Linux training emphasizes command-line proficiency, system architecture, and open-source environments, making it essential for users aiming to manage servers and development platforms. Windows training centers on graphical user interface navigation, system administration, and integration with Microsoft software, which is crucial for managing enterprise desktops and applications. Mastery in either platform depends on specific career goals, with Linux favored for cloud and development roles, while Windows remains dominant in corporate IT infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
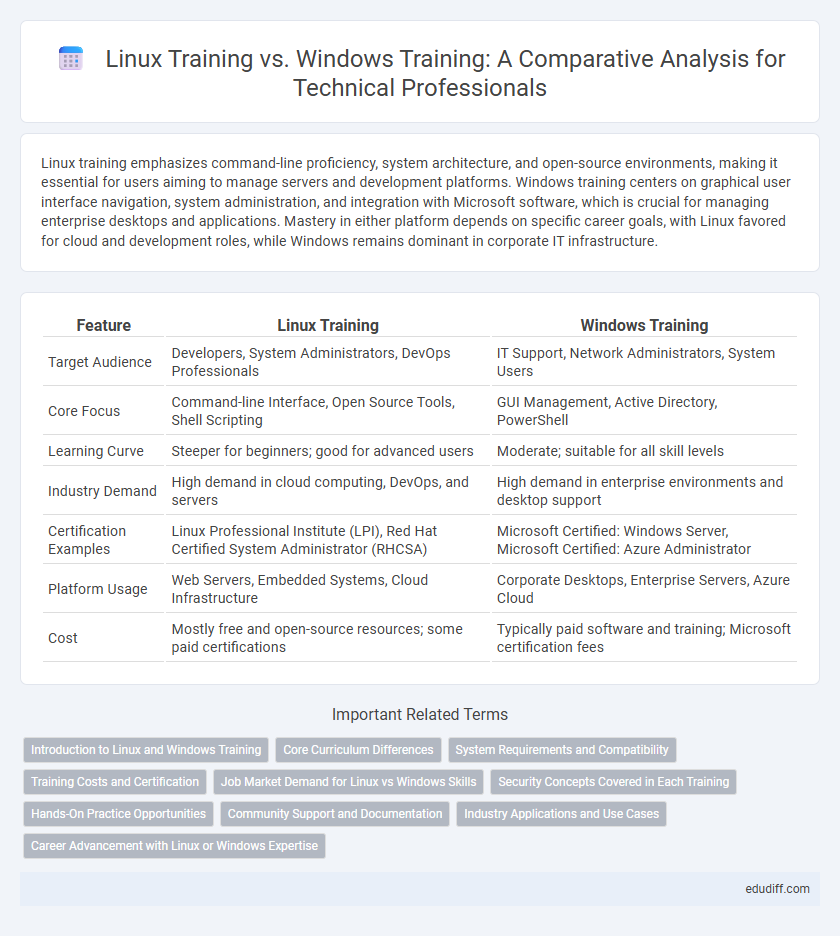
| Feature | Linux Training | Windows Training |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Developers, System Administrators, DevOps Professionals | IT Support, Network Administrators, System Users |
| Core Focus | Command-line Interface, Open Source Tools, Shell Scripting | GUI Management, Active Directory, PowerShell |
| Learning Curve | Steeper for beginners; good for advanced users | Moderate; suitable for all skill levels |
| Industry Demand | High demand in cloud computing, DevOps, and servers | High demand in enterprise environments and desktop support |
| Certification Examples | Linux Professional Institute (LPI), Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA) | Microsoft Certified: Windows Server, Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator |
| Platform Usage | Web Servers, Embedded Systems, Cloud Infrastructure | Corporate Desktops, Enterprise Servers, Azure Cloud |
| Cost | Mostly free and open-source resources; some paid certifications | Typically paid software and training; Microsoft certification fees |
Introduction to Linux and Windows Training
Linux training emphasizes open-source system mastery, focusing on command-line proficiency, shell scripting, and kernel understanding, which are critical for server management and development environments. Windows training concentrates on graphical user interface navigation, PowerShell scripting, and system administration within a Microsoft ecosystem, essential for enterprise and desktop management. Both trainings offer foundational knowledge but cater to different technical roles and industry requirements.
