Competency-based education prioritizes mastering specific skills and knowledge at an individual pace, ensuring learners achieve proficiency before progressing. Seat-time education relies on fixed schedules and credit hours, measuring progress by time spent rather than skill acquisition. This shift enhances personalization, improves learner outcomes, and better aligns educational goals with industry requirements.
Table of Comparison
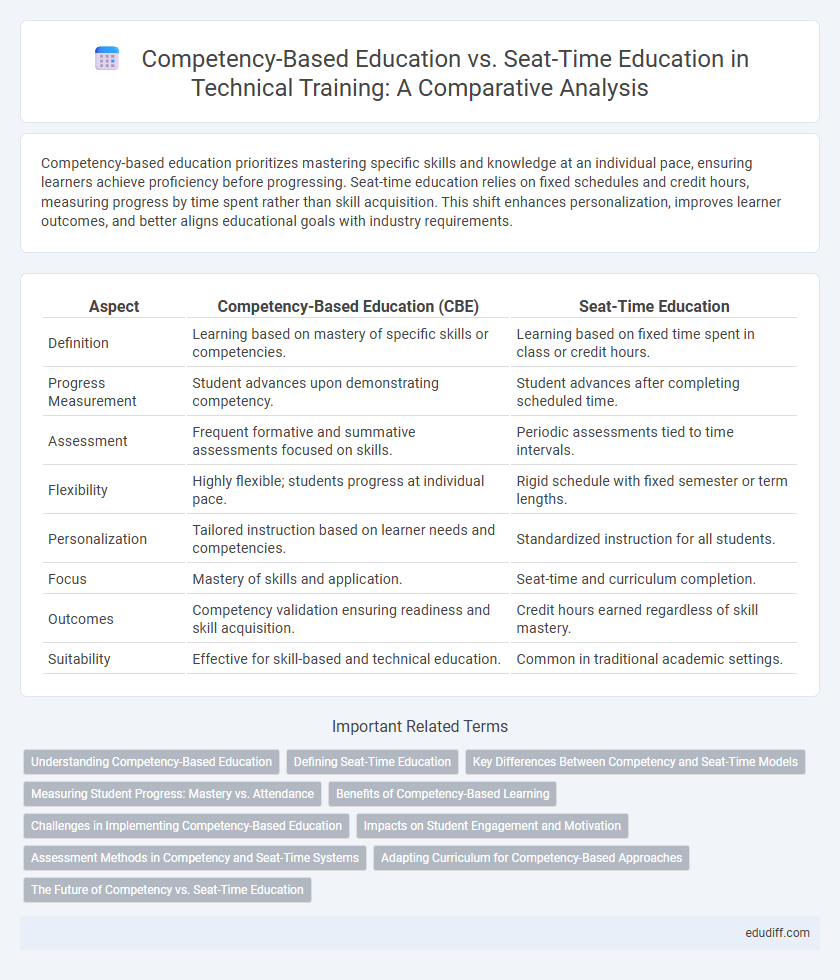
| Aspect | Competency-Based Education (CBE) | Seat-Time Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning based on mastery of specific skills or competencies. | Learning based on fixed time spent in class or credit hours. |
| Progress Measurement | Student advances upon demonstrating competency. | Student advances after completing scheduled time. |
| Assessment | Frequent formative and summative assessments focused on skills. | Periodic assessments tied to time intervals. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; students progress at individual pace. | Rigid schedule with fixed semester or term lengths. |
| Personalization | Tailored instruction based on learner needs and competencies. | Standardized instruction for all students. |
| Focus | Mastery of skills and application. | Seat-time and curriculum completion. |
| Outcomes | Competency validation ensuring readiness and skill acquisition. | Credit hours earned regardless of skill mastery. |
| Suitability | Effective for skill-based and technical education. | Common in traditional academic settings. |
Understanding Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) centers on mastering specific skills and knowledge at an individualized pace, contrasting with Seat-Time Education that requires fixed instructional hours. CBE emphasizes measurable outcomes and real-world application, enabling learners to progress upon demonstrating proficiency rather than accumulating classroom time. This model fosters personalized learning pathways, efficiency in skill acquisition, and alignment with industry standards.
