CLEP exams offer college credit by testing knowledge in specific subjects, allowing students to bypass introductory courses, while AP credits are earned through high school Advanced Placement exams, often with a standardized scoring threshold for college credit. CLEP is flexible for adult learners or transfer students seeking credit for prior knowledge, whereas AP credits benefit high school students aiming to accelerate their undergraduate education. Both options reduce time and cost for degree completion by fulfilling general education or elective requirements.
Table of Comparison
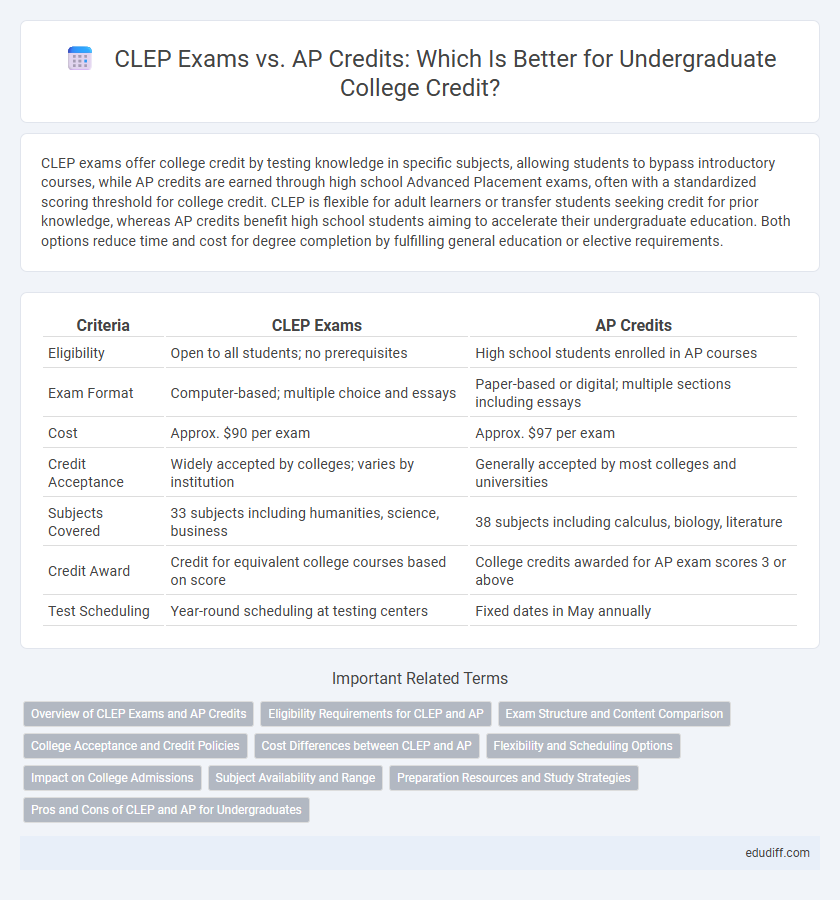
| Criteria | CLEP Exams | AP Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Open to all students; no prerequisites | High school students enrolled in AP courses |
| Exam Format | Computer-based; multiple choice and essays | Paper-based or digital; multiple sections including essays |
| Cost | Approx. $90 per exam | Approx. $97 per exam |
| Credit Acceptance | Widely accepted by colleges; varies by institution | Generally accepted by most colleges and universities |
| Subjects Covered | 33 subjects including humanities, science, business | 38 subjects including calculus, biology, literature |
| Credit Award | Credit for equivalent college courses based on score | College credits awarded for AP exam scores 3 or above |
| Test Scheduling | Year-round scheduling at testing centers | Fixed dates in May annually |
Overview of CLEP Exams and AP Credits
CLEP Exams allow undergraduate students to earn college credit by demonstrating mastery in specific subjects through standardized testing, covering over 30 courses in areas like math, science, and humanities. AP Credits are awarded based on high scores in Advanced Placement exams taken during high school, and colleges typically grant credit or advanced placement for scores of 3 or higher on a 5-point scale. Both CLEP and AP credits provide flexible pathways to accelerate degree completion and reduce tuition costs by bypassing introductory courses.
