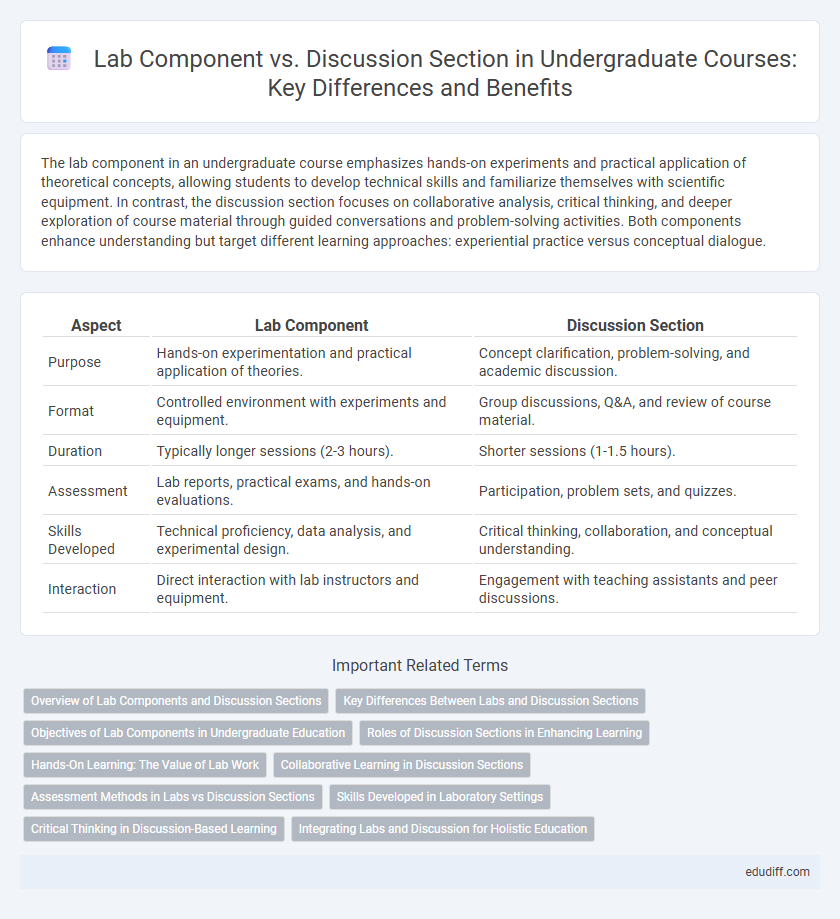
The lab component in an undergraduate course emphasizes hands-on experiments and practical application of theoretical concepts, allowing students to develop technical skills and familiarize themselves with scientific equipment. In contrast, the discussion section focuses on collaborative analysis, critical thinking, and deeper exploration of course material through guided conversations and problem-solving activities. Both components enhance understanding but target different learning approaches: experiential practice versus conceptual dialogue.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lab Component | Discussion Section |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hands-on experimentation and practical application of theories. | Concept clarification, problem-solving, and academic discussion. |
| Format | Controlled environment with experiments and equipment. | Group discussions, Q&A, and review of course material. |
| Duration | Typically longer sessions (2-3 hours). | Shorter sessions (1-1.5 hours). |
| Assessment | Lab reports, practical exams, and hands-on evaluations. | Participation, problem sets, and quizzes. |
| Skills Developed | Technical proficiency, data analysis, and experimental design. | Critical thinking, collaboration, and conceptual understanding. |
| Interaction | Direct interaction with lab instructors and equipment. | Engagement with teaching assistants and peer discussions. |
Overview of Lab Components and Discussion Sections
Lab components provide hands-on experience through experiments and practical application of theoretical concepts, reinforcing students' understanding of scientific methods and procedures in undergraduate courses. Discussion sections focus on collaborative learning, critical thinking, and deeper analysis of lecture material, encouraging student interaction and problem-solving skills. Both components complement each other by enhancing comprehension and engagement in STEM education.
Key Differences Between Labs and Discussion Sections
Lab components emphasize hands-on experiments and practical application of theoretical concepts, allowing students to engage directly with scientific materials and techniques. Discussion sections focus on analyzing lecture content, encouraging critical thinking through debates, problem-solving, and clarification of complex topics. Labs typically require active participation in experiments, while discussion sections center around collaborative dialogue and conceptual understanding.
Objectives of Lab Components in Undergraduate Education
Lab components in undergraduate education aim to enhance hands-on learning by allowing students to apply theoretical concepts through practical experiments and real-world problem-solving. These sessions focus on developing technical skills, critical thinking, and data analysis abilities essential for scientific inquiry. Integrating lab work fosters deeper comprehension of course material and prepares students for advanced research or professional practice.
Roles of Discussion Sections in Enhancing Learning
Discussion sections play a crucial role in enhancing learning by fostering critical thinking and deeper understanding of lecture material through active student engagement. They provide a platform for collaborative problem-solving, clarification of complex concepts, and immediate feedback from instructors and peers. Unlike lab components that emphasize hands-on experiments, discussion sections focus on analytical dialogue and application of theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Hands-On Learning: The Value of Lab Work
Lab components provide hands-on learning opportunities that reinforce theoretical knowledge through practical application, enhancing student comprehension and retention. Discussion sections facilitate critical thinking and conceptual understanding but lack the experiential aspect offered by labs. Integrating lab work allows undergraduates to develop technical skills, experiment with real-world data, and engage directly with scientific processes, which is crucial for disciplines like biology, chemistry, and engineering.
Collaborative Learning in Discussion Sections
Discussion sections emphasize collaborative learning by fostering peer interaction and group problem-solving, enhancing critical thinking and comprehension. Lab components primarily focus on hands-on experimentation and technical skills, while discussion sections promote deeper conceptual understanding through dialogue and teamwork. This collaborative approach in discussion sections improves student engagement and retention of course material.
Assessment Methods in Labs vs Discussion Sections
Lab components typically emphasize hands-on experiments assessed through practical reports, data analysis, and accuracy in experimental procedures. Discussion sections focus on evaluating understanding via participation, problem-solving exercises, and concept application during group discussions. Assessment methods in labs prioritize technical skills and empirical outcomes, whereas discussions assess critical thinking, communication, and theoretical comprehension.
Skills Developed in Laboratory Settings
Laboratory settings cultivate hands-on skills such as experimental design, data collection, and troubleshooting equipment that are essential for scientific inquiry. These environments also enhance critical thinking and technical proficiency through direct interaction with materials and technology. Discussion sections primarily develop interpretive, collaborative, and communication skills by analyzing findings and engaging in intellectual debates.
Critical Thinking in Discussion-Based Learning
Discussion sections in undergraduate courses enhance critical thinking by encouraging open dialogue, debate, and analytical reasoning among students. Unlike lab components that focus on hands-on experiments and technical skills, discussion-based learning promotes deeper understanding through evaluating diverse perspectives and constructing coherent arguments. This interactive environment sharpens students' ability to synthesize information, challenge assumptions, and apply theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios.
Integrating Labs and Discussion for Holistic Education
Integrating lab components with discussion sections enhances undergraduate education by fostering practical application alongside critical analysis, resulting in a comprehensive understanding of scientific concepts. Labs provide hands-on experience with experimental procedures and data collection, while discussions encourage collaborative problem-solving and theoretical exploration. This combined approach strengthens cognitive skills, deepens subject mastery, and better prepares students for real-world scientific challenges.
Lab Component vs Discussion Section Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com