Competency-based education prioritizes mastering specific skills and knowledge at an individual pace, ensuring learners achieve proficiency before progressing. Time-based education relies on fixed schedules and seat time, often advancing students regardless of skill mastery. This shift towards competency-based learning enhances workforce readiness by aligning education directly with practical job requirements.
Table of Comparison
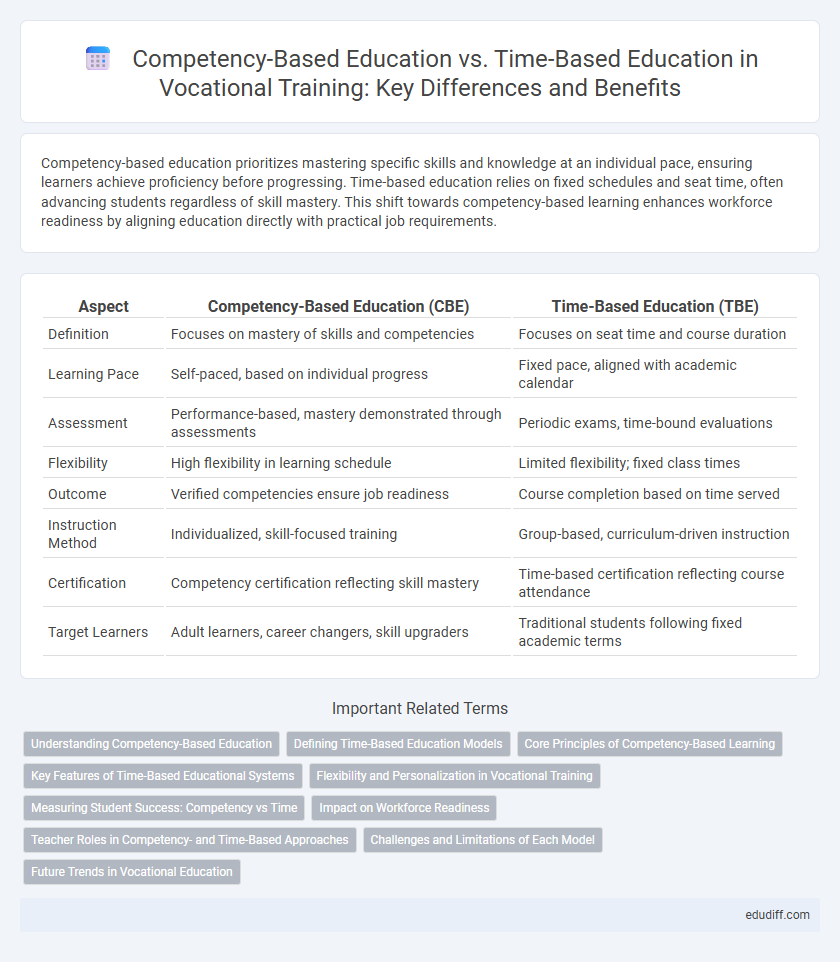
| Aspect | Competency-Based Education (CBE) | Time-Based Education (TBE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on mastery of skills and competencies | Focuses on seat time and course duration |
| Learning Pace | Self-paced, based on individual progress | Fixed pace, aligned with academic calendar |
| Assessment | Performance-based, mastery demonstrated through assessments | Periodic exams, time-bound evaluations |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in learning schedule | Limited flexibility; fixed class times |
| Outcome | Verified competencies ensure job readiness | Course completion based on time served |
| Instruction Method | Individualized, skill-focused training | Group-based, curriculum-driven instruction |
| Certification | Competency certification reflecting skill mastery | Time-based certification reflecting course attendance |
| Target Learners | Adult learners, career changers, skill upgraders | Traditional students following fixed academic terms |
Understanding Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) in vocational training emphasizes mastering specific skills and knowledge essential for job performance rather than accumulating classroom hours. This approach allows learners to progress upon demonstrating proficiency, ensuring personalized pacing and practical application in real-world scenarios. CBE aligns closely with industry standards, enhancing employability by focusing on measurable outcomes and essential competencies.
Defining Time-Based Education Models
Time-based education models organize learning around fixed durations, such as semesters or clock hours, emphasizing completion within set time frames rather than mastery of skills. These models standardize progression regardless of individual competency, often leading to varied skill acquisition among students. In vocational training, time-based approaches may limit personalized skill development compared to competency-based frameworks.
Core Principles of Competency-Based Learning
Competency-Based Learning centers on mastering specific skills and knowledge at an individualized pace, ensuring learners demonstrate practical proficiency before progressing. Unlike Time-Based Education, which measures progress by seat time and fixed schedules, Competency-Based Education emphasizes personalized learning pathways tailored to each student's needs and strengths. This approach promotes deeper understanding, real-world application, and accountability through clear, measurable learning outcomes aligned with workforce demands.
Key Features of Time-Based Educational Systems
Time-based educational systems organize curriculum around fixed time intervals, such as semesters or hours, emphasizing seat time rather than skill mastery. Key features include standardized schedules, uniform pacing for all students, and assessments aligned with calendar milestones. This approach prioritizes consistent time allocation over individual competency achievement in vocational training contexts.
Flexibility and Personalization in Vocational Training
Competency-based education (CBE) in vocational training offers greater flexibility by allowing learners to progress at their own pace based on skill mastery rather than fixed schedules. This personalized approach ensures that students acquire specific competencies essential for their trade, resulting in tailored learning experiences that address individual strengths and weaknesses. In contrast, time-based education adheres to predetermined durations, often limiting adaptability and individualized skill development.
Measuring Student Success: Competency vs Time
Competency-Based Education measures student success by demonstrating mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to progress at their own pace until competencies are achieved. In contrast, Time-Based Education evaluates students based on the amount of time spent in class or completing coursework, often prioritizing seat time over skill mastery. Competency models provide a more personalized and precise assessment of student achievement, aligning education outcomes with workforce demands.
Impact on Workforce Readiness
Competency-Based Education (CBE) accelerates workforce readiness by ensuring learners master specific skills crucial for job performance, promoting practical expertise over seat time. Time-Based Education often extends training regardless of actual skill acquisition, potentially delaying entry into the workforce. CBE aligns directly with employer demands, enhancing job placement rates and improving labor market outcomes.
Teacher Roles in Competency- and Time-Based Approaches
Teachers in competency-based education act as facilitators, guiding students through personalized learning paths and assessing mastery of skills at an individual pace. In contrast, time-based education requires teachers to deliver standardized content within fixed schedules, emphasizing seat time over skill mastery. This shift in roles impacts curriculum delivery, with competency-based educators focusing on tailored feedback and adaptive instruction to meet diverse learner needs.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Competency-Based Education (CBE) faces challenges such as the difficulty in accurately assessing diverse skill mastery and the need for flexible instructional resources, which can strain institutional capacity. Time-Based Education often limits learner progression to fixed schedules, potentially slowing down motivated students and causing disengagement among those who require more time to master content. Both models struggle with ensuring consistent quality and alignment with industry standards, posing limitations in adapting to the evolving vocational workforce demands.
Future Trends in Vocational Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) in vocational training emphasizes mastery of specific skills and allows learners to progress at their own pace, aligning with future workforce demands for adaptable and proficient professionals. Time-Based Education, traditionally structured around fixed durations, is increasingly challenged by rapid technological advancements that require flexible, personalized learning paths. Emerging trends suggest a stronger adoption of CBE models supported by digital platforms and real-time assessment tools to enhance skill validation and employability in evolving industries.
Competency-Based Education vs Time-Based Education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com