Core Curriculum Differences
Linux training emphasizes command-line proficiency, kernel architecture, and open-source system administration, while Windows training focuses on GUI management, Active Directory, and PowerShell scripting. The Linux core curriculum covers file system hierarchy, shell scripting, and package management using tools like apt or yum, contrasting with Windows' emphasis on registry editing, Group Policy, and Microsoft-specific automation. Understanding these core differences helps tailor IT training programs to specialized environments, optimizing workforce skill sets for respective operating system ecosystems.
System Requirements and Compatibility
Linux training requires familiarity with diverse distributions like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Fedora, each with specific system requirements typically lower than Windows. Windows training centers on mastering compatibility with versions such as Windows 10 or 11, demanding higher system specifications and regular updates. Understanding these differences ensures optimized resource allocation and effective skill development across operating system environments.
Training Costs and Certification
Linux training often has lower costs due to the abundance of free and open-source resources, whereas Windows training typically involves higher expenses linked to proprietary software licenses. Certification for Linux, such as the CompTIA Linux+ or Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE), tends to be more affordable compared to Windows certifications like Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate. Companies frequently choose Linux training for budget-conscious teams seeking valuable industry certifications without significant financial outlay.
Job Market Demand for Linux vs Windows Skills
Linux training is increasingly sought after in the job market due to the widespread adoption of Linux in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and server management roles. Windows training remains crucial for enterprises relying on Microsoft ecosystems, particularly in desktop support and enterprise software administration. Employers often prioritize Linux skills for DevOps, system administration, and open-source project roles, while Windows expertise dominates in corporate IT environments and helpdesk positions.
Security Concepts Covered in Each Training
Linux training emphasizes security concepts such as file permissions, SELinux policies, firewall configuration using iptables and nftables, and secure shell (SSH) management. Windows training covers security topics like Active Directory management, Group Policy configuration, Windows Defender, and Windows Firewall settings. Both trainings address user authentication, encryption methods, and system hardening tailored to their respective operating systems.
Hands-On Practice Opportunities
Linux training offers extensive hands-on practice with command-line interface and shell scripting, enabling learners to manage system processes, file permissions, and network configurations effectively. Windows training emphasizes practical skills in graphical user interface management, PowerShell scripting, and Active Directory administration, which are critical for enterprise environments. Both platforms provide virtual labs and real-world scenarios, but Linux training often includes more opportunities for open-source tool integration and kernel-level customization.
Community Support and Documentation
Linux training benefits from extensive community support through forums like Stack Exchange and kernel.org, offering vast, continuously updated documentation and open-source resources. Windows training relies on Microsoft's official documentation and TechNet, supplemented by a large user base and professional support networks, ensuring structured guidance and frequent updates. Both platforms provide robust documentation, but Linux's community-driven approach often leads to faster problem resolution and more diverse learning materials.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Linux training excels in industries like cloud computing, cybersecurity, and DevOps, where open-source flexibility and server management are critical, while Windows training is dominant in enterprise environments relying on Microsoft software, desktop applications, and Active Directory administration. Linux skills are essential for managing web servers, containers, and network infrastructure, facilitating automation and scripting with Bash and Python. Windows expertise supports desktop support, enterprise software deployment, and IT administration, particularly in organizations using Microsoft Azure and Office 365 ecosystems.
Career Advancement with Linux or Windows Expertise
Linux training enhances career advancement by equipping professionals with skills in open-source environments, system administration, and cloud infrastructure, aligning with industry trends in DevOps and cybersecurity. Windows training develops expertise in enterprise environments, Active Directory management, and Microsoft ecosystem integration, vital for roles in corporate IT, support, and network management. Mastery of either Linux or Windows can significantly boost job prospects, but Linux skills often command higher demand in emerging technology sectors and cloud-based roles.
Linux Training vs Windows Training Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com