-dimensional objects on two-dimensional media, ensuring clear communication across disciplines. Mastery of dimensioning, tolerancing, and geometric construction rules forms the foundation for producing unambiguous and interpretable technical drawings.
Core Features of CAD Modeling
CAD modeling integrates precise 3D geometry creation, parametric design capabilities, and real-time visualization to enhance accuracy and flexibility in technical projects. Its core features include automated dimensioning, version control, and seamless integration with simulation tools for performance analysis. These functionalities significantly reduce design errors and accelerate the product development cycle compared to traditional technical drawing methods.
Accuracy and Precision: Manual vs Digital Methods
Technical drawing relies on manual skills, making accuracy and precision dependent on the drafter's expertise and prone to human error. CAD modeling offers enhanced precision through automated tools, enabling exact dimensions and consistent replication across designs. Digital methods reduce variability and improve accuracy, facilitating complex modifications with minimal risk of errors compared to traditional manual techniques.
Workflow Differences: Sketching vs Modeling
Technical drawing relies on manual sketching techniques that emphasize precision and spatial reasoning, often requiring iterative adjustments on physical media. CAD modeling uses digital tools to create three-dimensional objects with parametric controls, enabling easier modifications and integration with simulation software. The workflow shift from 2D sketching to 3D modeling enhances accuracy, reduces errors, and improves collaboration in engineering design processes.
Tools and Equipment: Traditional vs Computer-Aided
Traditional technical drawing relies on manual tools such as compasses, T-squares, protractors, and drafting tables to create precise, hand-drawn designs. In contrast, CAD modeling utilizes sophisticated software platforms like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and CATIA, which integrate digital tools for enhanced accuracy, editing capabilities, and 3D visualization. The shift from physical instruments to computer-aided equipment significantly improves efficiency, reduces errors, and allows seamless modifications in engineering and architectural projects.
Collaboration and Revision Capabilities
Technical drawing offers a tangible, straightforward approach for initial design concepts but lacks the dynamic collaboration features found in CAD modeling. CAD modeling enables real-time multi-user collaboration, allowing seamless sharing, editing, and updating of design files with version control to track revisions accurately. Enhanced revision capabilities in CAD reduce errors and streamline workflow, ensuring design consistency across engineering and manufacturing teams.
Skill Sets Required for Technical Drawing and CAD
Technical drawing demands strong manual drafting skills, precise measurement interpretation, and the ability to visualize spatial relationships on paper. CAD modeling requires proficiency in specialized software such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or CATIA, alongside knowledge of 3D geometry, parametric design, and digital file management. Both skill sets emphasize attention to detail, technical accuracy, and an understanding of engineering standards, but CAD professionals benefit from expertise in virtual simulation and automation tools.
Future Trends in Technical Drawing and CAD Modeling
Future trends in technical drawing and CAD modeling emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for enhanced design accuracy and automation. Cloud-based collaboration platforms are revolutionizing project workflows by enabling real-time updates and multi-user access to complex CAD models. Advancements in virtual and augmented reality are increasingly being used for immersive design visualization and interactive technical drawing reviews.
Technical drawing vs CAD modeling Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com