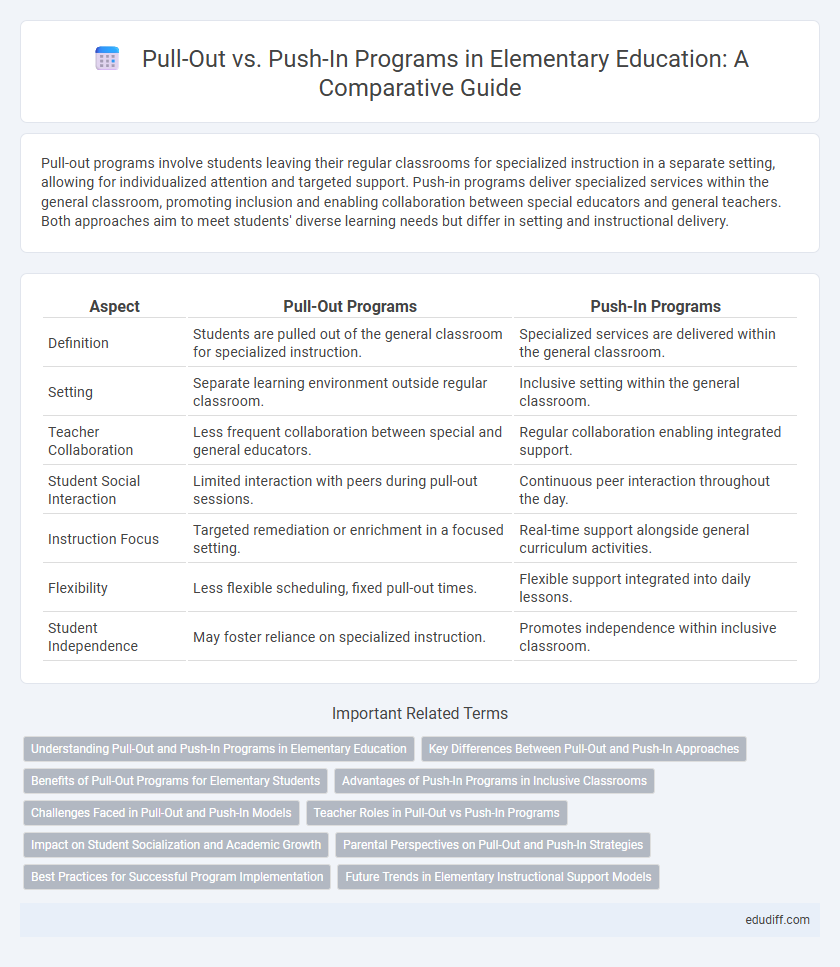
Pull-out programs involve students leaving their regular classrooms for specialized instruction in a separate setting, allowing for individualized attention and targeted support. Push-in programs deliver specialized services within the general classroom, promoting inclusion and enabling collaboration between special educators and general teachers. Both approaches aim to meet students' diverse learning needs but differ in setting and instructional delivery.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pull-Out Programs | Push-In Programs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students are pulled out of the general classroom for specialized instruction. | Specialized services are delivered within the general classroom. |
| Setting | Separate learning environment outside regular classroom. | Inclusive setting within the general classroom. |
| Teacher Collaboration | Less frequent collaboration between special and general educators. | Regular collaboration enabling integrated support. |
| Student Social Interaction | Limited interaction with peers during pull-out sessions. | Continuous peer interaction throughout the day. |
| Instruction Focus | Targeted remediation or enrichment in a focused setting. | Real-time support alongside general curriculum activities. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible scheduling, fixed pull-out times. | Flexible support integrated into daily lessons. |
| Student Independence | May foster reliance on specialized instruction. | Promotes independence within inclusive classroom. |
Understanding Pull-Out and Push-In Programs in Elementary Education
Pull-out programs in elementary education involve removing students from the general classroom for specialized instruction, often in areas like reading or speech therapy, allowing targeted skill development. Push-in programs integrate specialists directly into the general classroom environment, providing support without disrupting regular class activities and fostering inclusive learning. Both approaches aim to address diverse student needs while balancing academic progress and social integration.
