Synchronous instruction requires learners to participate in real-time interactions, enabling immediate feedback and dynamic discussions that enhance engagement and comprehension. Asynchronous instruction allows learners to access materials and complete tasks on their own schedule, offering flexibility and the opportunity for self-paced learning. Balancing synchronous and asynchronous methods optimizes instructional effectiveness by addressing diverse learner needs and promoting active knowledge retention.
Table of Comparison
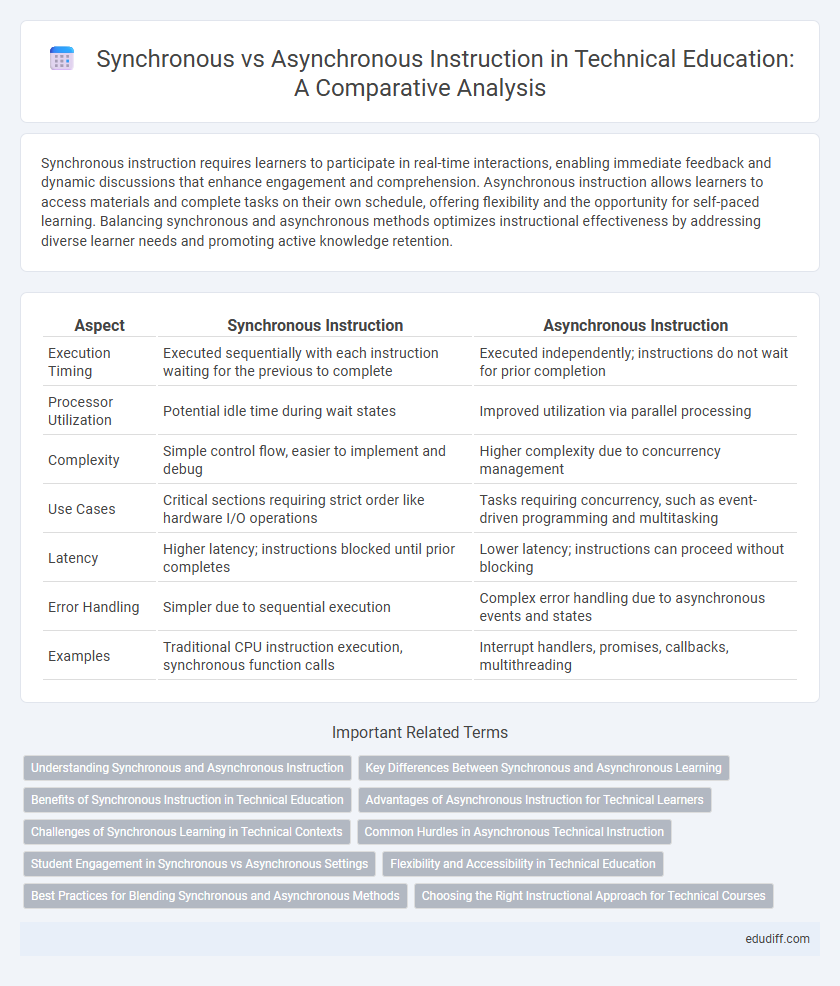
| Aspect | Synchronous Instruction | Asynchronous Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Timing | Executed sequentially with each instruction waiting for the previous to complete | Executed independently; instructions do not wait for prior completion |
| Processor Utilization | Potential idle time during wait states | Improved utilization via parallel processing |
| Complexity | Simple control flow, easier to implement and debug | Higher complexity due to concurrency management |
| Use Cases | Critical sections requiring strict order like hardware I/O operations | Tasks requiring concurrency, such as event-driven programming and multitasking |
| Latency | Higher latency; instructions blocked until prior completes | Lower latency; instructions can proceed without blocking |
| Error Handling | Simpler due to sequential execution | Complex error handling due to asynchronous events and states |
| Examples | Traditional CPU instruction execution, synchronous function calls | Interrupt handlers, promises, callbacks, multithreading |
Understanding Synchronous and Asynchronous Instruction
Synchronous instruction requires all participants to engage in learning simultaneously, enabling real-time interaction and immediate feedback, which enhances comprehension and collaboration. Asynchronous instruction allows learners to access materials and complete tasks at their own pace, providing flexibility but potentially delaying communication and support. Understanding the trade-offs between synchronous and asynchronous methods is crucial for designing effective technical training programs that balance interactivity and accessibility.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous learning requires participants to engage in real-time interaction, utilizing live lectures or video conferences to facilitate immediate feedback and collaboration. In contrast, asynchronous learning allows learners to access materials and complete assignments at their own pace, leveraging recorded videos, discussion boards, and digital resources for flexible study schedules. Key differences include timing of participation, communication style, and the level of immediate interaction, impacting learner engagement and adaptability in educational environments.
