AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting and detailed architectural plans, making it ideal for creating precise floor layouts and technical schematics. SolidWorks offers powerful 3D modeling capabilities, enabling the design and simulation of complex mechanical components with parametric features. Selecting between them depends on project requirements, with AutoCAD favoring detailed drawings and SolidWorks emphasizing product design and engineering analysis.
Table of Comparison
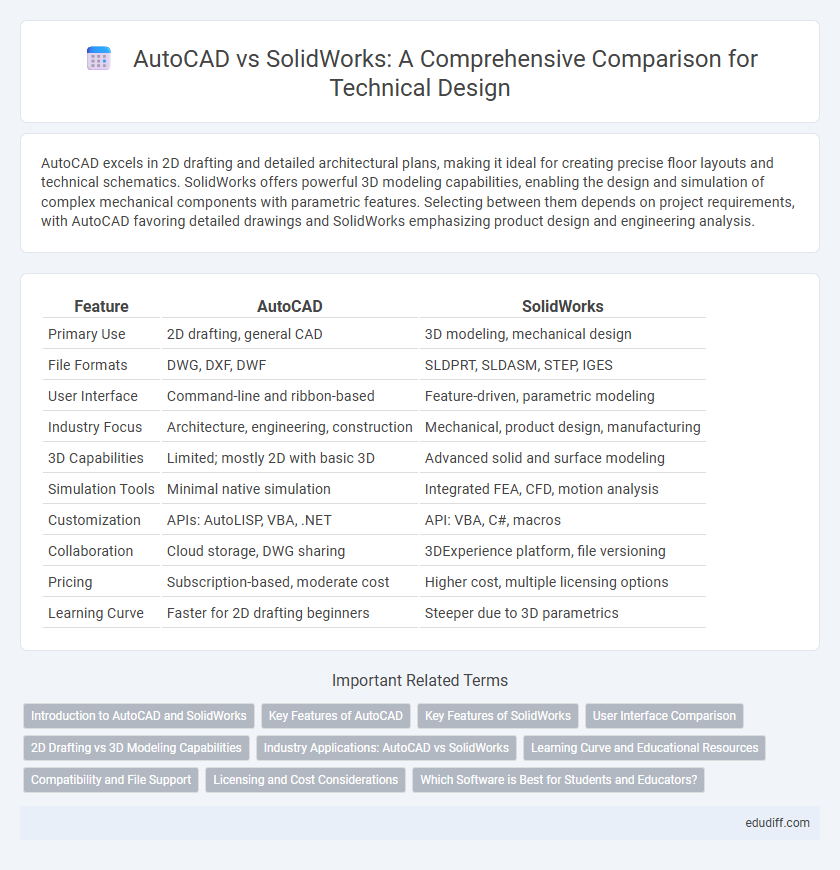
| Feature | AutoCAD | SolidWorks |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | 2D drafting, general CAD | 3D modeling, mechanical design |
| File Formats | DWG, DXF, DWF | SLDPRT, SLDASM, STEP, IGES |
| User Interface | Command-line and ribbon-based | Feature-driven, parametric modeling |
| Industry Focus | Architecture, engineering, construction | Mechanical, product design, manufacturing |
| 3D Capabilities | Limited; mostly 2D with basic 3D | Advanced solid and surface modeling |
| Simulation Tools | Minimal native simulation | Integrated FEA, CFD, motion analysis |
| Customization | APIs: AutoLISP, VBA, .NET | API: VBA, C#, macros |
| Collaboration | Cloud storage, DWG sharing | 3DExperience platform, file versioning |
| Pricing | Subscription-based, moderate cost | Higher cost, multiple licensing options |
| Learning Curve | Faster for 2D drafting beginners | Steeper due to 3D parametrics |
Introduction to AutoCAD and SolidWorks
AutoCAD is a versatile CAD software primarily used for 2D drafting and detailed architectural plans, known for its precision and wide industry adoption. SolidWorks specializes in 3D modeling and mechanical design, offering parametric features and simulation tools that streamline product development. Both platforms support extensive customization and integration, catering to distinct engineering and design workflows.