Defining Seat-Time Education
Seat-time education is a traditional instructional model where student progress is measured by the amount of time spent in a classroom rather than mastery of skills or knowledge. This system emphasizes fixed schedules and uniform learning periods, often leading to a one-size-fits-all approach regardless of individual student performance. Critics argue that seat-time education does not account for varying learning speeds, potentially hindering personalized education and mastery-based outcomes.
Key Differences Between Competency and Seat-Time Models
Competency-Based Education (CBE) prioritizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing students to progress at their own pace, whereas Seat-Time Education relies on fixed instructional hours irrespective of individual learning outcomes. In CBE, assessments are formative and performance-based, directly measuring a student's ability to apply competencies, while Seat-Time models use summative assessments primarily focused on time spent in class. This fundamental distinction impacts curriculum design, with CBE emphasizing personalized learning paths and Seat-Time adhering to standardized schedules and benchmarks.
Measuring Student Progress: Mastery vs. Attendance
Competency-Based Education measures student progress through demonstrated mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to advance once they have proven their understanding. Seat-Time Education relies on fixed instructional hours, tracking attendance rather than actual learning outcomes, which can limit personalized pacing. This mastery-centered approach in Competency-Based Education supports deeper learning and flexible progression, contrasting with the time-bound structure of traditional models.
Benefits of Competency-Based Learning
Competency-Based Learning offers personalized pacing that adapts to individual student mastery, ensuring deep understanding before progression. This approach enhances skill retention and real-world application by emphasizing practical competencies over fixed schedules. Education systems implementing Competency-Based models report higher student engagement and improved outcomes compared to traditional seat-time methodologies.
Challenges in Implementing Competency-Based Education
Implementing Competency-Based Education (CBE) faces significant challenges such as the need for robust assessment systems that accurately measure individual mastery, requiring advanced data analytics and personalized learning technologies. Institutions must navigate the complexity of redesigning curricula to align with competencies rather than fixed seat-time requirements, often demanding substantial faculty training and resource allocation. Furthermore, variability in regulatory policies and accreditation standards complicates the scalability of CBE models across different educational jurisdictions.
Impacts on Student Engagement and Motivation
Competency-Based Education (CBE) enhances student engagement and motivation by allowing learners to progress upon mastery of skills, fostering personalized pacing and deeper understanding. In contrast, Seat-Time Education often limits motivation as students advance based on fixed schedules regardless of individual readiness, potentially causing disengagement. Studies indicate that CBE's focus on demonstrated competencies cultivates intrinsic motivation and active participation, leading to improved academic outcomes.
Assessment Methods in Competency and Seat-Time Systems
Competency-based education relies on performance-based assessments that evaluate students' mastery of specific skills and knowledge through practical demonstrations, portfolios, and real-world tasks. In contrast, seat-time education typically employs standardized testing and timed exams designed to measure students' retention of information within a fixed instructional period. The emphasis on formative assessments in competency-based systems fosters personalized learning progress, while seat-time models prioritize summative assessments aligned with curriculum pacing.
Adapting Curriculum for Competency-Based Approaches
Adapting curriculum for competency-based education requires redesigning learning outcomes to prioritize mastery of specific skills and knowledge rather than time spent in class. This approach utilizes personalized learning pathways and formative assessments to ensure each learner achieves defined competencies before progressing. Emphasizing real-world applications and continuous feedback enhances student engagement and prepares learners for dynamic professional environments.
The Future of Competency vs. Seat-Time Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) emphasizes mastery of skills and knowledge, enabling personalized learning pathways that adapt to student needs, contrasting with traditional seat-time education which measures progress by fixed classroom hours. Innovations in digital assessment tools and adaptive learning platforms are accelerating the shift towards competency metrics, promising greater flexibility and efficiency in credentialing. The future of education hinges on scalable CBE models that integrate real-time data analytics to validate competencies, fostering workforce-ready graduates aligned with industry standards.
Competency-Based Education vs Seat-Time Education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com