Benefits of Synchronous Instruction in Technical Education
Synchronous instruction in technical education promotes real-time interaction between instructors and students, enhancing immediate feedback and clarifications crucial for complex concepts. It fosters collaborative learning environments where peer discussions and problem-solving activities improve practical skills and knowledge retention. This format ensures structured pacing and discipline, which helps students stay engaged and progress consistently through technically demanding curricula.
Advantages of Asynchronous Instruction for Technical Learners
Asynchronous instruction offers technical learners the advantage of flexible scheduling, enabling them to access complex coding tutorials, software simulations, and technical resources at their own pace without time constraints. This flexibility supports deep understanding by allowing repeated review of challenging concepts such as algorithm design and network protocols, enhancing retention and skill mastery. Furthermore, asynchronous formats facilitate personalized learning paths, accommodating diverse technical backgrounds and promoting independent problem-solving critical in fields like software development and IT.
Challenges of Synchronous Learning in Technical Contexts
Synchronous instruction in technical contexts poses challenges such as limited flexibility for diverse learner schedules and varying time zones, often hindering real-time collaboration and immediate feedback. Technical issues like unstable internet connections disrupt the flow of live sessions, reducing engagement and comprehension. Furthermore, synchronous learning can strain instructors' ability to manage diverse skill levels simultaneously, impacting the pace and effectiveness of technical training.
Common Hurdles in Asynchronous Technical Instruction
Common hurdles in asynchronous technical instruction include limited real-time interaction, which can delay clarification of complex concepts and reduce immediate feedback efficacy. Learners often face challenges in maintaining motivation and self-discipline without scheduled sessions, leading to inconsistent progress. Technical issues such as platform compatibility and lack of hands-on guidance further impede the effective delivery and comprehension of asynchronous content.
Student Engagement in Synchronous vs Asynchronous Settings
Student engagement in synchronous instruction benefits from real-time interaction, immediate feedback, and collaborative activities, enhancing motivation and participation. Asynchronous instruction allows flexibility in timing and pacing, supporting self-directed learning but may result in lower immediate engagement due to delayed responses. Effective engagement strategies in both settings include interactive content, discussion forums, and regular instructor presence to foster connection and accountability.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Technical Education
Synchronous instruction offers real-time interaction, fostering immediate feedback and collaboration essential for complex technical concepts. Asynchronous instruction enhances flexibility, allowing learners to access materials anytime, which accommodates diverse schedules and learning paces in technical education. Combining both methods maximizes accessibility, ensuring students can engage with content in a way that best suits their individual needs and technology constraints.
Best Practices for Blending Synchronous and Asynchronous Methods
Blending synchronous and asynchronous instruction leverages the real-time engagement of live sessions with the flexibility of self-paced learning, optimizing student interaction and content absorption. Best practices include scheduling synchronous sessions for complex discussions or collaborative activities, while allocating asynchronous components for foundational knowledge acquisition and reflection. Integrating clear communication, balanced workload distribution, and technology platforms that support seamless transitions enhances overall learning effectiveness and accessibility.
Choosing the Right Instructional Approach for Technical Courses
Synchronous instruction enables real-time interaction and immediate feedback, making it ideal for complex technical concepts requiring clear guidance and hands-on demonstrations. Asynchronous instruction offers flexibility, allowing learners to progress at their own pace and revisit intricate materials such as coding exercises or system simulations. Selecting the right approach depends on course objectives, learner needs, and resource availability to maximize engagement and knowledge retention in technical education.
Synchronous Instruction vs Asynchronous Instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com