Key Differences Between Pull-Out and Push-In Approaches
Pull-out programs involve removing students from the general classroom for specialized instruction, allowing targeted support in a separate setting. Push-in programs bring specialized educators into the general classroom to provide assistance within the mainstream learning environment. The key differences lie in location, instructional delivery, and student interaction, with pull-out offering individualized focus outside the classroom, while push-in promotes inclusivity and collaboration within the regular class.
Benefits of Pull-Out Programs for Elementary Students
Pull-out programs for elementary students provide targeted, individualized instruction that addresses specific learning needs, enhancing academic progress and confidence. These programs allow educators to use specialized teaching strategies in a focused environment, promoting skill development in areas like reading and math. Small group or one-on-one settings help minimize distractions and facilitate better understanding of concepts, resulting in improved student outcomes.
Advantages of Push-In Programs in Inclusive Classrooms
Push-in programs promote inclusivity by allowing special education teachers to collaborate directly with general education teachers within the same classroom, enhancing individualized support without removing students from their peers. This approach fosters social interaction and peer modeling, which improves communication skills and boosts self-esteem among students with diverse learning needs. Incorporating push-in support reduces stigmatization and helps create a more cohesive learning environment tailored to all students' abilities.
Challenges Faced in Pull-Out and Push-In Models
Pull-out programs often face challenges such as disrupting students' regular classroom routines and causing social separation from peers. Push-in programs may struggle with limited time allocation and balancing the special educator's support without hindering general classroom instruction. Both models require effective collaboration between special educators and general teachers to address individual student needs while maintaining instructional flow.
Teacher Roles in Pull-Out vs Push-In Programs
Teacher roles in Pull-Out Programs involve specialized educators working with small groups of students outside the regular classroom to provide targeted instruction, allowing for focused skill development. In Push-In Programs, teachers collaborate within the general education classroom, co-teaching and supporting students alongside the main teacher to promote inclusive learning. Both models require adaptable teaching strategies, but Push-In Programs emphasize collaboration and integration, while Pull-Out Programs concentrate on individualized support.
Impact on Student Socialization and Academic Growth
Pull-out programs provide targeted academic support by removing students from the general classroom, which can enhance individualized learning but may limit peer interaction and socialization opportunities. Push-in programs integrate support within the regular classroom setting, promoting inclusive socialization and continuous academic engagement alongside peers. Research indicates that push-in models often foster stronger social skills and sustained academic growth due to consistent interaction with classmates and collaborative learning environments.
Parental Perspectives on Pull-Out and Push-In Strategies
Parental perspectives on pull-out programs often highlight concerns about social isolation and academic disruption, while many appreciate the targeted support these sessions provide. In contrast, push-in programs receive positive feedback for fostering inclusion and allowing parents to see their children actively participating in the general education environment. Parents tend to support strategies that balance specialized instruction with opportunities for their children to engage with peers, emphasizing the importance of communication between educators and families.
Best Practices for Successful Program Implementation
Pull-Out Programs should focus on targeted instruction tailored to individual student needs, ensuring small group settings and frequent progress monitoring to maximize learning outcomes. Push-In Programs work best when general and special educators collaborate closely, integrating specialized support within the regular classroom environment to promote inclusion and minimize disruption. Effective communication, ongoing professional development, and data-driven decision-making are essential best practices for successfully implementing both program types in elementary education.
Future Trends in Elementary Instructional Support Models
Future trends in elementary instructional support models highlight a shift towards integrating pull-out and push-in programs to create more personalized learning experiences. Data-driven approaches enable educators to tailor interventions, enhancing student engagement and achievement while minimizing classroom disruption. Advances in technology facilitate seamless collaboration between specialists and classroom teachers, promoting continuous support within inclusive settings.
Pull-Out Programs vs Push-In Programs Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com