Key Features of AutoCAD
AutoCAD provides robust drafting tools optimized for 2D design, including precision drawing, annotation, and layering capabilities essential for architectural and engineering projects. Its versatile interface supports extensive customization through APIs and plugins, enabling automation and integration within diverse workflows. AutoCAD's compatibility with DWG files ensures seamless collaboration across multiple platforms and industries, enhancing productivity and project accuracy.
Key Features of SolidWorks
SolidWorks excels with its parametric design capabilities, enabling precise 3D modeling and efficient modification of components. It supports extensive simulation tools including stress analysis, thermal management, and motion studies to validate designs within the platform. Integrated features for assembly modeling and automated drawing generation streamline the product development workflow, distinguishing it in the CAD/CAM industry.
User Interface Comparison
AutoCAD's user interface emphasizes a command-line input combined with toolbars and ribbons, catering to precision drafting and 2D design workflows, while SolidWorks offers a feature-rich, parametric modeling interface optimized for 3D CAD with intuitive drag-and-drop components and real-time feedback. AutoCAD provides a customizable workspace supporting multiple drafting standards, whereas SolidWorks integrates design tree navigation and context-sensitive menus focused on part and assembly modeling efficiency. The contrast in UI design reflects AutoCAD's strength in detailed 2D drafting versus SolidWorks' robust capabilities in complex 3D mechanical design.
2D Drafting vs 3D Modeling Capabilities
AutoCAD excels in precise 2D drafting, offering industry-standard tools for architectural plans, mechanical drawings, and electrical schematics with robust annotation and layering features. SolidWorks specializes in advanced 3D modeling, providing parametric design, assembly simulation, and complex surface modeling essential for product development and engineering analysis. While AutoCAD is preferred for flat design documentation, SolidWorks delivers comprehensive solutions for 3D part and assembly creation with integrated CAD/CAM capabilities.
Industry Applications: AutoCAD vs SolidWorks
AutoCAD excels in architectural design, civil engineering, and 2D drafting due to its versatile drawing tools and broad compatibility with construction documentation workflows. SolidWorks specializes in mechanical engineering, product design, and complex 3D modeling with advanced simulation capabilities, making it ideal for manufacturing and prototyping. Both software platforms enhance industry-specific applications, but SolidWorks leads in parametric modeling for precision parts, while AutoCAD is preferred for detailed schematics and layout plans.
Learning Curve and Educational Resources
AutoCAD has a relatively straightforward learning curve with abundant online tutorials, official documentation, and academic courses tailored for beginners in 2D drafting and basic 3D modeling. SolidWorks presents a steeper learning curve due to its complex parametric modeling and simulation capabilities, but offers extensive educational resources such as certified training programs, community forums, and industry-specific webinars. Both platforms provide robust support through university partnerships and professional certifications that enhance skill acquisition and practical application in engineering and design fields.
Compatibility and File Support
AutoCAD supports a wide range of file formats including DWG, DXF, and DGN, ensuring seamless integration with various CAD software and platforms commonly used in architectural and engineering projects. SolidWorks primarily handles proprietary file types like SLDPRT, SLDASM, and SLDDRW, but also offers compatibility with neutral formats such as STEP, IGES, and STL for 3D modeling and manufacturing workflows. The choice between AutoCAD and SolidWorks depends heavily on project requirements for file interoperability and the specific CAD environment in which collaboration occurs.
Licensing and Cost Considerations
AutoCAD offers flexible subscription plans with monthly, annual, and multi-year options, making it suitable for various budget sizes, while SolidWorks typically requires a higher initial investment with perpetual licenses plus annual maintenance fees. AutoCAD's cost efficiency appeals to individual professionals and smaller firms, whereas SolidWorks targets larger enterprises needing advanced 3D modeling capabilities and extended technical support. Businesses must weigh AutoCAD's scalable pricing against SolidWorks' comprehensive feature set when considering long-term licensing expenses.
Which Software is Best for Students and Educators?
AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting and architectural design, making it ideal for students and educators focused on civil engineering and construction fields. SolidWorks offers powerful 3D modeling and simulation tools, better suited for mechanical engineering and product design education. Licensing options and educational support from both Autodesk and Dassault Systemes provide affordable access, but SolidWorks tends to offer more comprehensive features for advanced engineering curricula.
AutoCAD vs SolidWorks Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com