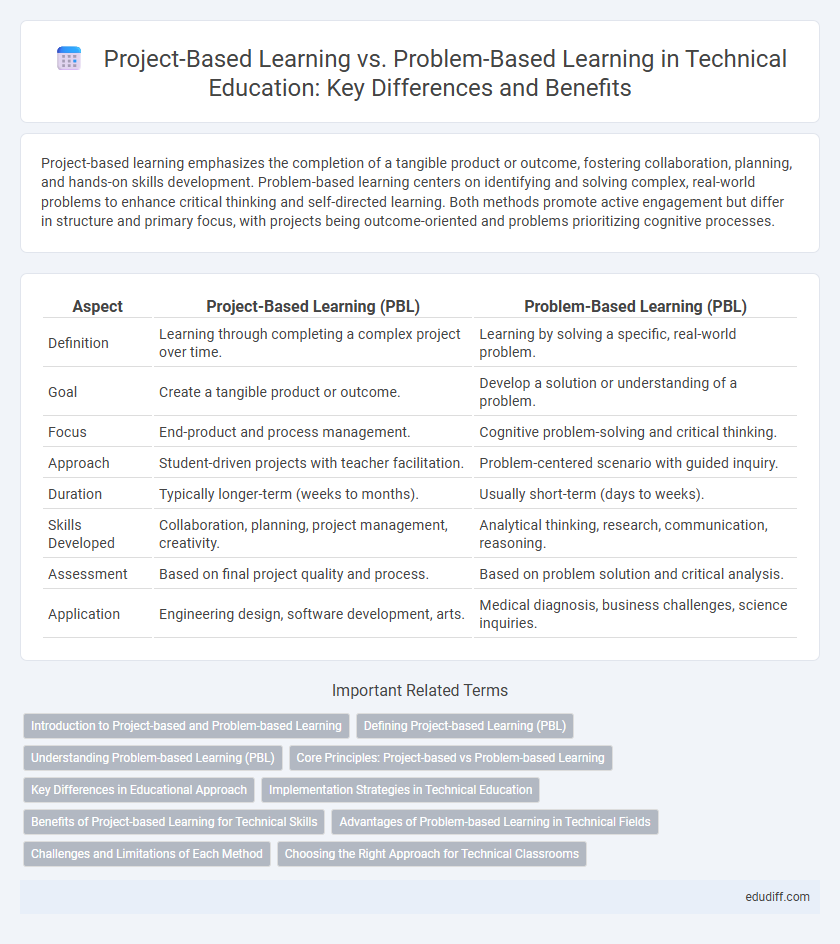
Project-based learning emphasizes the completion of a tangible product or outcome, fostering collaboration, planning, and hands-on skills development. Problem-based learning centers on identifying and solving complex, real-world problems to enhance critical thinking and self-directed learning. Both methods promote active engagement but differ in structure and primary focus, with projects being outcome-oriented and problems prioritizing cognitive processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Problem-Based Learning (PBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through completing a complex project over time. | Learning by solving a specific, real-world problem. |
| Goal | Create a tangible product or outcome. | Develop a solution or understanding of a problem. |
| Focus | End-product and process management. | Cognitive problem-solving and critical thinking. |
| Approach | Student-driven projects with teacher facilitation. | Problem-centered scenario with guided inquiry. |
| Duration | Typically longer-term (weeks to months). | Usually short-term (days to weeks). |
| Skills Developed | Collaboration, planning, project management, creativity. | Analytical thinking, research, communication, reasoning. |
| Assessment | Based on final project quality and process. | Based on problem solution and critical analysis. |
| Application | Engineering design, software development, arts. | Medical diagnosis, business challenges, science inquiries. |
Introduction to Project-based and Problem-based Learning
Project-based learning (PBL) engages students in designing, planning, and executing a project that results in a tangible product or outcome, fostering skills in research, collaboration, and time management. Problem-based learning (PBL) centers on solving a complex, real-world problem by applying critical thinking and domain knowledge, emphasizing inquiry and self-directed learning. Both approaches enhance active learning, but project-based learning typically emphasizes product development, while problem-based learning focuses on mastering problem-solving processes.
Defining Project-based Learning (PBL)
Project-based learning (PBL) is an instructional methodology emphasizing student engagement through the completion of complex, extended projects that integrate real-world challenges and interdisciplinary knowledge. PBL requires learners to apply critical thinking, collaboration, and research skills to develop tangible outcomes or presentations, fostering deeper understanding and retention of subject matter. This approach contrasts with traditional instruction by prioritizing active exploration and creation over passive absorption of information.
Understanding Problem-based Learning (PBL)
Problem-based learning (PBL) centers on students tackling complex, real-world problems without predefined solutions, fostering critical thinking and collaborative skills. This approach encourages self-directed learning by requiring learners to identify knowledge gaps, research, and apply interdisciplinary concepts effectively. PBL enhances deep comprehension and practical application, contrasting with project-based learning's emphasis on creating tangible end-products.
Core Principles: Project-based vs Problem-based Learning
Project-based learning centers on developing a final product through extended inquiry, emphasizing collaboration and real-world application. Problem-based learning prioritizes solving a specific, often open-ended problem, fostering critical thinking and self-directed research. Both methods integrate active learning but differ in scope: projects yield tangible outcomes, while problems focus on analytical processes.
Key Differences in Educational Approach
Project-based learning centers on students completing comprehensive projects that integrate multiple skills over a longer period, fostering collaboration and real-world application. Problem-based learning emphasizes identifying and solving specific problems, promoting critical thinking and self-directed learning through focused inquiry. The key difference lies in scope and structure: project-based learning adopts a broader, outcome-oriented approach while problem-based learning focuses narrowly on developing problem-solving abilities within defined scenarios.
Implementation Strategies in Technical Education
Project-based learning (PBL) in technical education emphasizes designing and developing tangible outputs, requiring structured timelines and resource management to simulate real-world engineering or IT projects. Problem-based learning (PBL) focuses on critical thinking and knowledge application through complex, open-ended technical challenges, fostering collaborative problem-solving and adaptive learning environments. Effective implementation involves integrating industry-relevant tools, continuous assessment, and scaffolding that aligns with students' technical skill levels and learning outcomes.
Benefits of Project-based Learning for Technical Skills
Project-based learning enhances technical skills by providing hands-on experience with real-world tools and technologies, fostering practical problem-solving and innovation. It encourages collaboration, critical thinking, and the application of theoretical knowledge in designing, developing, and implementing technical projects. This approach builds proficiency in project management, coding, engineering design, and other industry-specific competencies crucial for technical career readiness.
Advantages of Problem-based Learning in Technical Fields
Problem-based learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and complex problem-solving skills essential in technical fields by simulating real-world challenges. It fosters collaborative teamwork and communication among learners, mirroring professional engineering and IT environments. PBL also promotes self-directed research and adaptability, preparing students to quickly integrate emerging technologies and methodologies.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Project-based learning often faces challenges such as time-intensive planning and resource allocation, which can limit scalability in large classrooms. Problem-based learning struggles with the risk of insufficient foundational knowledge among students, potentially hindering problem-solving effectiveness. Both methods require skilled facilitators to balance guidance and student autonomy, making implementation complex in diverse educational settings.
Choosing the Right Approach for Technical Classrooms
Project-based learning emphasizes hands-on creation of tangible products over an extended timeline, promoting deep understanding through real-world applications. Problem-based learning centers on diagnosing and solving specific technical challenges, enhancing critical thinking and adaptive skills within shorter, focused activities. Selecting the right approach depends on curriculum goals, skill development priorities, and available resources in technical classrooms.
Project-based learning vs Problem-based learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com