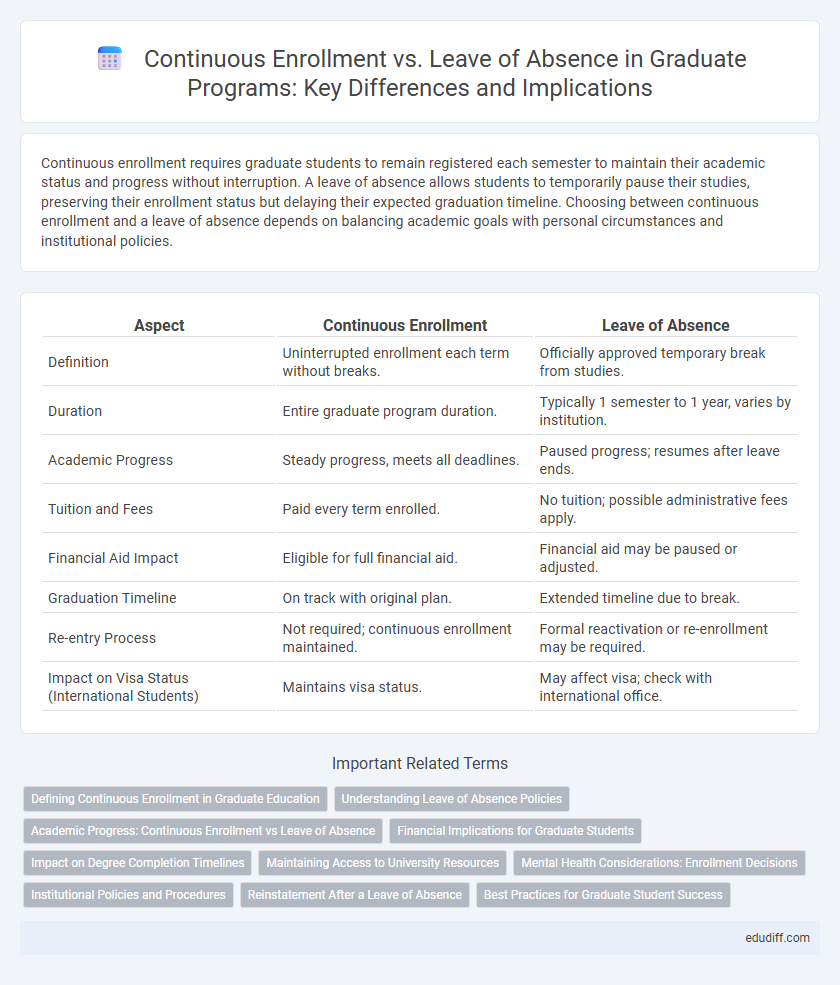
Continuous enrollment requires graduate students to remain registered each semester to maintain their academic status and progress without interruption. A leave of absence allows students to temporarily pause their studies, preserving their enrollment status but delaying their expected graduation timeline. Choosing between continuous enrollment and a leave of absence depends on balancing academic goals with personal circumstances and institutional policies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Continuous Enrollment | Leave of Absence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uninterrupted enrollment each term without breaks. | Officially approved temporary break from studies. |
| Duration | Entire graduate program duration. | Typically 1 semester to 1 year, varies by institution. |
| Academic Progress | Steady progress, meets all deadlines. | Paused progress; resumes after leave ends. |
| Tuition and Fees | Paid every term enrolled. | No tuition; possible administrative fees apply. |
| Financial Aid Impact | Eligible for full financial aid. | Financial aid may be paused or adjusted. |
| Graduation Timeline | On track with original plan. | Extended timeline due to break. |
| Re-entry Process | Not required; continuous enrollment maintained. | Formal reactivation or re-enrollment may be required. |
| Impact on Visa Status (International Students) | Maintains visa status. | May affect visa; check with international office. |
Defining Continuous Enrollment in Graduate Education
Continuous enrollment in graduate education requires students to maintain active registration for courses or research each academic term without interruption, ensuring steady academic progress. This policy typically mandates enrollment every semester, including summer sessions, to avoid administrative withdrawal or status changes. Maintaining continuous enrollment helps graduate students remain eligible for university resources, financial aid, and faculty supervision throughout their program.
