Special pets often require specific modifications rather than accommodations to thrive in their environments, as modifications involve changing the pet's surroundings or routines to better suit their needs. Accommodations typically refer to adjustments made without altering the fundamental context, which may not be sufficient for pets with unique health or behavioral challenges. Understanding the difference ensures that owners provide the most effective support for their special pets' well-being and comfort.
Table of Comparison
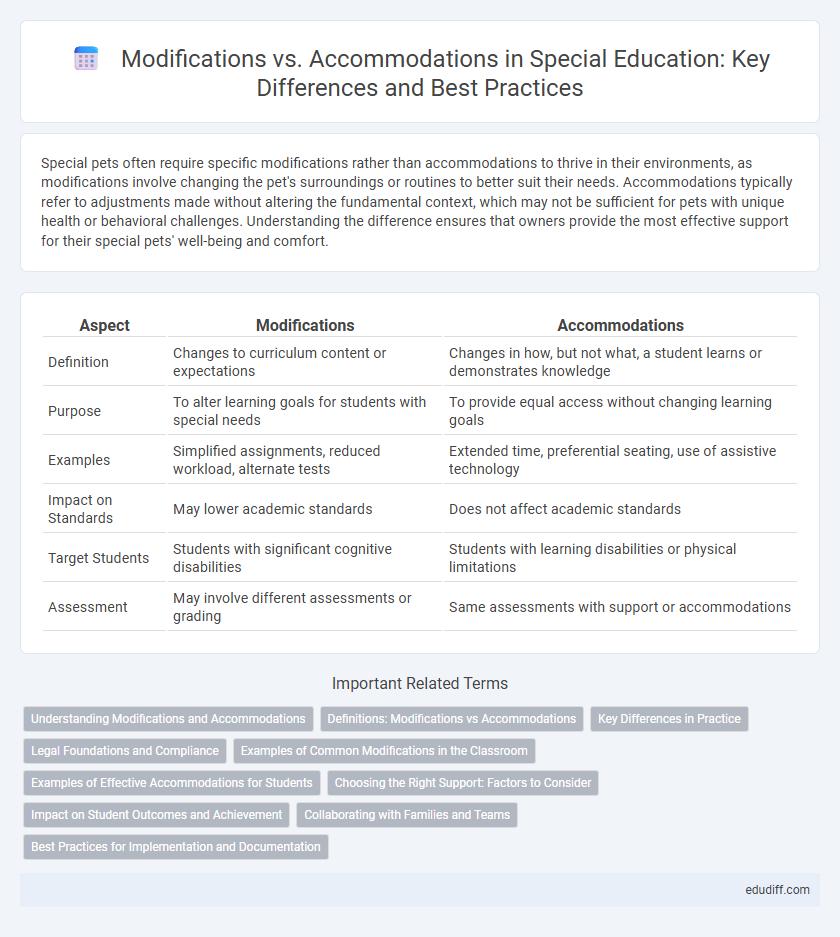
| Aspect | Modifications | Accommodations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changes to curriculum content or expectations | Changes in how, but not what, a student learns or demonstrates knowledge |
| Purpose | To alter learning goals for students with special needs | To provide equal access without changing learning goals |
| Examples | Simplified assignments, reduced workload, alternate tests | Extended time, preferential seating, use of assistive technology |
| Impact on Standards | May lower academic standards | Does not affect academic standards |
| Target Students | Students with significant cognitive disabilities | Students with learning disabilities or physical limitations |
| Assessment | May involve different assessments or grading | Same assessments with support or accommodations |
Understanding Modifications and Accommodations
Modifications involve altering the curriculum or expectations for a student, often changing the learning goals to better suit individual needs, while accommodations provide support that allows the student to access the same curriculum without altering the content. Understanding the distinction between modifications and accommodations is crucial for educators to implement appropriate strategies that comply with IDEA and Section 504 regulations. Accurate application enhances inclusive education and improves student outcomes by tailoring instructional methods and assessment techniques effectively.
Definitions: Modifications vs Accommodations
Modifications refer to significant changes made to curriculum expectations or performance standards to meet the needs of students with disabilities, often altering the content or level of difficulty. Accommodations involve adjustments in the way instruction or assessments are delivered, allowing access to the same curriculum without changing the learning expectations. Both strategies are essential in special education to support diverse learning needs while maintaining appropriate educational goals.
Key Differences in Practice
Modifications involve altering the content or expectations of a curriculum to reduce learning goals, often used for students with significant learning disabilities, while accommodations provide support that allows students to access the same curriculum without changing the learning expectations. Key differences in practice include that modifications change what a student is taught or expected to learn, whereas accommodations change how a student accesses information and demonstrates knowledge. Examples include simplifying assignments for modifications versus providing extra time or preferential seating as accommodations.
Legal Foundations and Compliance
Legal foundations for modifications vs accommodations stem primarily from the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, which mandate schools to provide appropriate educational support to students with disabilities. Accommodations maintain the standard curriculum while providing access through adjustments, whereas modifications alter learning expectations and curriculum standards. Compliance requires individualized education programs (IEPs) or 504 plans to clearly specify whether accommodations or modifications are implemented, ensuring adherence to federal mandates and protecting students' educational rights.
Examples of Common Modifications in the Classroom
Common modifications in the classroom include reducing the length or complexity of assignments, altering grading criteria to focus on essential skills, and providing simplified texts or alternative materials. Students might receive modified tests with fewer questions or different formats tailored to their learning needs. These adjustments help ensure that academic expectations align realistically with the student's abilities while maintaining access to the curriculum.
Examples of Effective Accommodations for Students
Effective accommodations for students include providing extended time on tests, offering alternative formats for reading materials such as audiobooks or large print, and allowing the use of assistive technology like speech-to-text software. Modifying physical environments by creating quiet study spaces or preferential seating can significantly enhance focus and engagement. Adjusting instructional methods, such as breaking assignments into smaller tasks or using visual aids, supports diverse learning needs without altering educational standards.
Choosing the Right Support: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right support involves assessing individual student needs, academic goals, and the complexity of the learning material. Modifications alter the content or expectations to better fit the student's abilities, while accommodations provide access to the same curriculum without changing the standard. Effective decision-making requires collaboration among educators, specialists, and families to ensure supports align with legal guidelines and promote student success.
Impact on Student Outcomes and Achievement
Modifications alter the curriculum expectations and often lower academic standards, which can limit a student's mastery of grade-level content and hinder long-term achievement. Accommodations provide access to the same curriculum by adjusting instructional methods or assessments without changing learning goals, supporting students in demonstrating their true potential. Research indicates that accommodations promote higher student engagement and better outcomes by maintaining rigorous standards while addressing individual needs.
Collaborating with Families and Teams
Effective collaboration with families and teams ensures that both modifications and accommodations are tailored to meet the unique needs of each student. Clear communication channels foster shared decision-making, promoting consistency between home and school environments. Engaging all stakeholders in ongoing discussions enhances the implementation of personalized educational strategies that support student success.
Best Practices for Implementation and Documentation
Effective implementation of modifications and accommodations requires clear documentation that distinguishes the two, ensuring individualized education plans (IEPs) accurately reflect student needs. Best practices include collaboration among educators, specialists, and families to tailor supports that maintain academic rigor while addressing functional barriers. Comprehensive record-keeping and ongoing progress monitoring are essential to verify the appropriateness and effectiveness of adjustments in educational settings.
Modifications vs Accommodations Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com