Technical education emphasizes practical skills and hands-on training tailored to specific trades or industries, enabling students to quickly enter the workforce with job-ready expertise. Academic education centers on theoretical knowledge and broader critical thinking skills, preparing students for diverse career paths and advanced studies. The balance between these educational approaches depends on career goals and learning preferences, with technical education offering immediate applicability and academic education fostering long-term adaptability.
Table of Comparison
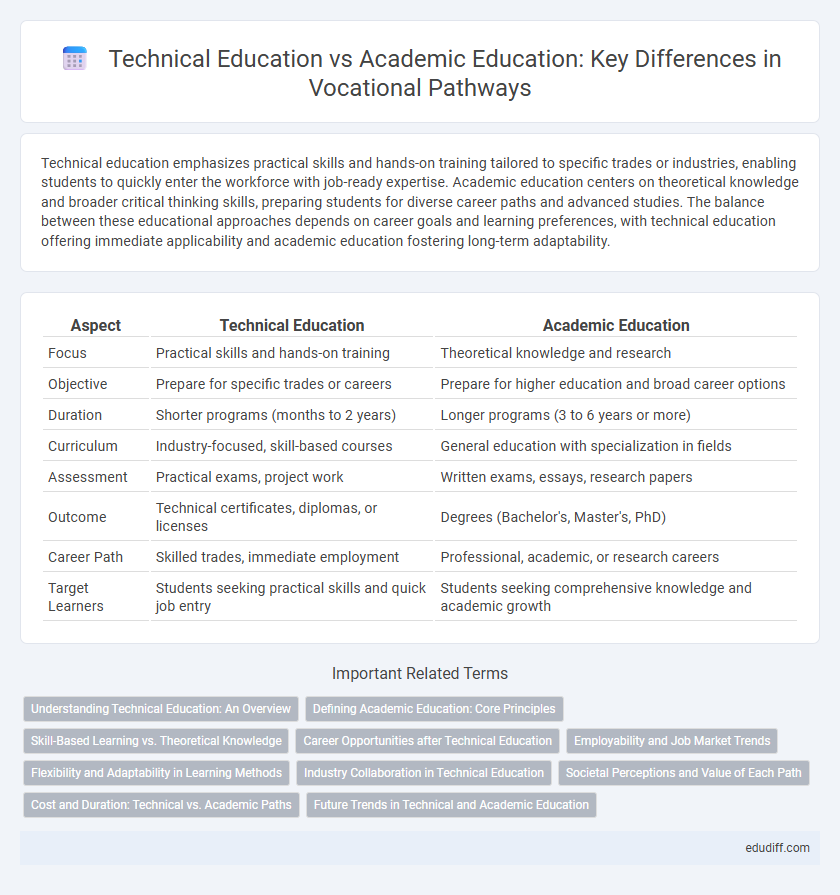
| Aspect | Technical Education | Academic Education |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Practical skills and hands-on training | Theoretical knowledge and research |
| Objective | Prepare for specific trades or careers | Prepare for higher education and broad career options |
| Duration | Shorter programs (months to 2 years) | Longer programs (3 to 6 years or more) |
| Curriculum | Industry-focused, skill-based courses | General education with specialization in fields |
| Assessment | Practical exams, project work | Written exams, essays, research papers |
| Outcome | Technical certificates, diplomas, or licenses | Degrees (Bachelor's, Master's, PhD) |
| Career Path | Skilled trades, immediate employment | Professional, academic, or research careers |
| Target Learners | Students seeking practical skills and quick job entry | Students seeking comprehensive knowledge and academic growth |
Understanding Technical Education: An Overview
Technical education emphasizes hands-on skills and practical knowledge essential for specific trades and industries, offering direct pathways to employment in sectors such as manufacturing, IT, and healthcare. This form of education prioritizes vocational training, internships, and apprenticeships to bridge the gap between theoretical concepts and real-world applications. By focusing on competency-based learning, technical education equips students with industry-relevant expertise tailored to meet labor market demands.
Defining Academic Education: Core Principles
Academic education emphasizes theoretical knowledge, critical thinking, and a broad understanding of various subjects such as mathematics, science, literature, and social studies. It prioritizes abstract concepts, research skills, and intellectual development, preparing students for higher education and professions that require analytical abilities. Core principles include curriculum standardization, assessment through exams, and fostering cognitive skills that support lifelong learning and adaptability.
Skill-Based Learning vs. Theoretical Knowledge
Technical education emphasizes skill-based learning through hands-on training and practical applications, enabling students to directly apply specific trades and technologies in the workforce. Academic education prioritizes theoretical knowledge, fostering critical thinking and conceptual understanding often linked to broader scientific principles and research. Vocational programs bridge these approaches by integrating practical skills with foundational theory, preparing learners for immediate employment and long-term adaptability in technical careers.
Career Opportunities after Technical Education
Technical education provides specialized skills and practical training directly aligned with industry demands, leading to rapid employment in sectors such as manufacturing, IT, healthcare, and engineering. Graduates of technical programs often experience higher job placement rates and accelerated career growth due to hands-on experience and industry certifications. This pathway enhances employability in technical trades and STEM fields, often offering competitive salaries compared to traditional academic routes.
Employability and Job Market Trends
Technical education equips students with practical skills tailored to industry demands, enhancing employability in sectors such as manufacturing, IT, and healthcare. Academic education provides a theoretical foundation, preparing learners for research and roles requiring critical thinking but may not align directly with immediate job market needs. Current job market trends show a growing preference for candidates with technical expertise and hands-on experience due to rapid technological advancements and evolving workforce requirements.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Learning Methods
Technical education emphasizes hands-on training and practical skills, allowing learners to quickly adapt to evolving industry technologies and job requirements. Academic education focuses on theoretical knowledge, promoting critical thinking but often with less immediate application flexibility. Vocational programs typically offer modular courses and flexible schedules, enhancing adaptability to various learning styles and career pathways.
Industry Collaboration in Technical Education
Industry collaboration in technical education enhances practical skills by integrating real-world projects, internships, and expert mentorship directly into the curriculum. Partnerships with companies ensure that vocational training aligns with current market demands, fostering job readiness and innovation in sectors such as manufacturing, IT, and healthcare. This close cooperation bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and workplace application, offering students a competitive advantage over purely academic programs.
Societal Perceptions and Value of Each Path
Technical education is often perceived as a practical pathway that equips students with specialized skills directly applicable to the workforce, leading to high employability and economic contribution. Academic education is traditionally valued for fostering critical thinking, theoretical knowledge, and research capabilities, which are seen as essential for innovation and leadership roles. Societal perceptions increasingly recognize the complementary value of both paths, emphasizing that technical expertise and academic knowledge jointly drive sustainable development and workforce diversity.
Cost and Duration: Technical vs. Academic Paths
Technical education programs often offer lower tuition costs and shorter durations, typically ranging from six months to two years, enabling faster entry into the workforce. In contrast, academic education usually involves higher expenses and longer time commitments, with undergraduate degrees spanning three to four years or more. These differences significantly impact students' financial investment and time-to-career opportunities in vocational versus traditional academic paths.
Future Trends in Technical and Academic Education
Emerging trends in technical education emphasize hands-on skills in AI, robotics, and renewable energy, aligning closely with industry demands and technological advancements. Academic education increasingly integrates interdisciplinary studies and digital literacy to prepare students for complex problem-solving and innovation across diverse fields. Growth in hybrid learning models and personalized education platforms is expected to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical expertise, reshaping future career pathways.
Technical education vs Academic education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com