ABA therapy uses structured techniques to improve specific behaviors in pets through consistent reinforcement, making it highly effective for training and behavior modification. Play therapy emphasizes natural interaction and emotional bonding, helping pets reduce anxiety and develop social skills in a more relaxed environment. Choosing between ABA therapy and play therapy depends on the pet's individual needs and the desired outcomes for behavior and emotional well-being.
Table of Comparison
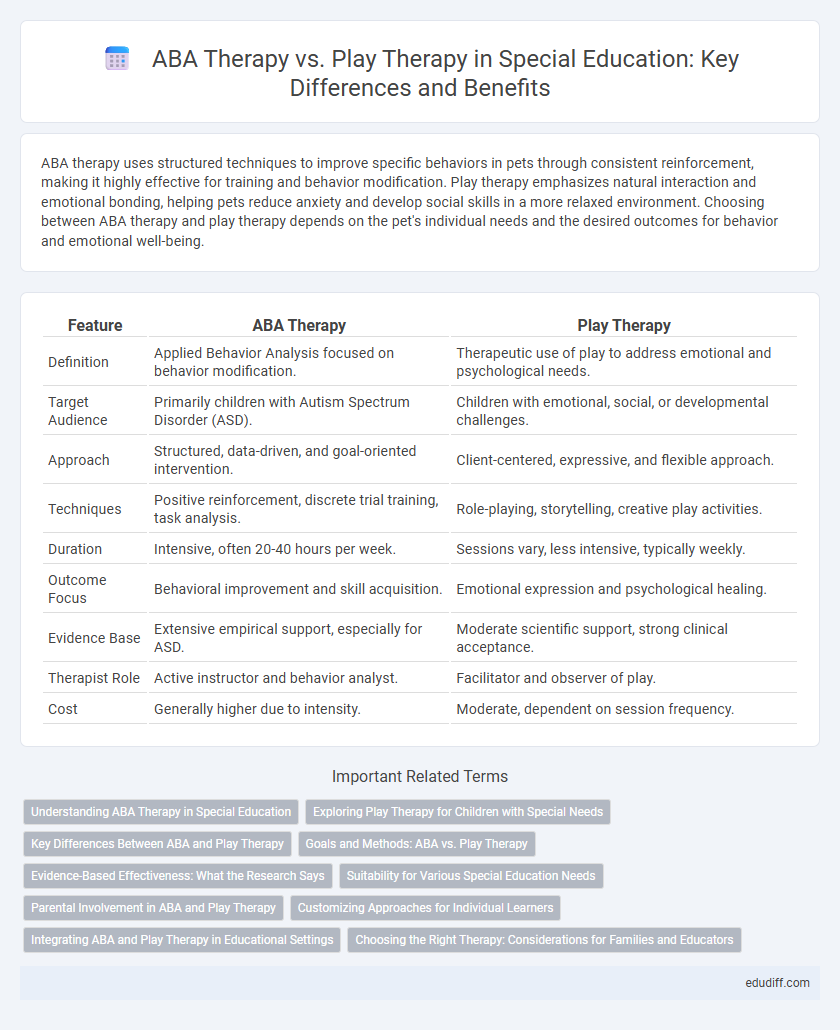
| Feature | ABA Therapy | Play Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applied Behavior Analysis focused on behavior modification. | Therapeutic use of play to address emotional and psychological needs. |
| Target Audience | Primarily children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). | Children with emotional, social, or developmental challenges. |
| Approach | Structured, data-driven, and goal-oriented intervention. | Client-centered, expressive, and flexible approach. |
| Techniques | Positive reinforcement, discrete trial training, task analysis. | Role-playing, storytelling, creative play activities. |
| Duration | Intensive, often 20-40 hours per week. | Sessions vary, less intensive, typically weekly. |
| Outcome Focus | Behavioral improvement and skill acquisition. | Emotional expression and psychological healing. |
| Evidence Base | Extensive empirical support, especially for ASD. | Moderate scientific support, strong clinical acceptance. |
| Therapist Role | Active instructor and behavior analyst. | Facilitator and observer of play. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to intensity. | Moderate, dependent on session frequency. |
Understanding ABA Therapy in Special Education
ABA therapy in special education uses applied behavior analysis principles to improve social, communication, and learning skills for children with autism and developmental disorders. Data-driven techniques in ABA focus on reinforcing positive behaviors and reducing maladaptive ones through structured interventions tailored to individual needs. Unlike play therapy, ABA emphasizes measurable outcomes and skill acquisition through systematic behavior modification strategies.
