Linux offers a cost-effective, customizable environment with open-source software ideal for technical classrooms, fostering hands-on learning and development. Windows provides a familiar interface with extensive software compatibility and support, making it suitable for standardized testing and widely used educational applications. Both operating systems present unique advantages depending on curriculum needs and technical proficiency requirements.
Table of Comparison
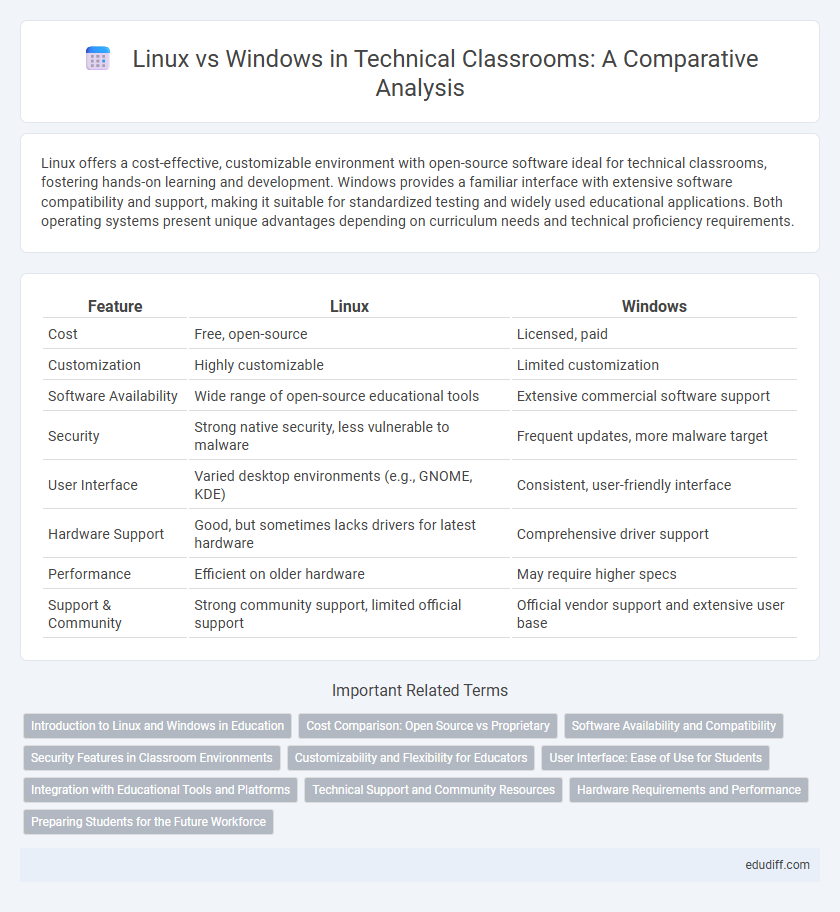
| Feature | Linux | Windows |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free, open-source | Licensed, paid |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited customization |
| Software Availability | Wide range of open-source educational tools | Extensive commercial software support |
| Security | Strong native security, less vulnerable to malware | Frequent updates, more malware target |
| User Interface | Varied desktop environments (e.g., GNOME, KDE) | Consistent, user-friendly interface |
| Hardware Support | Good, but sometimes lacks drivers for latest hardware | Comprehensive driver support |
| Performance | Efficient on older hardware | May require higher specs |
| Support & Community | Strong community support, limited official support | Official vendor support and extensive user base |
Introduction to Linux and Windows in Education
Linux offers a customizable and cost-effective operating system ideal for educational environments, supporting a wide range of open-source software tailored for classroom learning. Windows provides a familiar interface with extensive compatibility for mainstream educational applications and proprietary software commonly used in schools. Both platforms enhance digital literacy, but Linux emphasizes flexibility and security, while Windows focuses on ease of use and widespread software integration.
Cost Comparison: Open Source vs Proprietary
Linux offers significant cost savings in classroom environments due to its open-source nature, eliminating licensing fees that are mandatory with proprietary Windows systems. Schools benefit from reduced total cost of ownership by avoiding expensive software licenses and leveraging freely available educational resources compatible with Linux. Although Windows provides extensive commercial support and a wide range of applications, the financial burden of continual license renewals and hardware requirements can strain educational budgets.
Software Availability and Compatibility
Windows offers broader software availability and compatibility in classroom settings, supporting a wide range of educational programs and commercial applications essential for curriculum requirements. Linux, while excellent for programming, open-source tools, and customization, may face limitations with proprietary educational software and multimedia applications frequently used in schools. Compatibility with popular classroom management platforms and standardized testing software often favors Windows, enhancing its ease of integration in diverse educational environments.
Security Features in Classroom Environments
Linux offers robust security features such as customizable user permissions, strong encryption tools, and regular open-source updates that enhance protection against malware and unauthorized access in classroom environments. Windows provides integrated security solutions like Windows Defender, BitLocker encryption, and frequent automated patches, designed to safeguard students' data and system integrity. Educational institutions benefit from Linux's flexibility and transparency, while Windows delivers user-friendly, centralized security management tailored for classroom settings.
Customizability and Flexibility for Educators
Linux offers unparalleled customizability and flexibility, enabling educators to tailor the operating system to specific teaching needs through open-source software and extensive configuration options. Its modular architecture allows installation of lightweight distributions optimized for older hardware, ensuring cost-effective deployment in diverse classroom environments. Windows, while providing a stable and user-friendly interface, limits deep customization and often requires commercial licenses, which can restrict adaptability and increase expenses for educational institutions.
User Interface: Ease of Use for Students
Linux offers a customizable and intuitive user interface that can be tailored to different student needs, enhancing ease of navigation and reducing distractions. Windows provides a familiar, standardized interface that most students are already accustomed to, minimizing learning curves and technical support requirements. Both platforms support a range of educational software, but Linux's flexibility allows for lightweight desktop environments that perform well on older hardware often found in classrooms.
Integration with Educational Tools and Platforms
Linux offers strong integration with a wide range of open-source educational tools and platforms such as Moodle, Open Sankore, and GCompris, providing flexible customization options for classroom needs. Windows supports numerous proprietary educational applications like Microsoft Teams for Education and OneNote Class Notebooks, ensuring seamless compatibility with widely-used commercial software. The choice between Linux and Windows depends on the school's preference for open-source adaptability versus commercial ecosystem integration for efficient digital learning environments.
Technical Support and Community Resources
Linux offers extensive community-driven technical support through forums, wikis, and IRC channels, providing quick solutions for classroom-related technical issues. Windows benefits from comprehensive official support and a large network of certified professionals readily available for on-site or remote assistance. The open-source nature of Linux fosters customizable troubleshooting tools, whereas Windows delivers streamlined, user-friendly support interfaces backed by Microsoft's robust service infrastructure.
Hardware Requirements and Performance
Linux generally requires lower hardware specifications compared to Windows, enabling older or less powerful machines to run efficiently in classroom settings. Windows often demands higher RAM, CPU, and storage resources to maintain smooth performance, which can increase costs for educational institutions. Linux's lightweight distributions optimize resource usage, resulting in faster boot times and reduced system lag during multitasking in an academic environment.
Preparing Students for the Future Workforce
Linux offers students extensive experience with open-source software, programming environments, and command-line tools essential for careers in IT and software development. Windows provides familiarity with widely used enterprise applications and productivity suites critical for business and administrative roles. Integrating both operating systems in classrooms equips students with versatile digital skills, enhancing their adaptability in a diverse and evolving workforce.
Linux vs Windows in Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com