Audit allows undergraduate students to attend courses without receiving a grade or credit, providing an opportunity for learning without academic pressure. Enroll requires formal registration in courses, earning grades that contribute to degree requirements. Choosing between audit and enroll depends on a student's academic goals and commitment to coursework.
Table of Comparison
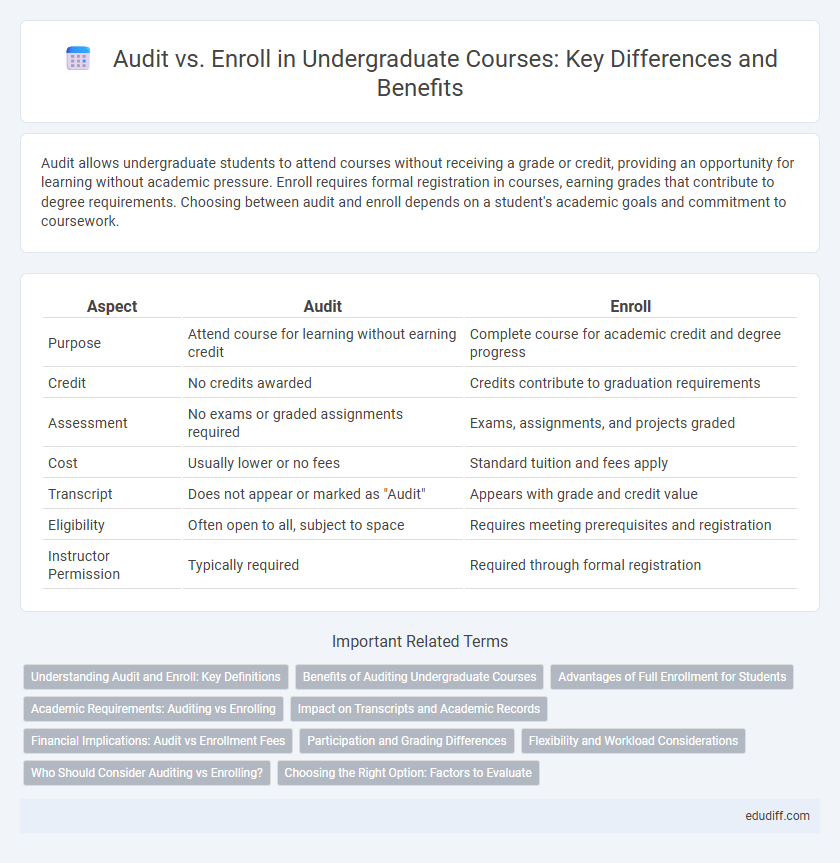
| Aspect | Audit | Enroll |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Attend course for learning without earning credit | Complete course for academic credit and degree progress |
| Credit | No credits awarded | Credits contribute to graduation requirements |
| Assessment | No exams or graded assignments required | Exams, assignments, and projects graded |
| Cost | Usually lower or no fees | Standard tuition and fees apply |
| Transcript | Does not appear or marked as "Audit" | Appears with grade and credit value |
| Eligibility | Often open to all, subject to space | Requires meeting prerequisites and registration |
| Instructor Permission | Typically required | Required through formal registration |
Understanding Audit and Enroll: Key Definitions
Audit allows undergraduate students to attend classes without receiving academic credit or a grade, primarily for learning enrichment without pressure. Enroll requires registration for credit-bearing courses, contributing to degree requirements and impacting GPA. Understanding these key definitions helps students make informed decisions about course participation aligned with their academic goals.
Benefits of Auditing Undergraduate Courses
Auditing undergraduate courses allows students to explore subjects without the pressure of grades, enhancing learning flexibility and fostering intellectual curiosity. This option enables individuals to deepen knowledge, improve skills, and engage with course material at their own pace while benefiting from access to lectures and resources. Unlike enrolling, auditing reduces academic stress and supports lifelong learning without impacting GPA or credit requirements.
Advantages of Full Enrollment for Students
Full enrollment grants students access to comprehensive course materials, graded assignments, and official credit, enhancing academic credentials and graduate opportunities. Enrolled students benefit from personalized instructor feedback and participation in discussions, fostering deeper understanding and skill development. Access to campus resources, including libraries and study groups, supports a more immersive and collaborative learning environment.
Academic Requirements: Auditing vs Enrolling
Auditing a course allows undergraduate students to attend lectures without fulfilling formal academic requirements like assignments, exams, or earning credit, which differs from enrolling, where students must actively participate and meet all course obligations. Enrolled students receive grades that contribute to their GPA and degree progress, while auditors do not receive academic credit or grades. This distinction impacts transcript records, degree completion timelines, and eligibility for financial aid tied to course credits.
Impact on Transcripts and Academic Records
Auditing a course allows students to participate without earning academic credit, which results in the course appearing as "Audit" on transcripts without affecting GPA or credit hours. Enrolling in a course for credit records the grade and credits earned, directly impacting the transcript and contributing to cumulative GPA. This distinction influences academic standing, scholarship eligibility, and graduate program applications.
Financial Implications: Audit vs Enrollment Fees
Auditing a course generally involves paying a lower fee compared to full enrollment, as auditors do not receive academic credit or access to certain resources like graded assignments. Enrollment fees cover full access to course materials, instructor support, and credit towards a degree, often justifying the higher cost. Understanding these financial distinctions helps undergraduate students make cost-effective decisions aligned with their academic goals.
Participation and Grading Differences
Auditing a course allows undergraduate students to participate in classes without receiving a grade or academic credit, facilitating learning without the pressure of exams or assignments. Enrolling requires active participation in assessments and contributes to the student's GPA, making it essential for degree completion. The choice between auditing and enrolling impacts academic records, student engagement, and degree progress tracking.
Flexibility and Workload Considerations
Auditing a course offers significant flexibility by allowing undergraduate students to attend lectures without the pressure of assignments or exams, reducing overall workload. Enrolling in a course demands full participation, including completing all assessments and meeting deadlines, which increases time commitment and academic responsibility. Selecting audit status can benefit those seeking knowledge without the stress of grades, while enrollment suits students aiming for credit and degree progress.
Who Should Consider Auditing vs Enrolling?
Students seeking flexible learning experiences without the pressure of grades should consider auditing courses to explore subjects or enhance skills without commitment. Those aiming for degree credit, formal assessment, and academic recognition must enroll officially to meet graduation requirements and professional standards. Auditing benefits lifelong learners and professionals updating knowledge, whereas enrollment suits traditional undergraduates pursuing structured academic progress.
Choosing the Right Option: Factors to Evaluate
Choosing between auditing and enrolling depends on your academic goals and course engagement level. Enrollment offers full credit and access to assessments, crucial for degree requirements or GPA improvement, while auditing allows learning without grade pressure, ideal for skill exploration or interest without affecting transcripts. Evaluate factors like time commitment, transcript impact, and personal motivation to decide which option aligns best with your undergraduate objectives.
Audit vs Enroll Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com