Understanding Leave of Absence Policies
Understanding Leave of Absence (LOA) policies is essential for graduate students deciding between continuous enrollment and temporary withdrawal. LOA allows students to pause their studies for specified reasons such as medical issues, personal challenges, or professional opportunities without losing their enrollment status, often requiring formal approval and documentation. Familiarity with university-specific LOA durations, reinstatement procedures, and potential impacts on financial aid or academic progress ensures informed decisions that protect academic standing and future graduation timelines.
Academic Progress: Continuous Enrollment vs Leave of Absence
Continuous enrollment ensures uninterrupted academic progress by maintaining full-time status and access to university resources, which supports timely degree completion. In contrast, a leave of absence temporarily pauses coursework and may delay graduation, potentially requiring reactivation procedures that impact academic momentum. Careful consideration of program deadlines and advisor consultation is crucial when choosing between continuous enrollment and a leave of absence to optimize academic progression.
Financial Implications for Graduate Students
Continuous enrollment for graduate students often incurs consistent tuition fees and associated charges each term, impacting financial planning and eligibility for certain scholarships or assistantships. In contrast, a leave of absence typically suspends tuition payments but may limit access to university resources and delay graduation, potentially affecting financial aid renewal or loan repayment schedules. Understanding these financial implications is crucial for graduate students balancing academic progress with budget constraints.
Impact on Degree Completion Timelines
Continuous enrollment ensures steady progress toward degree completion by maintaining active student status each term, which typically shortens the overall timeline. A leave of absence pauses academic activities and can delay graduation by extending the time required to fulfill program requirements. Students should carefully weigh the implications of each option on their individual degree plans to optimize timely completion.
Maintaining Access to University Resources
Continuous enrollment ensures uninterrupted access to university resources such as libraries, research databases, and academic advising crucial for graduate students' success. Leave of absence may restrict or temporarily suspend access to these services, impacting progress on thesis work or coursework. Graduate students must carefully consider these implications to maintain seamless academic support during their studies.
Mental Health Considerations: Enrollment Decisions
Graduate students facing mental health challenges should carefully weigh continuous enrollment against a leave of absence, considering the impact on academic progress and well-being. Maintaining continuous enrollment often provides ongoing access to campus resources and support services critical for mental health management. Conversely, a leave of absence can offer necessary time for recovery, but may disrupt academic momentum and access to institutional benefits.
Institutional Policies and Procedures
Graduate institutional policies distinguish continuous enrollment as a mandatory, uninterrupted registration every term to maintain active student status and progress toward degree completion. Leave of absence procedures allow students to temporarily pause enrollment, typically requiring formal approval and adherence to specific deadlines to preserve re-entry rights and financial aid eligibility. Understanding these institutional policies ensures compliance, prevents academic penalties, and supports strategic planning for successful graduate program completion.
Reinstatement After a Leave of Absence
Reinstatement after a Leave of Absence requires submitting a formal application to the registrar's office along with any necessary supporting documents, ensuring compliance with university policies. Students must typically meet academic performance standards and pay outstanding fees before regaining continuous enrollment status. Timely communication with the graduate program coordinator facilitates a smooth transition back into active student status without delaying degree progress.
Best Practices for Graduate Student Success
Graduate students maintain academic progress and financial aid eligibility through continuous enrollment by registering every term without interruption. Leave of absence policies offer structured breaks during unforeseen circumstances but require formal approval and careful planning to avoid delays in degree completion. Best practices emphasize proactive communication with advisors and timely submission of petitions to balance personal needs and academic goals effectively.
Continuous Enrollment vs Leave of Absence Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com