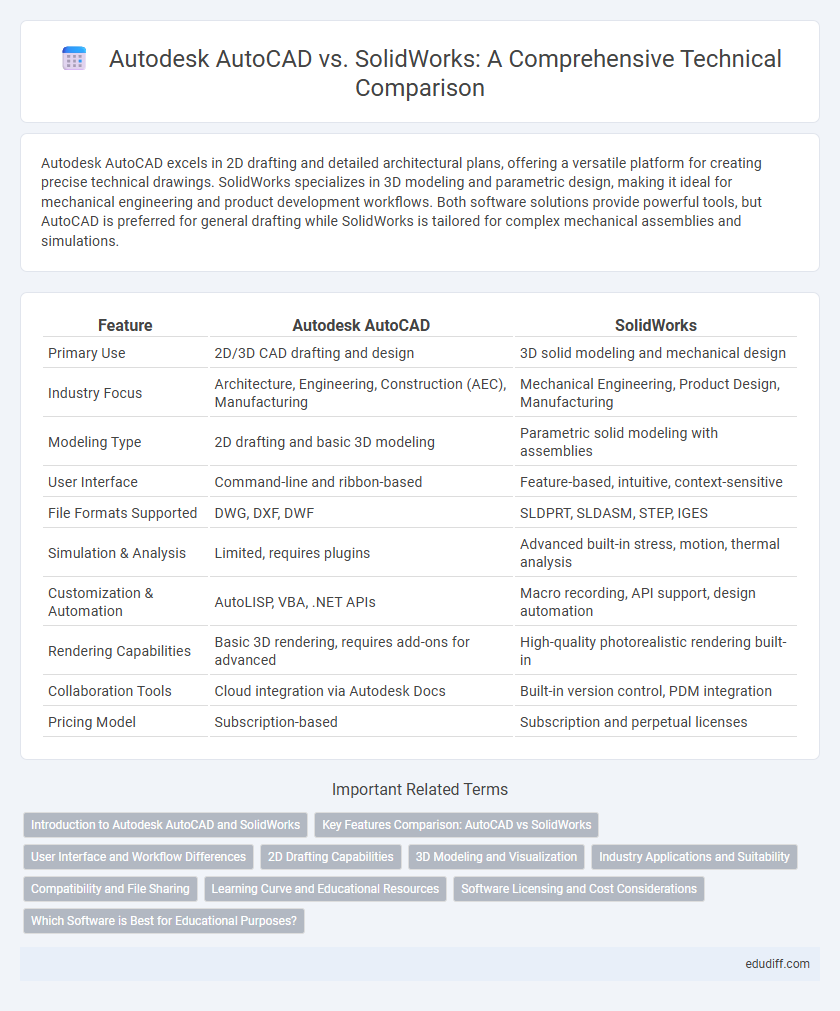
Autodesk AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting and detailed architectural plans, offering a versatile platform for creating precise technical drawings. SolidWorks specializes in 3D modeling and parametric design, making it ideal for mechanical engineering and product development workflows. Both software solutions provide powerful tools, but AutoCAD is preferred for general drafting while SolidWorks is tailored for complex mechanical assemblies and simulations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Autodesk AutoCAD | SolidWorks |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | 2D/3D CAD drafting and design | 3D solid modeling and mechanical design |
| Industry Focus | Architecture, Engineering, Construction (AEC), Manufacturing | Mechanical Engineering, Product Design, Manufacturing |
| Modeling Type | 2D drafting and basic 3D modeling | Parametric solid modeling with assemblies |
| User Interface | Command-line and ribbon-based | Feature-based, intuitive, context-sensitive |
| File Formats Supported | DWG, DXF, DWF | SLDPRT, SLDASM, STEP, IGES |
| Simulation & Analysis | Limited, requires plugins | Advanced built-in stress, motion, thermal analysis |
| Customization & Automation | AutoLISP, VBA, .NET APIs | Macro recording, API support, design automation |
| Rendering Capabilities | Basic 3D rendering, requires add-ons for advanced | High-quality photorealistic rendering built-in |
| Collaboration Tools | Cloud integration via Autodesk Docs | Built-in version control, PDM integration |
| Pricing Model | Subscription-based | Subscription and perpetual licenses |
Introduction to Autodesk AutoCAD and SolidWorks
Autodesk AutoCAD excels in detailed 2D drafting and precise technical drawings, widely used in architecture and engineering for creating scalable plans. SolidWorks specializes in 3D CAD modeling with robust parametric design capabilities, enabling complex product development and simulation in mechanical engineering. Both platforms offer extensive toolsets for design, but AutoCAD is preferred for flat designs while SolidWorks leads in 3D part and assembly creation.
