Sixth Form offers a structured environment closely linked to secondary schools, emphasizing A-levels with a strong academic focus. College provides a broader range of vocational courses and practical skills, catering to diverse career paths and hands-on learning. The choice between Sixth Form and College depends on whether students prefer a traditional academic route or more flexible, career-oriented education.
Table of Comparison
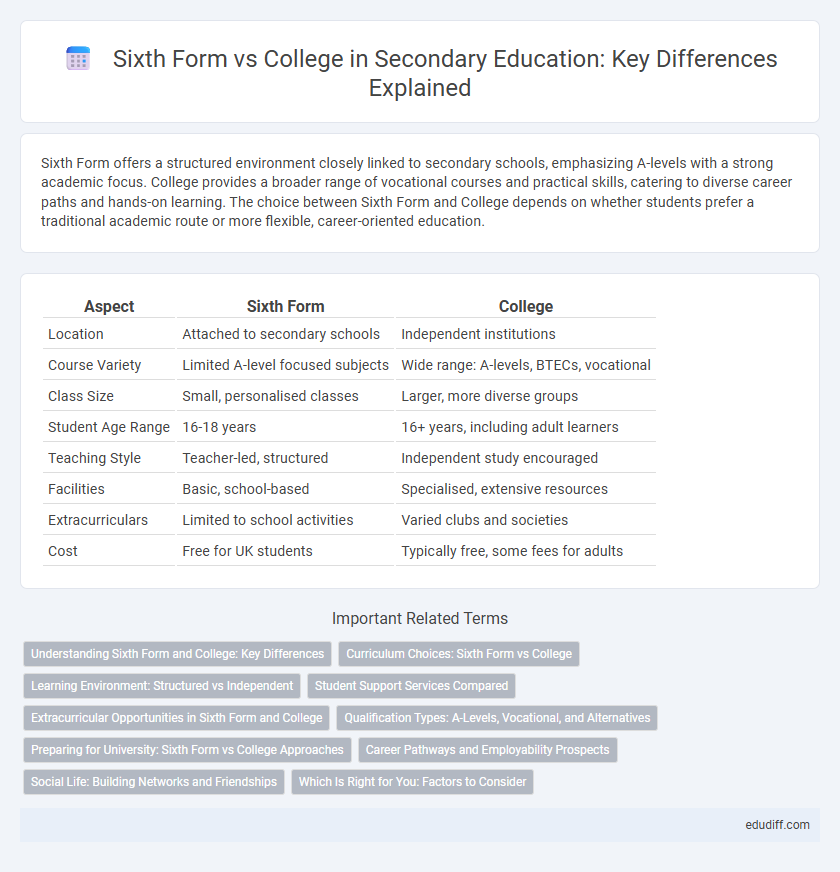
| Aspect | Sixth Form | College |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Attached to secondary schools | Independent institutions |
| Course Variety | Limited A-level focused subjects | Wide range: A-levels, BTECs, vocational |
| Class Size | Small, personalised classes | Larger, more diverse groups |
| Student Age Range | 16-18 years | 16+ years, including adult learners |
| Teaching Style | Teacher-led, structured | Independent study encouraged |
| Facilities | Basic, school-based | Specialised, extensive resources |
| Extracurriculars | Limited to school activities | Varied clubs and societies |
| Cost | Free for UK students | Typically free, some fees for adults |
Understanding Sixth Form and College: Key Differences
Sixth Form primarily focuses on A-level courses, preparing students aged 16-19 for university entry, while colleges offer a broader range of vocational and academic qualifications, such as BTECs and apprenticeships. Sixth Form is often attached to secondary schools, fostering a closer transition for students continuing their studies, whereas colleges operate independently with diverse student demographics and flexible study options. Understanding these differences helps students align their educational choices with career goals and preferred learning environments.
Curriculum Choices: Sixth Form vs College
Sixth Form offers a more traditional A-level curriculum with a focus on academic subjects tailored for university preparation, while colleges provide a broader range of vocational courses alongside A-levels, catering to diverse career paths. The flexibility in colleges allows students to combine academic and practical qualifications, supporting both higher education and direct employment goals. Students choosing Sixth Form typically experience a more structured environment, whereas colleges emphasize personalized learning tailored to individual career interests.
Learning Environment: Structured vs Independent
Sixth Form offers a structured learning environment with a timetable designed around scheduled lessons and close teacher supervision, promoting consistent study habits and direct academic support. In contrast, College emphasizes independent learning, encouraging students to manage their own time, complete assignments autonomously, and develop self-discipline essential for higher education. This shift from structured to independent learning prepares students for university-style study and personal responsibility in managing their academic progress.
Student Support Services Compared
Sixth Form colleges typically provide tailored student support services, including personalized academic counseling and close mentorship from subject specialists, enhancing individual learning paths. College settings often offer broader support resources such as extensive career advice, mental health services, and study skill workshops, catering to a larger, more diverse student body. Evaluating the availability and scope of these support services helps students choose the environment best suited to their academic and personal development needs.
Extracurricular Opportunities in Sixth Form and College
Sixth Form offers a wide range of extracurricular opportunities including academic clubs, sports teams, and leadership roles tailored to enhance university applications and personal development. Colleges often provide more diverse vocational and creative extracurricular options, such as industry-linked projects, community volunteering, and specialized workshops. Both settings support student growth beyond academics, with Sixth Form emphasizing traditional academic enrichment and Colleges focusing on practical skill-building activities.
Qualification Types: A-Levels, Vocational, and Alternatives
Sixth Form primarily offers A-Levels, which are academic qualifications recognized for university entry, emphasizing subject depth and specialization. Colleges provide a broader range of qualification types, including vocational courses like BTECs, NVQs, and apprenticeships, focused on practical skills and direct employment pathways. Alternatives such as Cambridge Technicals and International Baccalaureate (IB) are available in both settings, catering to diverse learning styles and career goals in secondary education.
Preparing for University: Sixth Form vs College Approaches
Sixth Form offers a structured curriculum closely aligned with traditional A-levels, fostering rigorous academic preparation ideal for university entry, especially for students targeting competitive courses. Colleges provide a more flexible, diverse range of qualifications including BTECs and T-levels, emphasizing practical skills alongside theory, which benefits students seeking vocational pathways or alternative entry routes to higher education. Both pathways support university readiness but differ in teaching styles and qualification types, impacting student choice based on academic goals and preferred learning environments.
Career Pathways and Employability Prospects
Sixth Form offers specialized A-level courses that prepare students for university pathways, often favoring academic careers, while colleges provide vocational qualifications such as BTECs and apprenticeships that focus on practical skills for specific industries. Career services in colleges typically include employer partnerships and work placements, enhancing employability through real-world experience. Choosing between Sixth Form and College depends on whether students aim for academic progression or direct entry into the workforce.
Social Life: Building Networks and Friendships
Sixth Form environments foster closer-knit social networks due to smaller, more consistent class sizes, encouraging long-term friendships and peer support. Colleges offer a wider range of extracurricular activities and diverse student bodies, enhancing opportunities for social interaction and broader networking. Both settings provide valuable platforms for developing interpersonal skills essential for future academic and professional success.
Which Is Right for You: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Sixth Form and college depends on your preferred learning style, course variety, and career goals. Sixth Form often offers a more structured academic environment with A-levels, while colleges provide a wider range of vocational courses and apprenticeships. Consider factors such as teaching methods, campus facilities, and university progression rates to determine the best fit for your future ambitions.
Sixth Form vs College Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com