Exploring Play Therapy for Children with Special Needs
Play therapy offers a natural, child-centered approach that enhances emotional expression and social skills in children with special needs by leveraging imaginative play and creativity. Unlike ABA therapy, which emphasizes behavior modification through structured reinforcement, play therapy fosters self-regulation and problem-solving in a less rigid, more flexible environment. Research indicates that integrating play therapy can improve communication and emotional resilience, making it a valuable complement or alternative in special needs interventions.
Key Differences Between ABA and Play Therapy
ABA therapy emphasizes structured interventions using behavioral techniques to reinforce desired behaviors, targeting measurable outcomes primarily in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Play therapy centers on child-led, imaginative play to address emotional and psychological challenges, enhancing social skills and emotional regulation. Unlike ABA's data-driven approach, play therapy values spontaneous interaction for therapeutic development.
Goals and Methods: ABA vs. Play Therapy
ABA therapy emphasizes structured, data-driven interventions targeting specific behavioral goals such as communication, social skills, and self-management through reinforcement techniques and systematic skill-building. Play therapy focuses on emotional expression and development by using child-led, imaginative play activities to improve social interaction, emotional regulation, and problem-solving skills. Both approaches employ distinct methodologies tailored to different therapeutic objectives, where ABA prioritizes measurable behavior change and play therapy enhances emotional growth and self-awareness.
Evidence-Based Effectiveness: What the Research Says
Research indicates that ABA therapy demonstrates strong evidence-based effectiveness in improving communication, social skills, and behavior in individuals with autism spectrum disorder, supported by numerous randomized controlled trials. Play therapy shows benefits in emotional expression and social development but lacks the breadth of rigorous empirical studies confirming its efficacy for autism-specific interventions. Meta-analyses consistently highlight ABA as the preferred evidence-based treatment for developmental and behavioral outcomes, whereas play therapy primarily complements ABA by addressing emotional and psychological needs.
Suitability for Various Special Education Needs
ABA therapy demonstrates high effectiveness for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) due to its data-driven approach targeting behavioral skills and communication deficits. Play therapy suits children with emotional and social challenges, promoting emotional expression and social development through creative, child-led activities. Selecting the appropriate therapy depends on the specific educational needs, with ABA excelling in structured behavioral interventions and play therapy supporting emotional regulation and interpersonal skills.
Parental Involvement in ABA and Play Therapy
Parental involvement in ABA therapy is integral, with parents actively participating in structured sessions to reinforce behavioral goals and consistency across environments. In play therapy, parents engage primarily through observational roles and guided interactions that promote emotional expression and development in naturalistic settings. Both approaches emphasize collaboration, but ABA therapy requires more direct, hands-on involvement from parents to ensure effective intervention outcomes.
Customizing Approaches for Individual Learners
ABA therapy and play therapy offer distinct methods tailored to individual learning needs, with ABA emphasizing structured behavioral interventions based on data-driven analysis, while play therapy prioritizes creativity and emotional expression through imaginative activities. Customizing approaches involves assessing the learner's specific challenges, strengths, and preferences to determine the optimal balance between behavioral skill-building and fostering emotional development. Integrating both therapies can enhance personalized treatment plans by addressing diverse aspects of cognitive, social, and emotional growth in learners with developmental differences.
Integrating ABA and Play Therapy in Educational Settings
Integrating ABA therapy and play therapy in educational settings enhances individualized learning by combining structured behavioral interventions with naturalistic play-based strategies. This approach supports skill acquisition and social development, leveraging ABA's data-driven methods alongside play therapy's emphasis on creativity and emotional expression. Educators can optimize student outcomes by tailoring interventions that blend behavioral goals with engaging, therapeutic play activities.
Choosing the Right Therapy: Considerations for Families and Educators
Families and educators must evaluate individual child needs, developmental goals, and behavioral challenges when choosing between ABA therapy and play therapy. ABA therapy offers data-driven techniques targeting specific behavioral improvements, while play therapy emphasizes emotional expression and social skills through guided interaction. Understanding these distinct methodologies aids in selecting the most effective intervention for optimal child development and well-being.
ABA therapy vs play therapy Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com