Key Features Comparison: AutoCAD vs SolidWorks
AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting and detailed architectural plans, offering extensive compatibility with DWG files and customizable toolsets for precise design workflows. SolidWorks specializes in 3D parametric modeling with advanced features like assembly management, motion simulation, and integrated CAM capabilities, enhancing product development efficiency. Both platforms support robust collaboration but cater to different engineering disciplines, with AutoCAD favored for civil and architectural projects and SolidWorks preferred for mechanical and product design.
User Interface and Workflow Differences
Autodesk AutoCAD features a command-line interface with customizable tool palettes, emphasizing precision drafting and 2D design workflows, which enhances efficiency for architectural and engineering projects. In contrast, SolidWorks offers an intuitive, icon-based ribbon interface tailored for 3D parametric modeling, promoting streamlined part and assembly creation with real-time simulation capabilities. Workflow differences highlight AutoCAD's strength in detailed 2D documentation, while SolidWorks excels in product design and mechanical engineering through integrated 3D modeling and analysis tools.
2D Drafting Capabilities
Autodesk AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting with precise linework, extensive annotation tools, and robust layer management, making it ideal for architectural and engineering blueprints. SolidWorks, while primarily a 3D CAD software, offers limited 2D drafting capabilities focused on creating detailed drawings from 3D models rather than standalone 2D drafting projects. AutoCAD's specialized tools for 2D drawing, such as dynamic blocks and customizable tool palettes, provide greater efficiency and control compared to SolidWorks' integrated but basic 2D drafting functions.
3D Modeling and Visualization
Autodesk AutoCAD and SolidWorks both excel in 3D modeling and visualization, yet they serve different engineering needs. AutoCAD offers versatile design options with strong drafting capabilities and supports complex 3D wireframe and surface modeling ideal for architectural and civil projects. SolidWorks provides advanced parametric modeling, realistic rendering, and simulation tools, making it preferable for mechanical design, product development, and manufacturing workflows.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Autodesk AutoCAD excels in architectural design and civil engineering due to its robust 2D drafting capabilities and flexibility in creating detailed blueprints. SolidWorks is favored in mechanical engineering and product design industries for its advanced 3D modeling, simulation, and assembly features tailored to complex machinery and component creation. Both software solutions cater to different industry needs, with AutoCAD being indispensable for construction and infrastructure projects, while SolidWorks drives innovation in manufacturing and automotive sectors.
Compatibility and File Sharing
Autodesk AutoCAD supports DWG and DXF formats widely used in architectural and engineering projects, facilitating seamless file sharing across various CAD platforms. SolidWorks primarily uses proprietary SLDPRT and SLDDRW formats, but offers compatibility through STEP, IGES, and STL file exports to integrate with other design software. Both programs enable cross-platform collaboration, though AutoCAD's format dominance ensures broader compatibility in diverse project environments.
Learning Curve and Educational Resources
Autodesk AutoCAD features a moderate learning curve with extensive online tutorials, official training courses, and a vast user community that supports skill development for beginners and advanced users alike. SolidWorks offers a steeper learning curve due to its parametric design complexity but provides comprehensive educational resources, including certified training programs, detailed documentation, and interactive simulations tailored for engineering students and professionals. Both software platforms integrate with academic institutions, enhancing practical learning through hands-on projects and real-world application scenarios.
Software Licensing and Cost Considerations
Autodesk AutoCAD offers flexible subscription-based licensing with monthly, annual, and multi-year options, making it accessible for short-term projects and scalable business needs. SolidWorks primarily uses a perpetual licensing model combined with annual maintenance fees, which can be cost-effective for long-term users but requires a higher upfront investment. Evaluating total cost of ownership should include software updates, support, and the specific licensing model that aligns with project duration and budget constraints.
Which Software is Best for Educational Purposes?
Autodesk AutoCAD offers a versatile platform widely used in educational institutions for teaching 2D drafting and foundational design skills, making it ideal for students in architecture, engineering, and construction fields. SolidWorks excels in parametric 3D modeling and simulation, providing engineering students with advanced tools for mechanical design, product development, and practical hands-on experience. The choice depends on the curriculum focus, where AutoCAD suits general drafting education and SolidWorks is preferred for specialized mechanical engineering and industrial design courses.
Autodesk AutoCAD vs SolidWorks Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com