Project-based learning fosters critical thinking and real-world problem-solving by engaging students in hands-on tasks, whereas exam-based assessment primarily measures rote memorization and theoretical knowledge. Project-based approaches encourage collaboration and creativity, enhancing practical skills essential for technical fields. Exam-based assessments, while efficient for standardization, may overlook students' ability to apply concepts in dynamic, real-life scenarios.
Table of Comparison
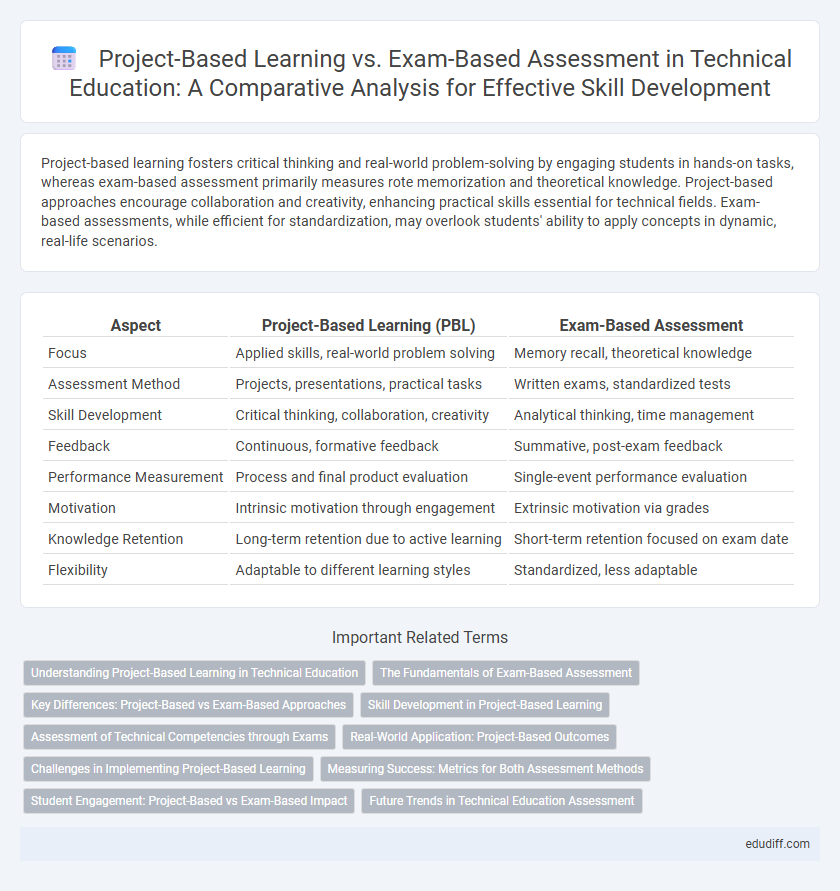
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Exam-Based Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Applied skills, real-world problem solving | Memory recall, theoretical knowledge |
| Assessment Method | Projects, presentations, practical tasks | Written exams, standardized tests |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, collaboration, creativity | Analytical thinking, time management |
| Feedback | Continuous, formative feedback | Summative, post-exam feedback |
| Performance Measurement | Process and final product evaluation | Single-event performance evaluation |
| Motivation | Intrinsic motivation through engagement | Extrinsic motivation via grades |
| Knowledge Retention | Long-term retention due to active learning | Short-term retention focused on exam date |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to different learning styles | Standardized, less adaptable |
Understanding Project-Based Learning in Technical Education
Project-Based Learning (PBL) in technical education emphasizes hands-on experience and real-world problem-solving, fostering deeper comprehension of complex concepts compared to traditional exam-based assessment. By engaging students in collaborative projects, PBL cultivates critical thinking, adaptability, and technical skills essential for innovation in fields such as engineering, computer science, and information technology. This approach aligns with industry demands by preparing learners to apply theoretical knowledge practically, resulting in enhanced retention and job readiness.
The Fundamentals of Exam-Based Assessment
Exam-based assessment fundamentally measures students' ability to recall and apply knowledge within constrained timeframes, emphasizing memorization and standardized testing techniques. This approach relies on structured, objective criteria to evaluate cognitive skills such as analysis, synthesis, and problem-solving under pressure. Despite its limitations in assessing practical competencies, exam-based assessment remains a key method for benchmarking academic achievement and ensuring uniformity across educational institutions.
Key Differences: Project-Based vs Exam-Based Approaches
Project-based learning emphasizes hands-on application, fostering critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills through extended tasks, while exam-based assessment focuses on measuring knowledge retention and recall under timed conditions. Project-based approaches encourage collaboration and deeper understanding by engaging students in active creation, contrasting with exams that prioritize individual performance and standardized testing criteria. The key difference lies in experiential learning versus summative evaluation, impacting student engagement and skill development outcomes.
Skill Development in Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) significantly enhances skill development by promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving abilities, which are often underemphasized in traditional exam-based assessments. PBL engages students in active learning processes, fostering creativity and adaptability necessary for modern technical fields. This hands-on approach equips learners with practical skills and deeper content understanding, aligning education outcomes with industry demands.
Assessment of Technical Competencies through Exams
Exam-based assessment of technical competencies emphasizes standardized testing methods that measure theoretical knowledge and problem-solving skills under timed conditions. This approach enables objective grading, ensuring consistency and comparability across different cohorts and institutions through structured tasks such as coding tests, multiple-choice questions, and technical case studies. While exams effectively evaluate individual understanding of fundamental concepts, they may not fully capture practical application or collaborative abilities essential for real-world technical proficiency.
Real-World Application: Project-Based Outcomes
Project-Based Learning emphasizes real-world application by requiring students to create tangible solutions that address practical challenges, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential in professional settings. Exam-Based Assessment primarily evaluates theoretical knowledge, often lacking direct correlation to workplace scenarios and hands-on experience. Project-Based outcomes better prepare students for industry demands by simulating complex tasks and collaborative workflows commonly encountered in real-world environments.
Challenges in Implementing Project-Based Learning
Implementing project-based learning (PBL) faces challenges such as resource limitations, including insufficient access to technology and materials, which hinder effective project completion. Teachers often require additional training to design and facilitate projects that align with learning objectives while managing diverse student needs and assessment criteria. Furthermore, PBL demands more time for planning and assessment compared to traditional exam-based methods, complicating curriculum scheduling and standardization.
Measuring Success: Metrics for Both Assessment Methods
Project-based learning measures success through metrics such as project completion rates, quality of deliverables, collaboration effectiveness, and critical thinking skills demonstrated. Exam-based assessment relies on metrics like exam scores, time efficiency, accuracy, and knowledge retention under timed conditions. Both methods evaluate distinct competencies, requiring tailored metrics to accurately quantify student learning outcomes and skill mastery.
Student Engagement: Project-Based vs Exam-Based Impact
Project-based learning significantly enhances student engagement by fostering active participation, critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving skills, whereas exam-based assessment primarily encourages rote memorization and passive study habits. Research reveals that students involved in project-based activities exhibit higher motivation and retention rates compared to those prepared solely for exams. Consequently, project-based learning creates a dynamic educational environment that aligns with cognitive development and long-term knowledge application.
Future Trends in Technical Education Assessment
Project-Based Learning (PBL) fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application skills, aligning with future trends emphasizing competency over rote memorization in technical education assessment. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven analytics enable personalized feedback and adaptive evaluation, enhancing the effectiveness of project-based assessments. The shift towards integrating industry-relevant projects reflects an increasing demand for graduates proficient in practical skills required by evolving technical fields.
Project-Based Learning vs Exam-Based Assessment Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com