Hybrid course design integrates face-to-face instruction with online learning activities, providing a balanced approach that enhances student engagement and flexibility. Fully online courses rely exclusively on digital platforms, enabling access from any location but requiring strong self-motivation and time management skills. Both models utilize technology to deliver content, yet hybrid courses often offer more opportunities for in-person collaboration and immediate feedback.
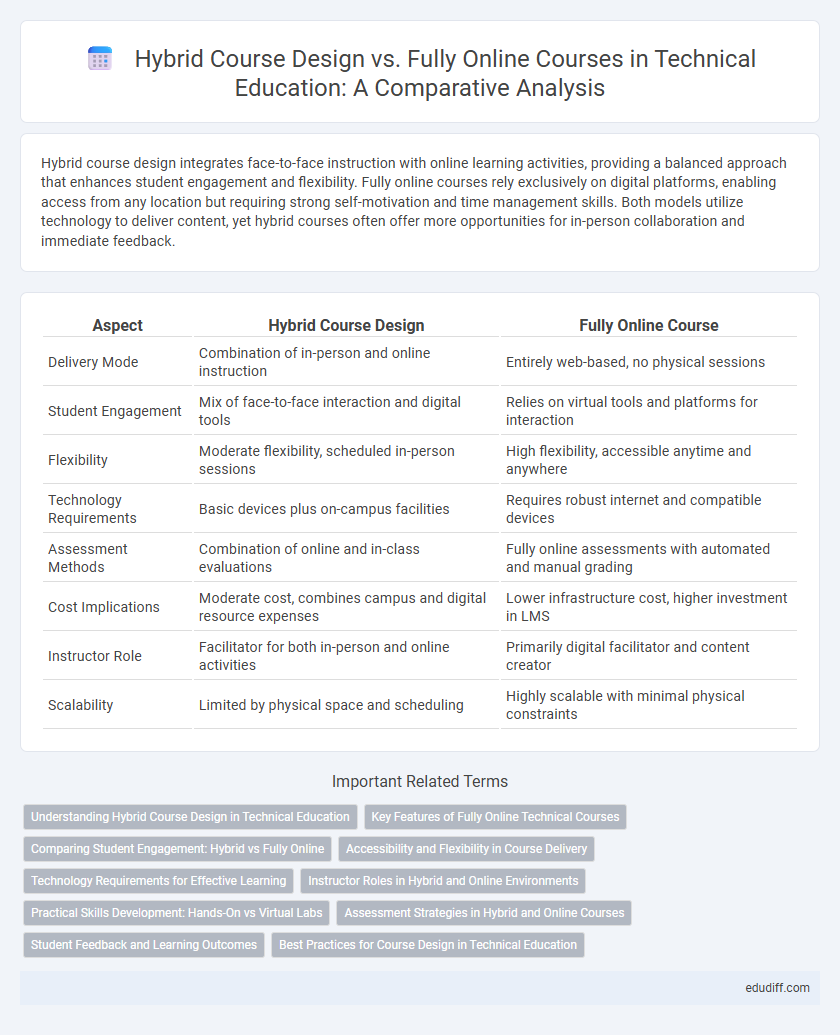
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hybrid Course Design | Fully Online Course |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Mode | Combination of in-person and online instruction | Entirely web-based, no physical sessions |
| Student Engagement | Mix of face-to-face interaction and digital tools | Relies on virtual tools and platforms for interaction |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, scheduled in-person sessions | High flexibility, accessible anytime and anywhere |
| Technology Requirements | Basic devices plus on-campus facilities | Requires robust internet and compatible devices |
| Assessment Methods | Combination of online and in-class evaluations | Fully online assessments with automated and manual grading |
| Cost Implications | Moderate cost, combines campus and digital resource expenses | Lower infrastructure cost, higher investment in LMS |
| Instructor Role | Facilitator for both in-person and online activities | Primarily digital facilitator and content creator |
| Scalability | Limited by physical space and scheduling | Highly scalable with minimal physical constraints |
Understanding Hybrid Course Design in Technical Education
Hybrid course design in technical education integrates face-to-face instruction with online learning platforms, enhancing flexibility and accessibility for students while maintaining hands-on, practical training essential for technical skill development. This model leverages advanced digital tools and real-time collaboration technologies to simulate lab environments and provide immediate feedback, which is often challenging to achieve in fully online courses. Compared to fully online courses, hybrid designs improve student engagement and knowledge retention by combining theoretical content delivery with interactive, experiential learning.