Eligibility Requirements for CLEP and AP
CLEP exams generally require candidates to be enrolled in or have access to a college or university, but there are no strict prerequisites, making them accessible to a wide range of undergraduates seeking to earn college credits. AP credits are awarded based on high school students scoring typically 3 or higher on AP exams administered by the College Board, with specific score requirements varying by institution. Eligibility for CLEP exams is more flexible, while AP credits depend heavily on prior enrollment in AP courses and successful exam performance.
Exam Structure and Content Comparison
CLEP exams consist of 33 subject-specific tests designed to evaluate college-level knowledge in areas such as History, Mathematics, and Business, typically lasting 90 to 120 minutes and primarily featuring multiple-choice questions. AP exams offer a broader curriculum range with standardized assessments in subjects like Biology, Calculus, and English Literature, combining multiple-choice and free-response sections within a 2 to 3-hour timeframe. While CLEP exams focus on assessing foundational college course equivalency through concise testing formats, AP exams emphasize both content mastery and analytical skills to award college credit based on high school Advanced Placement coursework.
College Acceptance and Credit Policies
CLEP exams offer flexible credit earning opportunities accepted by over 2,900 colleges, enabling students to bypass introductory courses and reduce college costs. AP credits are widely recognized by prestigious universities, often requiring a minimum score of 3 or higher on AP exams to grant advanced placement or credit. Both CLEP and AP credit policies vary by institution, making it crucial for undergraduate students to verify specific college acceptance criteria and credit transfer guidelines before relying on these exams for degree progress.
Cost Differences between CLEP and AP
CLEP exams typically cost around $90, making them a more affordable option compared to AP exams, which usually cost about $97 per test but may include additional fees for registration and study materials. CLEP offers a one-time fee per exam, whereas AP exams can lead to higher overall expenses due to required courses or retakes. Students seeking to minimize educational expenses often find CLEP exams provide significant cost savings in earning college credits.
Flexibility and Scheduling Options
CLEP exams offer greater flexibility by allowing students to take tests year-round at various approved testing centers, accommodating diverse schedules and pacing. AP credits require scoring well on standardized exams administered once annually, typically in May, limiting scheduling options. This flexibility makes CLEP exams a practical choice for undergraduates balancing coursework and external commitments.
Impact on College Admissions
CLEP exams offer a flexible, cost-effective way for undergraduates to earn college credits by demonstrating proficiency in specific subjects, often resulting in accelerated degree completion. AP credits, earned through standardized high school exams, are widely recognized by colleges and can positively influence admissions decisions by showcasing academic rigor and preparedness. Both CLEP and AP credits improve college admissions profiles by reducing course loads and enabling students to focus on advanced coursework.
Subject Availability and Range
CLEP exams cover over 30 subjects, including college-level material in chemistry, history, and business, offering broad options for earning credit. AP credits are tied to high school Advanced Placement courses with around 38 subjects available, such as calculus, biology, and English literature, providing depth in a wide academic spectrum. While CLEP emphasizes flexible college credit across general education and elective courses, AP credits primarily reflect mastery in more advanced or specialized high school curricula.
Preparation Resources and Study Strategies
CLEP Exams require focused self-study through official College Board practice tests and CLEP preparation books that emphasize multiple-choice question practice and time management. AP Credits demand rigorous review of course-specific materials such as College Board AP Course Descriptions and past exam free response questions to master in-depth subject content. Effective study strategies for CLEP include using online CLEP prep resources and flashcards, while AP students benefit from guided study groups and comprehensive subject textbooks.
Pros and Cons of CLEP and AP for Undergraduates
CLEP exams offer undergraduate students the advantage of testing out of multiple college courses quickly, potentially saving time and tuition costs, but may be limited in acceptance at some institutions compared to AP credits, which are widely recognized and can demonstrate mastery of high school-level subjects. AP credits provide a structured curriculum with the benefit of advanced placement and potential scholarship opportunities, yet require a significant time investment in preparing for standardized exams during high school. CLEP allows more flexible testing schedules and subject variety ideal for non-traditional or returning students, while AP exams are best suited for high school students aiming for early college credit.
CLEP Exams vs AP Credits Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com