Academic advising provides structured guidance from faculty or professional advisors to help undergraduate students navigate course selection, degree requirements, and career planning. Peer mentoring offers personalized support from fellow students who share similar experiences, fostering a sense of community and easing the transition into college life. Combining both resources enhances academic success and social integration for undergraduates.
Table of Comparison
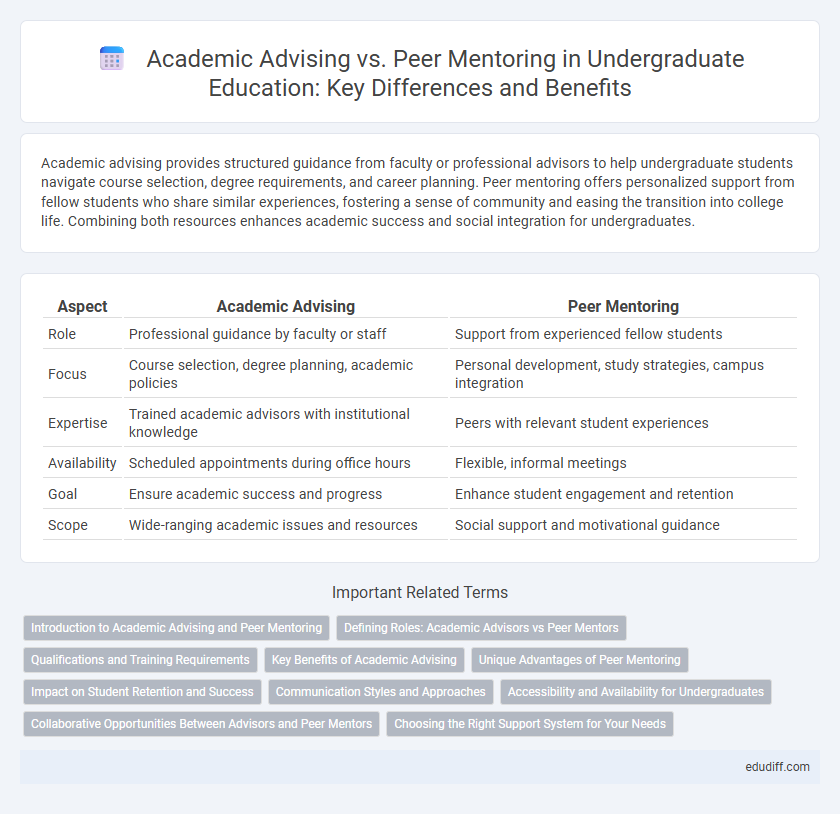
| Aspect | Academic Advising | Peer Mentoring |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Professional guidance by faculty or staff | Support from experienced fellow students |
| Focus | Course selection, degree planning, academic policies | Personal development, study strategies, campus integration |
| Expertise | Trained academic advisors with institutional knowledge | Peers with relevant student experiences |
| Availability | Scheduled appointments during office hours | Flexible, informal meetings |
| Goal | Ensure academic success and progress | Enhance student engagement and retention |
| Scope | Wide-ranging academic issues and resources | Social support and motivational guidance |
Introduction to Academic Advising and Peer Mentoring
Academic advising provides students with professional guidance on course selection, degree requirements, and career planning to enhance academic success. Peer mentoring offers a supportive environment where experienced students share insights, study strategies, and campus resources to help mentees navigate college life. Both services play a vital role in fostering student engagement and improving retention rates.
Defining Roles: Academic Advisors vs Peer Mentors
Academic advisors are university staff or faculty members who provide expert guidance on course selection, degree requirements, and academic policies to ensure students meet graduation criteria. Peer mentors, typically upper-level students, offer social support, share personal experiences, and help new undergraduates navigate campus resources and student life. The distinct roles emphasize formal academic planning for advisors and informal, experience-based support for peer mentors.
Qualifications and Training Requirements
Academic advising requires professional qualifications, typically a degree in education or counseling, along with specialized training in academic policies and student development. Peer mentoring involves trained students who receive guidance on communication skills, campus resources, and confidentiality practices but do not need formal credentials. Both roles complement each other by providing tailored support to undergraduates through distinct expertise and training levels.
Key Benefits of Academic Advising
Academic advising provides personalized guidance tailored to a student's academic goals, ensuring proper course selection and degree progression. It offers expert support from faculty or professional advisors with in-depth knowledge of program requirements and university policies. This individualized approach enhances academic success and timely graduation compared to peer mentoring, which primarily offers social support and general advice.
Unique Advantages of Peer Mentoring
Peer mentoring offers personalized guidance rooted in shared experiences, fostering a relatable and supportive learning environment that enhances academic growth. It encourages skill development in communication, leadership, and problem-solving through peer-to-peer interaction, which is less formal than academic advising. This approach often results in increased student engagement, confidence, and retention by promoting a sense of community and mutual understanding.
Impact on Student Retention and Success
Academic advising provides personalized guidance from faculty or professional advisors, directly influencing student retention by aligning course selections with degree requirements and career goals. Peer mentoring fosters a supportive community through shared experiences, enhancing student engagement and persistence by reducing feelings of isolation. Both strategies significantly contribute to academic success, but combining them can optimize retention rates and overall student achievement in undergraduate programs.
Communication Styles and Approaches
Academic advising typically employs a structured communication style centered on goal-setting, academic requirements, and institutional policies, fostering a formal advisor-advisee relationship. Peer mentoring emphasizes informal, empathetic dialogue that encourages shared experiences, personalized support, and collaborative problem-solving among undergraduate students. Both approaches utilize distinct conversational techniques that align with their unique roles in student development and academic success.
Accessibility and Availability for Undergraduates
Academic advising for undergraduates typically offers structured, scheduled sessions with trained professionals who provide personalized guidance on course selection and degree requirements. Peer mentoring, often facilitated by fellow students, enhances accessibility by providing informal support and availability outside traditional office hours, fostering a relatable and approachable environment. Both approaches complement each other by balancing expert advice with flexible, readily accessible peer support to address diverse student needs.
Collaborative Opportunities Between Advisors and Peer Mentors
Academic advising and peer mentoring create collaborative opportunities that enhance undergraduate student success by combining professional guidance with relatable peer experiences. Advisors provide expert academic planning and resource navigation, while peer mentors offer personalized support and firsthand insights into campus life. This synergy fosters a comprehensive support network, improving student engagement, retention, and overall academic performance.
Choosing the Right Support System for Your Needs
Academic advising provides professional guidance tailored to course selection, degree requirements, and career planning by trained advisors, ensuring alignment with institutional policies and academic success. Peer mentoring offers relatable support through experienced students who share firsthand knowledge about campus resources, study habits, and social integration, fostering a sense of community and personal growth. Choosing the right support system depends on individual needs for expert advice versus relatable peer experiences, with many benefiting from a combination of both for comprehensive academic and personal development.
Academic Advising vs Peer Mentoring Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com