Key Features of Fully Online Technical Courses
Fully online technical courses offer flexible access to multimedia instructional materials, enabling learners to study at their own pace and revisit complex topics as needed. These courses leverage interactive tools such as virtual labs, simulations, and discussion forums to facilitate hands-on practice and collaborative problem-solving. Robust learning management systems integrate real-time assessments, automated grading, and detailed analytics to track student progress and tailor personalized feedback.
Comparing Student Engagement: Hybrid vs Fully Online
Hybrid course design enhances student engagement by combining face-to-face interaction with online flexibility, fostering active participation and immediate feedback. Fully online courses rely heavily on digital tools and self-motivation, which can reduce real-time student-instructor interaction and collaborative learning opportunities. Studies indicate hybrid models often yield higher engagement metrics, such as attendance and discussion frequency, compared to fully online formats.
Accessibility and Flexibility in Course Delivery
Hybrid course design offers enhanced accessibility by combining in-person sessions with online components, allowing students to choose learning modes that fit their schedules and physical needs. Fully online courses maximize flexibility by enabling learners to access materials anytime and anywhere, supporting diverse time zones and personal commitments. Both formats incorporate assistive technologies and adaptive tools to accommodate students with disabilities, ensuring inclusivity in course delivery.
Technology Requirements for Effective Learning
Hybrid course design demands robust technology infrastructure, including reliable internet access, LMS platforms with synchronous and asynchronous capabilities, and multimedia tools to facilitate both in-person and online engagement. Fully online courses require advanced virtual classroom software, cloud storage solutions, and compatibility with diverse devices to support seamless distance learning. Effective learning hinges on integrating interactive technologies such as video conferencing, real-time assessments, and adaptive learning systems tailored to the specific delivery mode.
Instructor Roles in Hybrid and Online Environments
In hybrid course design, instructors balance face-to-face interaction with online facilitation, requiring adaptability in managing both synchronous and asynchronous activities. Fully online courses demand instructors to excel in digital communication, provide timely feedback, and create engaging virtual learning experiences to maintain student motivation. The instructor's role shifts from content delivery to mentorship and technical support, emphasizing the need for proficiency in learning management systems and multimedia tools.
Practical Skills Development: Hands-On vs Virtual Labs
Hybrid course design integrates in-person hands-on labs that enhance practical skills through direct manipulation of tools and real-time feedback. Fully online courses rely on virtual labs and simulations, providing flexible access but often limiting tactile experience and immediate instructor guidance. Research shows hybrid models improve skill retention by 25% compared to purely virtual environments due to increased learner engagement and authenticity of practice.
Assessment Strategies in Hybrid and Online Courses
Assessment strategies in hybrid and fully online courses must address diverse learner interactions and technological constraints while maintaining academic integrity. Hybrid course assessments often combine in-person exams with online quizzes and projects, enabling real-time feedback alongside flexible digital submissions. Fully online courses rely heavily on automated grading, proctored exams, and interactive assignments to ensure valid evaluation of student performance across virtual platforms.
Student Feedback and Learning Outcomes
Student feedback consistently highlights increased engagement and satisfaction in hybrid course designs compared to fully online courses, citing real-time interaction and hands-on activities. Learning outcomes in hybrid courses often surpass those of fully online formats, demonstrated by higher retention rates and improved critical thinking skills. Data from multiple studies indicate that blending synchronous and asynchronous elements optimizes comprehension and application of complex technical concepts.
Best Practices for Course Design in Technical Education
Hybrid course design in technical education integrates hands-on practice with online theoretical content, enhancing skill acquisition and knowledge retention. Fully online courses offer flexibility and accessibility but require robust multimedia resources and interactive platforms to simulate practical experiences effectively. Best practices include aligning learning objectives with appropriate delivery methods, incorporating real-time feedback, and utilizing industry-standard tools to mirror workplace environments.
Hybrid Course Design vs Fully Online Course Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com