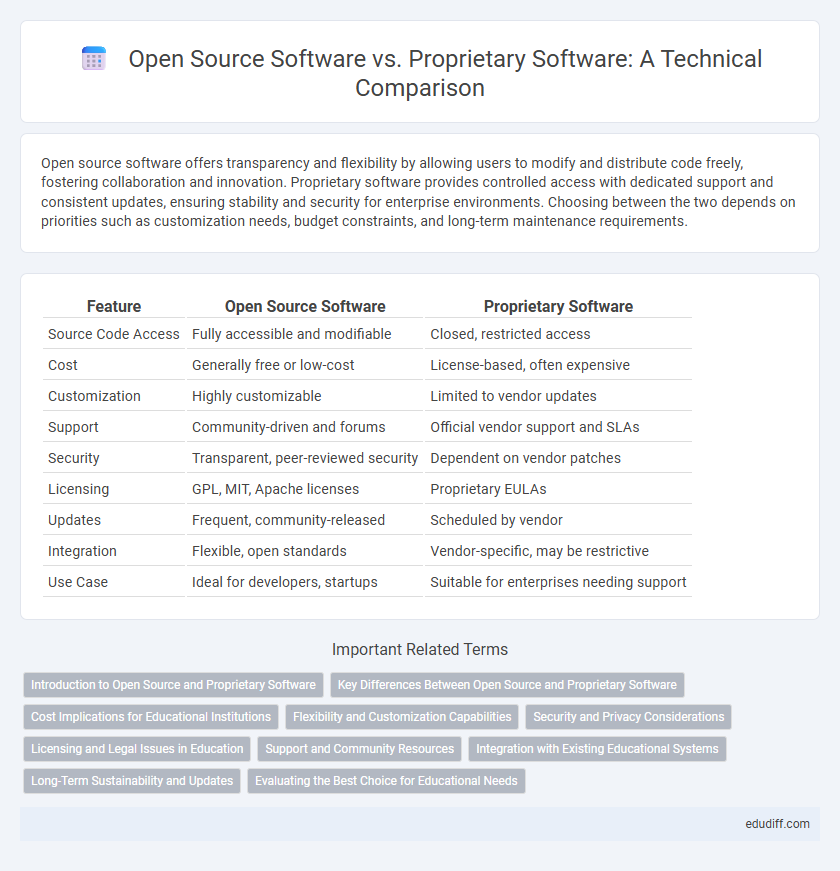
Open source software offers transparency and flexibility by allowing users to modify and distribute code freely, fostering collaboration and innovation. Proprietary software provides controlled access with dedicated support and consistent updates, ensuring stability and security for enterprise environments. Choosing between the two depends on priorities such as customization needs, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open Source Software | Proprietary Software |
|---|---|---|
| Source Code Access | Fully accessible and modifiable | Closed, restricted access |
| Cost | Generally free or low-cost | License-based, often expensive |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited to vendor updates |
| Support | Community-driven and forums | Official vendor support and SLAs |
| Security | Transparent, peer-reviewed security | Dependent on vendor patches |
| Licensing | GPL, MIT, Apache licenses | Proprietary EULAs |
| Updates | Frequent, community-released | Scheduled by vendor |
| Integration | Flexible, open standards | Vendor-specific, may be restrictive |
| Use Case | Ideal for developers, startups | Suitable for enterprises needing support |
Introduction to Open Source and Proprietary Software
Open Source Software (OSS) allows users to access, modify, and distribute the source code freely, fostering collaboration and innovation in software development. Proprietary Software restricts access to its source code, maintaining exclusive control by the developer or company to protect intellectual property and ensure revenue generation. Choosing between OSS and proprietary solutions depends on factors such as customization needs, budget constraints, security requirements, and licensing preferences.
Key Differences Between Open Source and Proprietary Software
Open source software offers transparent access to its source code, enabling users to modify, distribute, and collaborate freely, which fosters innovation and customization at lower costs. Proprietary software restricts access to its source code, enforcing licensing agreements that limit user modifications and distribution, often providing dedicated support and guaranteed stability. The key differences center on accessibility, flexibility, cost structure, and control, influencing user choice based on business needs and development preferences.
Cost Implications for Educational Institutions
Open source software offers significant cost savings for educational institutions by eliminating licensing fees and enabling free distribution and modification. Proprietary software often requires costly licenses, maintenance, and upgrade fees, which strain educational budgets. Institutions leveraging open source solutions benefit from customizable tools while reallocating funds towards hardware, training, and support services.
Flexibility and Customization Capabilities
Open source software offers superior flexibility and customization capabilities by providing access to source code, allowing developers to modify and adapt the software to specific needs. Proprietary software typically restricts access to source code, limiting user ability to tailor features or integrate with other systems. This distinction significantly impacts organizations requiring agile and customizable technology solutions.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Open Source Software (OSS) enables transparent code inspection, allowing developers and security experts to identify and patch vulnerabilities rapidly, enhancing overall security. Proprietary Software relies on closed-source code, limiting external audits and potentially delaying the discovery of security flaws or privacy breaches. Privacy considerations favor OSS as users can verify data handling practices, whereas proprietary solutions often operate under opaque data policies that may compromise user privacy.
Licensing and Legal Issues in Education
Open source software in education offers flexible licensing that allows users to modify, distribute, and use the software without paying royalties, fostering innovation and collaboration. Proprietary software licenses restrict usage, modification, and redistribution, often requiring costly fees and strict compliance with end-user license agreements (EULAs). Legal challenges in education arise from proprietary licensing limitations, such as limited user access and audit risks, while open source licensing demands careful attention to copyleft provisions and intellectual property rights.
Support and Community Resources
Open Source Software benefits from extensive community-driven support, including forums, documentation, and user-contributed code that rapidly address issues and enhance functionality. Proprietary Software typically offers dedicated customer service teams and official technical support packages, ensuring accountability and structured problem resolution. Users must weigh the collaborative innovation of open source communities against the guaranteed reliability and personalized assistance provided by proprietary vendors.
Integration with Existing Educational Systems
Open source software offers customizable integration with existing educational systems through accessible APIs and community-driven plugins, enabling seamless data exchange and interoperability. Proprietary software often provides specialized integration tools but can be limited by vendor lock-in and restricted access to underlying code, potentially complicating customization and compatibility. Evaluating the balance between flexibility and vendor support is critical when aligning software solutions with educational infrastructure requirements.
Long-Term Sustainability and Updates
Open source software offers long-term sustainability due to community-driven development and continuous updates from a diverse contributor base, reducing dependency on a single vendor. Proprietary software relies on dedicated company support for updates and sustainability, potentially facing obsolescence if the vendor discontinues the product or changes strategic priorities. Open source solutions enable greater adaptability and extended lifecycle management, essential for evolving technical environments.
Evaluating the Best Choice for Educational Needs
Open source software offers customizable and cost-effective solutions ideal for educational institutions aiming to enhance learning through adaptable tools and collaborative development. Proprietary software delivers robust support, specialized features, and stability, which can benefit schools requiring reliable performance and dedicated vendor assistance. Evaluating software choices involves assessing budget constraints, technical expertise, curriculum requirements, and long-term sustainability to ensure alignment with educational goals.
Open Source Software vs Proprietary Software Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com